Why ASTM Standards Matter for Medical-Grade Nitinol Tubing

Material standards are very important in healthcare. This is true for things like nitinol tubing in medical devices. Nitinol has special features. But it is only safe if ASTM standards are followed closely. ASTM F2063 gives exact rules for nonmetallic inclusions and voids in medical nitinol tubing. These rules help stop cracks from forming. Cracks can make devices fail and put patients at risk. Medical devices like heart valves need nitinol tubing that meets F2063 purity rules. New updates in F2063 let even smaller inclusions be found. This makes medical tubing last longer. Makers use F2063 to give nitinol tubing that meets top medical needs. ASTM standards are very important because medical work is demanding. Nitinol Tubing ASTM standards keep patients and healthcare workers safe. They do this by making sure every tube follows strict F2063 rules.
Key Takeaways
ASTM F2063 gives clear rules for nitinol tubing. These rules help keep medical devices safe, strong, and clean.
Nitinol tubing can bend and go back to its shape. This makes it good for tools like stents and catheters.
Tests and checks with ASTM standards stop problems like defects, rust, and breaking in nitinol tubing.
When makers follow ASTM standards, they get approval faster. This also helps doctors and patients trust the devices.
Using medical-grade nitinol tubing that follows ASTM rules keeps patients safer. It also helps devices work better in surgeries.
Nitinol Tubing in Medicine
Nitinol Properties
Nitinol tubing is special in medicine because it has many helpful features. It belongs to the nickel-titanium shape memory alloys group. Nitinol can stretch and bend, then go back to its original shape when heated. Doctors like nitinol tubing because it bends many times and does not break. The tubing does not rust because it has a protective layer. This makes it safe to use inside the body for a long time. Nitinol tubing is light but also strong. Thin tubes made from nitinol can move through tricky paths in the body. It works well with the body and does not cause bad reactions. This helps people heal faster. The tubing changes with body temperature, so medical devices work better during procedures. Nitinol tubing does not wear out easily, so it lasts longer in tough medical jobs. These features make nitinol tubing a great choice for medical devices and implants.
Note: Nitinol tubing can return to its shape after being bent. This is important for medical devices used in small surgeries.
Medical Uses
Nitinol tubing is used in many medical tools. Doctors use it in stents, catheters, guidewires, and other devices that need to bend and be strong. The tubing is very useful in surgeries that do not need big cuts. It helps patients heal faster and feel less pain. The table below shows where nitinol tubing is used and how common it is in these surgeries:
Application Area | Description | Prevalence in Minimally Invasive Procedures |
|---|---|---|
Nitinol Tubing | Used for hollow parts like stents and catheters. Made for shape memory and superelasticity. | Used a lot in heart and blood vessel stents and catheters. |
Nitinol Stents | Mesh tubes that open blocked arteries; they expand by themselves and do not need balloons. | Most common; very important in heart and blood vessel surgeries. |
Tools to help move through blood vessels; they bend, twist, and do not kink. | Needed in many small surgeries, especially for the heart. | |
Other Devices | Used in baskets, needles, dental and orthodontic tools, and stylets. | Used in many small and special medical procedures. |
Doctors get good results with nitinol tubing in devices that remove blood clots, fix heart valves, and treat with ablation catheters. Studies show patients do better, stay in the hospital less, and have fewer problems. The tubing’s ability to bend and stay strong helps devices move through blood vessels and return to their shape. Nitinol tubing is used in many medical areas, like heart stents and dental tools. More doctors want nitinol tubing as they do more small surgeries. F2063 standards make sure every tube is safe and works well for these important uses in medicine and engineering.
ASTM Standards for Nitinol

ASTM F2063 Overview
ASTM F2063 is a set of rules for nitinol tubing. These rules are for tubing used in medical devices. The standard tells what chemicals and features the tubing must have. Makers must follow these rules to make good nitinol tubing for doctors.
ASTM F2063 says nitinol tubing needs 54.5% to 57% nickel. The rest is titanium.
Oxygen and nitrogen together must be less than 500 parts per million. This keeps the tubing pure for medical use.
Inclusions in the nitinol melt cannot be bigger than 39 micrometers. This helps stop problems that could break the device.
The tubing must be smooth. The roughness should be about 1-2 micrometers (Ra). This helps the tubing stay in place and connect with body tissue.
The TiO2 oxide layer on the tubing helps stop rust. It also helps the tubing stick to body parts.
Makers must lower fretting wear. This keeps nickel from coming out, which is safer for patients.
The way the tubing is made must not add new problems. This makes sure the tubing is always high quality for medical use.
