What is ultra-thin wall PET shrink tubing material science

Ultra-thin wall pet shrink tubing material science looks at the special features of pet tubing with very thin walls. This heat shrink tubing uses pet because it is strong and can shrink tightly around things. Big companies like TE Connectivity and Sumitomo Electric make tubing with walls as thin as 0.15 mm. The special shrinking process helps the tubing fit around tricky shapes in medical device making and other uses. Material science helps engineers learn how pet tubing gives high strength, exact shrinking, and works well every time.
The table below shows global trends in ultra-thin wall pet shrink tubing material science:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Leading Applications | Medical devices, aerospace, EV battery insulation, electronics |
Global Consumption | 250 million units each year (medical) by 2025 |
Innovation Focus | Biocompatibility, miniaturization, radiation resistance |
Market Growth Rate | 6-8% growth each year is expected |
Ultra-thin wall pet shrink tubing gives steady shrinking, a smooth surface, and tight sizes for delicate devices. These things make pet tubing a top pick in heat shrink jobs, especially for making medical devices.
Key Takeaways
Ultra-thin wall PET shrink tubing is very strong and thin. It shrinks tightly around things. This makes it good for small medical devices and electronics.
The special structure and cross-linking of PET make the tubing strong. It has a smooth surface. It also shrinks the same way every time.
Makers watch the extrusion and cooling steps closely. This keeps the tubing’s wall thickness even and exact.
PET tubing can handle heat and chemicals. It also works with many ways to clean it. So, it stays safe and strong after many cleanings.
Medical devices use PET tubing to seal and hold parts. It also gives electrical insulation. It fits well and protects sensitive parts.
Material Science of Ultra-Thin Wall PET Shrink Tubing

PET Structure
PET is a strong plastic used in many tubes. It is made from two parts: ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. These parts join together to make long chains. The chains are packed close to each other. This close packing makes PET tubing strong and clear. Ultra-thin wall PET shrink tubing material science studies how these chains let the walls stay thin but strong. The smooth look of PET tubing comes from the way the chains are lined up. Engineers pick PET for heat shrink tubing because it can make thin, tough walls that protect small parts. The way the chains are arranged and packed changes the tubing’s properties. This structure also helps PET tubing fight off chemicals and keep its shape when used.
Cross-Linking
Cross-linking changes how PET tubing acts when heated or stretched. In this step, chemical bonds link the polymer chains together. These bonds hold the chains, making the tubing stronger and harder to melt or bend. Cross-linking in PET forms a network that keeps its shape even with heat. This network makes heat shrink tubing tougher and helps it go back to its size after shrinking. Medical device makers use cross-linking to keep PET tubing strong and bendy. Cross-linking also helps the tubing shrink evenly and hold tightly to wires or parts. This process makes PET tubing a top pick for jobs needing strength and accuracy. There are six steps in cross-linking: mixing, heating, shaping, cooling, testing, and finishing. Each step changes how the tubing will work in the end.
Shrink Mechanism
PET tubing shrinks because it is a thermoplastic. When heated, the chains in PET tubing move and relax. This lets the tubing shrink tightly around things. PET heat shrink tubing can quickly go back to its shape. For example, a PET sheet folded and put in hot water at 82°C opens up in just 4 seconds. This quick change shows how PET’s thermoplastic nature helps it shrink and fit well. How PET tubing shrinks depends on how the chains were stretched during making. If the chains are pulled in one way, the tubing shrinks more that way when heated. Mixing PETG with polycarbonate changes how the tubing shrinks. When polycarbonate is 10% of the mix, the tubing stops shrinking in one direction below 130°C. This is because the chains cannot move as much, so the tubing shrinks less. Ultra-thin wall PET shrink tubing material science uses this to control how much and how fast the tubing shrinks. PET heat shrink tubing gives a tight, even fit to protect small parts in medical devices and electronics. Shrinking also makes the tubing smooth and helps it stand up to chemicals or heat.
Tip: Always pick PET tubing with the right shrink ratio for your project. This helps the tubing fit well and keep your device safe.
Manufacturing Process
Extrusion
Manufacturers use extrusion to make ultra-thin wall PET tubing. They put PET pellets into a hot barrel. The machine melts the PET. Then, it pushes the melted PET through a die. This die shapes the PET into a tube. It is important to be very exact. Tooling suppliers make sure dies and tips are shaped right. They also check that everything lines up perfectly. Even a tiny scratch or dirt can cause problems. Workers keep the area clean and use special tools. They do this to stop damage. They also watch the temperature and pressure closely. If PET gets too hot or cold, the tubing can look uneven. Cleaning and careful work help keep the tubing the same all over. Sensors and monitors check melt temperature, pressure, and flow. These controls help the PET tubing stay the same and ready for the next step.