ASTM F2063 makes sure every nitinol tube is made with care. The rules help keep the tubing strong and safe for medical work.
The table below shows what chemicals and features nitinol tubing must have for ASTM F2063:
Chemical Composition Limits (wt%) for Nitinol Tubing per ASTM F2063
Element | Limit |
|---|---|
Fe | ≤ 0.05 |
Ni | 54.5 - 57.0 |
Cr | ≤ 0.01 |
Cu | ≤ 0.01 |
Nb | ≤ 0.025 |
C | ≤ 0.05 |
Ti | Balanced |
Co | ≤ 0.05 |
N + O | ≤ 0.050 |
H | ≤ 0.005 |
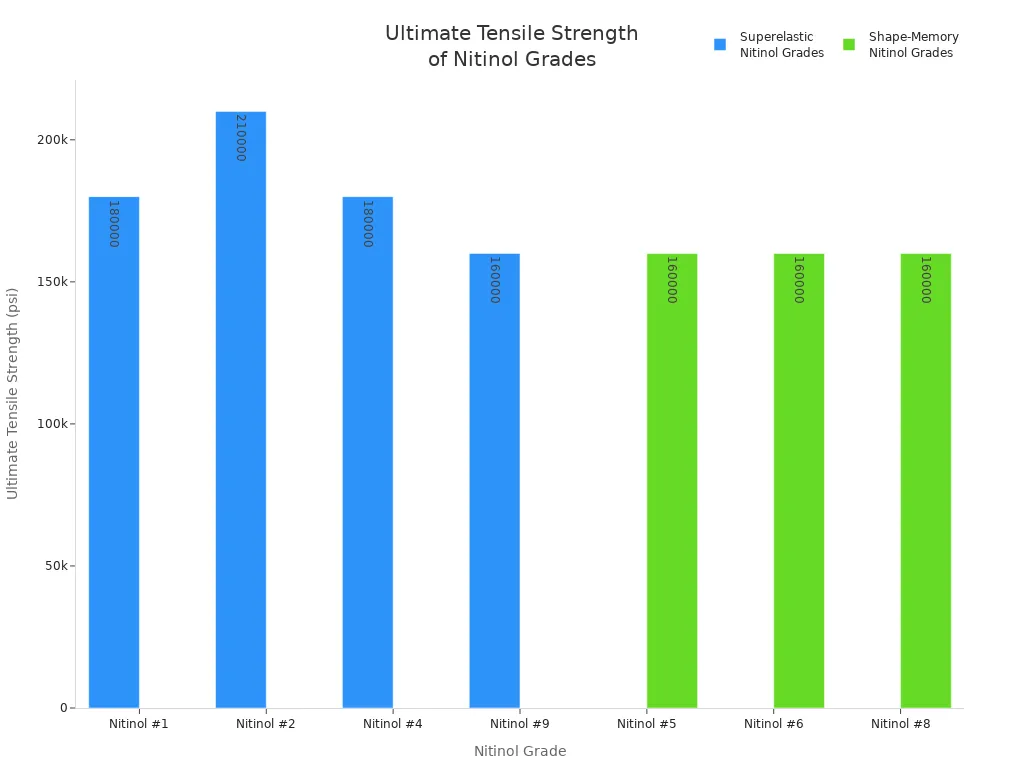
Mechanical Properties for Superelastic Nitinol Grades
Grade | Af Temperature (°C) | Min Ultimate Tensile Strength (psi) | Elongation (%) | Loading Plateau (ksi) | Unloading Plateau (ksi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Nitinol #1 | +10 to +18 | 180,000 | >10 | >70 | >20 |
Nitinol #2 | 0 to +18 | 210,000 | >10 | >80 | >35 |
Nitinol #4 | +14 to +22 | 180,000 | >10 | >65 | >7 |
Nitinol #9 | ≤ 0 | 160,000 | >10 | >75 | >25 |
Mechanical Properties for Shape-Memory Nitinol Grades
Grade | Af Temperature (°C) | Min Ultimate Tensile Strength (psi) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
Nitinol #5 | ≥ +85 | 160,000 | >10 |
Nitinol #6 | +40 to +80 | 160,000 | >10 |
Nitinol #8 | +22 to +40 | 160,000 | >10 |
These rules help make sure nitinol tubing is always good quality. ASTM F2063 helps doctors trust the tubing in their devices.
Biocompatibility and Corrosion Resistance
Nitinol tubing must be safe for the body. Medical grade ASTM F2063 tubing should not hurt people. Tests check if the tubing is safe for the body. These tests look for things like cell damage, allergies, and other bad effects. The tests show if the tubing is safe for medical tools.
The tubing must also not rust inside the body. Medical devices can stay in the body for a long time. The tubing must not break down in body fluids. ASTM F2129 is a test to see if the tubing can resist rust. This test uses fake body fluids to check how strong the tubing is. If the tubing does not break down, it is safer for patients.
Electropolished nitinol tubing resists rust better than oxidized tubing.
The TiO2 oxide layer helps stop rust and helps the tubing join with body tissue.
Fewer and smaller inclusions mean less chance for rust spots. This keeps the device strong.
How smooth the tubing is, how much surface it has, and test settings all change how well the tubing resists rust.
ASTM standards for nitinol make sure every tube is safe and works well. These rules help protect patients and make medical devices last longer.
Fatigue and Strength Testing
Nitinol tubing must be strong and last a long time. Medical devices bend and move a lot in the body. ASTM F2082 and other rules tell how to test nitinol tubing for these jobs.
Testing steps include:
Cutting samples from nitinol tubing and making them smooth.
Putting samples in fake body fluid at 37°C to copy body heat.
Bending and loading the samples over and over, like in real use.
Running tests until the tubing breaks or up to 10 million bends. At least six samples are tested each time.
Using computer models to check stress and looking at the tubing under a microscope.
These tests find out how long nitinol tubing can last. The results show if the tubing can handle tough jobs in the body. Nitinol’s special features depend on the right mix of chemicals and a smooth surface, as ASTM F2063 says.
New ASTM rules for nitinol help keep up with new medical devices. Better safety, less rust, and longer life mean fewer problems for patients.
Nitinol tubing ASTM standards, like ASTM F2063, are very important. They make sure every tube is safe, strong, and works well. ASTM standards help doctors and patients trust medical devices.
Nitinol Tubing ASTM Standards and Specifications
ASTM Standard Nitinol Specifications
Nitinol tubing ASTM standards have strict rules. These rules help make medical devices safe and strong. ASTM standard nitinol specifications, like nitinol ASTM F2063, say what chemicals and strength the tubing must have. The rules say nickel must be between 54.5% and 57%. The rest is titanium. Other elements, like iron and copper, must be very low. This keeps the tubing pure and tough.
Medical grade ASTM F2063 also limits oxygen and nitrogen. These gases must be under 500 parts per million. High quality ASTM F2063 stops tiny unwanted bits from getting too big. The biggest allowed is 39 micrometers. This helps stop weak spots that could break the tubing.
Nitinol ASTM F2063 says the tubing must be smooth. The roughness should be 1 to 2 micrometers. A smooth tube helps stop rust and connects better with body tissue. The oxide layer, made of TiO2, keeps the tubing from rusting and helps it work in the body.
Nitinol ASTM F2063 also says how the tubing should act. It must show shape memory and superelasticity. The tubing should go back to its shape after bending. Tests check for strength, shape recovery, and temperature changes. These tests make sure the tubing is safe for medical use.
ASTM standards help doctors and engineers trust nitinol tubing. This trust is important for keeping patients safe.
Nitinol tubing ASTM standards also help with getting approval. When makers follow nitinol ASTM F2063, they can prove the tubing is good. This helps get approval from groups like the FDA. The standards need:
Records for each batch, including cleaning steps.
Biocompatibility tests that follow ISO 10993-1, checking for cell damage.
Proof of all tests, like strength and nickel release, to meet FDA rules.
Tracking every tube, from start to finish.
Using high quality ASTM F2063 tubing lowers the risk of device failure. It also helps companies sell their products faster by meeting industry rules.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance is very important for making nitinol tubing. Nitinol ASTM F2063 and medical grade ASTM F2063 need strict checks at every step. These checks keep the tubing safe and strong.
Makers start with pure nickel and titanium. They control the nickel and titanium mix to keep temperatures steady. Vacuum Arc Remelting melts the metals and removes bad stuff. Cold working and heat treatment make the tubing strong and keep its special features.
Nitinol ASTM F2063 needs many tests to check the tubing. These tests include:
Ultrasonic and eddy current tests to find hidden cracks.
Size checks for diameter, wall thickness, and roundness. The sizes must be very exact, within ±0.0005 inches.
Strength, elasticity, and fatigue tests.
Heat tests like Bend and Free Recovery and Differential Scanning Calorimetry to check temperatures.
Rust tests using ASTM F2129 to make sure the tubing will not rust in the body.