Expansion and Cooling
After extrusion, the PET tubing is stretched and cooled. Machines pull the tubing to make the walls very thin. Calibrators and dies shape the hot tubing to almost-final sizes. Vacuum and cooling tanks take away heat and help the tubing keep its shape. Temperature control units keep the coolant at the right level. This step stops the tubing from warping or losing its round shape. Pullers set the speed as the tubing moves along. If the speed changes, the wall thickness can change too. In-line measurement systems check the tubing size right away. These systems give feedback to fix the process if needed. Industry 4.0 tech, like automation and data analytics, helps keep the tubing exact and lowers defects.
Wall Thickness Control
Wall thickness control is very important for ultra-thin PET tubing. Manufacturers use laser micrometers, ultrasonic gauges, and optical tools. These tools measure the tubing as it is made. Real-time checks let them fix problems fast. They keep tolerances as tight as ±0.0005 inches. The table below shows how good process control keeps wall thickness steady:
Process Condition | Wall Thickness Deviation (%) |
|---|---|
Proper Parameters | Approximately 4.8% |
Improper Parameters | Approximately 12.0% |
Quality control teams check the tubing for accuracy, strength, and defects. They follow strict rules for medical-grade heat shrink tubing. These steps make sure the PET tubing is safe and works well in medical devices. AI inspection systems and following ISO and FDA rules help keep every piece of tubing safe and reliable.
Properties of PET Tubing
Mechanical Strength
PET tubing is known for being very strong and tough. Makers test PET tubing in many ways to make sure it is safe. The table below shows how PET tubing does in important tests:
Mechanical Performance Test | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|
Tensile Strength | PET tubing stays strong after many chemical cleanings. It keeps more than 88% of its strength, so it lasts a long time. |
Thermal Stability | The tubing can handle high heat during cleaning, like in an autoclave. It does not lose its shape or break. |
Chemical Resistance | PET tubing stands up to cleaners and chemicals. It does not get weak even after many uses. |
Flexibility | Cross-linked PET tubing bends around tricky shapes. It keeps wires safe and works well. |
Microbial Lethality Tests | There is little difference between gamma and e-beam sterilization. Only 13% of tests show big changes, so PET tubing works well for both. |
Regulatory Compliance | PET tubing meets ISO 10993 and USP Class VI rules. This means it is safe for medical use. |
These tests show PET tubing is strong and works well in tough places. Medical device makers use PET tubing because it lasts and keeps its shape after many uses.
Electrical Insulation
PET tubing is great at stopping electricity from passing through. It keeps wires and parts safe from short circuits. PET tubing protects devices by blocking electricity and stopping faults. Engineers like PET tubing because it keeps working even with heat or chemicals. This makes PET tubing a top pick for medical and electronic jobs where safety is very important.
Surface Finish
PET tubing has a smooth and nice-looking surface. Chemical treatments can change how PET tubing looks and works. Special pictures show untreated PET tubing looks different from treated tubing. Tests show saponification makes the surface more water-friendly. Lysine and gelatin can also change the surface, making it stronger and better. These changes help PET tubing stay strong, protect better, and look good. A smooth surface also keeps dirt and germs away, which is important for medical tools.
Some studies prove how making PET tubing changes its surface:
Regression plots help guess how rough the surface will be.
Mean effects plots show how cutting speed, feed rate, and depth change roughness.
Error histograms and error checks show the models are right.
Genetic algorithms help find the best way to cut for a smoother surface.
Better pictures and roughness checks show machining can make the surface much smoother, from 16 μm to about 2 μm.
Chemical Resistance
PET tubing does not break down when cleaned with strong chemicals. This helps PET tubing stay tough and keep protecting things for a long time. PET tubing stands up to many acids, bases, and solvents. This makes it good for hospitals and labs. Chemical resistance means PET tubing can be cleaned many times and still stay strong and bendy. This is why PET tubing is a good choice for medical devices that need to last and protect well.
Note: PET tubing gives strength, insulation, a smooth surface, and chemical resistance. This makes it very good at protecting sensitive things.
Applications in Medical Device Manufacturing

Ultra-thin wall PET tubing is very important in making medical devices. Engineers pick PET tubing because it is safe for the body and shrinks well. It can also be cleaned many times without problems. These things help make devices that are safe and work well. PET tubing is used in many medical tools, like catheters and for covering wires. The tubing is smooth, has even walls, and shrinks tightly. This makes it good for small and careful medical jobs. PET tubing does not get damaged after being cleaned many times. This helps keep medical devices safe and working right.
Catheters and Shafts
Catheters and shafts need tubing that is thin, strong, and bends easily. PET tubing is good for this because it is tough and safe for the body. It is used to make catheters that move smoothly in blood vessels. The tubing can shrink to fit tightly over wires and other parts. This helps doctors move catheters with less risk of getting stuck or breaking.