Finishing steps, like electropolishing and passivation, make the tubing’s surface better. These steps help the tubing last longer and resist rust. In-house checks use metallography and SEM to look for heat damage and make sure the tubing has no defects.
Process checks follow ISO 13485:2016 rules. Skilled teams check every step and tool. Automated checks look at every tube to make sure it is right. Statistical quality control helps find problems early.
These quality checks, set by nitinol tubing ASTM standards, help makers give tubing with steady, reliable features. This is very important for safe medical devices.
Nitinol ASTM F2063 and high quality ASTM F2063 make sure every batch is the same. These standards help with approval, lower recall risks, and build trust in healthcare.
Benefits of Compliance
Patient Safety
ASTM standards like nitinol astm f2063 help keep patients safe. These rules say how much nickel and titanium should be in the tubing. They also limit bad stuff and make sure the surface is smooth. Medical devices need tubing that does not break or rust inside the body. When makers follow f2063, devices are less likely to fail. Nitinol tubing that meets f2063 stays strong and keeps its shape after many uses. This means implants last longer and work better for people. Doctors trust nitinol astm f2063 because it helps protect patients during important surgeries.
Tip: Good quality nitinol tubing means fewer problems for patients who use medical devices.
Regulatory Acceptance
Groups that check medical devices want proof that they are safe and good quality. Nitinol astm f2063 makes it easier to get approval. Makers who follow f2063 can show papers and test results. These papers prove the tubing has the right chemicals and strength. Groups like the FDA look for this proof before letting devices be sold. Nitinol astm f2063 also helps new devices get approved faster. Companies that use f2063 tubing do not wait as long and can help patients sooner.
Papers show the tubing has the right chemicals and strength.
Checks and tests make sure every batch follows f2063.
Good records help get faster approval for medical devices.
Market Confidence
Makers who use nitinol astm f2063 become trusted in medicine. Customers believe in suppliers who meet f2063 rules. These companies give proof, help with questions, and offer special tubing for different needs. Nitinol astm f2063 makes sure tubing works well in tough medical jobs. Good tubing means fewer recalls and better results. Over time, following f2063 helps companies get noticed in a busy market.
Good quality and trust bring more customers.
Expert help solves special problems in medical jobs.
Following f2063 for a long time helps companies grow and get more buyers.
Doctors and makers use f2063 to check nitinol tubing safety. Medical grade astm f2063 helps stop rust, works well with the body, and lasts long. Tests like breakdown potential and nickel leach show these features. Experts say to pick suppliers who follow f2063, have ISO 13485, and track every tube. Groups like the FDA use f2063 and other rules to approve devices. Medical grade astm f2063 is needed for safe nitinol tubing in medicine. Makers and health teams should use f2063 at every step.
Picking medical grade astm f2063 tubing keeps patients safe and helps devices work better.
Measurement Type | Description | Impact on Medical Grade ASTM F2063 Tubing |
|---|---|---|
Breakdown Potential (Eb) | Voltage level that shows when rust starts | Helps stop rust and keeps devices safe |
Nickel Leach Testing | Measures how much nickel comes out | Makes sure tubing is safe for people |
Use f2063 and other rules for every device.
Choose nitinol tubing that meets medical grade astm f2063.
Keep good records and test results for approval.
FAQ
What is f2063 and why does it matter for nitinol tubing?
F2063 is a set of rules for nitinol tubing in medical devices. It tells what chemicals, strength, and surface quality the tubing must have. Following f2063 helps make sure tubing is safe and works well in healthcare.
How does f2063 improve patient safety?
F2063 keeps bad elements low and makes the surface smooth. This lowers the chance of the device breaking or rusting inside the body. Medical teams trust tubing that meets f2063 because it helps keep patients safe during procedures.
Does f2063 help with regulatory approval?
Yes. Groups that check medical devices want proof that tubing meets f2063. Makers who follow f2063 can show test results and records. This helps new medical devices get approved faster.
How do manufacturers test nitinol tubing for f2063 compliance?
Makers test for strength, bending, and rust resistance. They check the chemicals and how smooth the tubing is. Every batch must pass these tests to meet f2063 before being used in medical devices.
Are there other standards besides f2063 for nitinol tubing?
Yes. F2063 is the main rule for nitinol tubing, but other rules may be needed for special tests or device types. Makers should always check which rules fit their product and use.
See Also
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Modern Medicine
The Process Behind Manufacturing Nitinol Tubing For Healthcare
Ways Nitinol Tubing Is Transforming Medical Device Technology
Nitinol Tubing’s Contribution To Progress In Medical Technology
Discovering Various Uses Of Nitinol Tubing In Healthcare Tools