The table below shows how PET tubing helps make delivery assist catheters:
Device (Delivery Assist Catheter) | Design Feature | Size Variants | Max Outer Diameter (OD) | Internal Diameter (ID) | Guidewire Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Zipline (Perfuze) | Consistent proximal OD with tapered distal tip | Zipline70, Zipline88 | 0.061" / 0.080" | 0.021" | ≤0.018" |
Tenzing (Route 92 Medical) | Consistent proximal OD with tapered distal tip | Tenzing 7, Tenzing 8 | 0.062" / 0.083" | 0.019" | ≤0.016" |
Carrier (Balt) | Consistent proximal OD with tapered distal tip | SM, MD, LG | 0.059" / 0.062" / 0.069" | 0.021" | ≤0.018" |
Offset (Stryker) | Consistent proximal OD with tapered distal tip | One Size | 0.050" | 0.021" | ≤0.018" |
Cheetah (Q'Apel) | Consistent proximal OD with tapered distal tip | One Size | 0.068" | 0.026" | ≤0.014" |
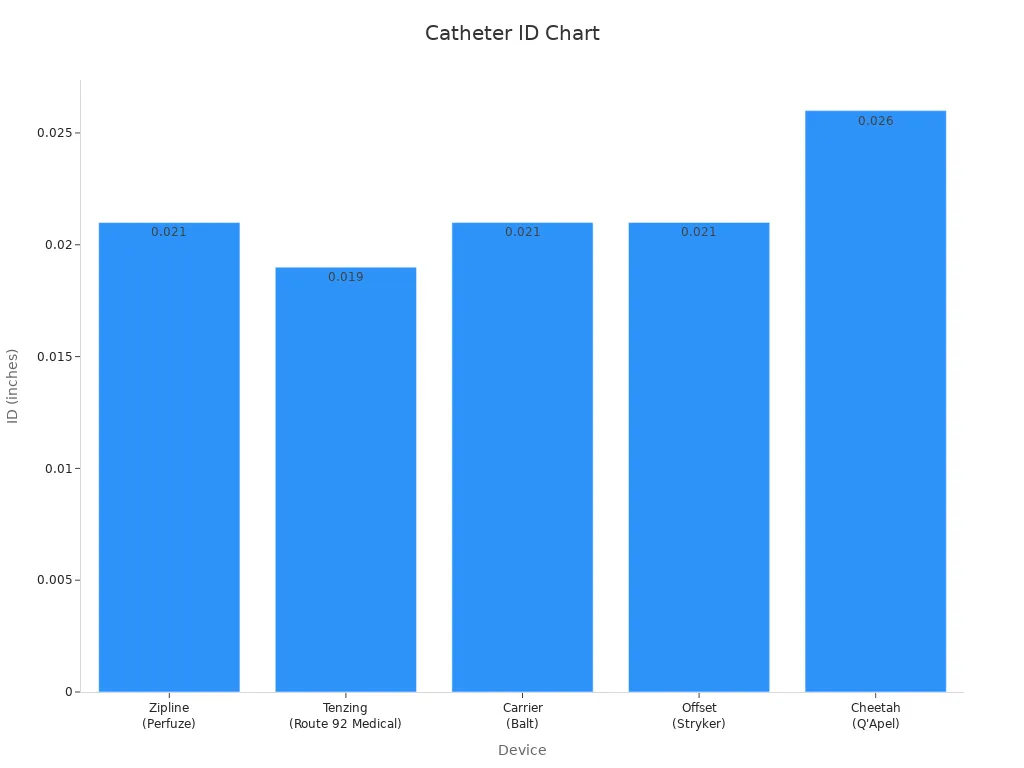
PET tubing helps catheters stay smooth and fit tightly. This stops gaps and bumps, so catheters move easier in the body. The tubing can shrink to make tips that are thinner. This helps doctors guide catheters through tricky blood vessels. PET tubing keeps its shape after being cleaned many times, which is important for using them again.
Big companies like TE Connectivity and Sumitomo Electric make PET tubing with walls thinner than 0.15 mm. This helps make tools that do not hurt the body much. Zeus Industrial Products uses special PET blends that the body can absorb. This lowers the body’s reaction to some devices by 40%. These things show why PET tubing is a top pick for catheters and shafts in medical tools.
Sealing and Fixation
Sealing and holding parts in place is important in medical tools. PET tubing can shrink and hold tightly around wires and parts. This stops leaks and keeps things from moving. PET tubing is safe for the body, so it can be used inside people.
Makers use PET tubing to help parts bend without breaking. PET yarns with special coatings are used to make sensors in fabrics. These sensors can feel when something bends and help protect wires. PET tubing’s smooth surface and shrinking help seals stay strong, even after cleaning many times.
PET tubing helps with:
Sealing connectors and joints tightly
Holding small parts in place in good devices
Helping flexible tools bend without breaking
Shrinking the same way every time for good seals
Medoplast GmbH has patents for adding color to PET tubing. This stops blurry images in endoscopy tools, so doctors see better. 3M makes PET tubes with glue inside. These tubes are used in almost half of vascular access devices in U.S. hospitals. They help seal and hold parts, making treatments safer.
Electrical Safety
Electrical safety is very important in medical tools. PET tubing is great at stopping electricity from leaking. This keeps patients and devices safe from shocks. The tubing is safe for the body and passes many safety tests. It also meets FDA and CE rules, so it is safe to use with people.
PET tubing gives:
Strong insulation over 4,000 V/mil
High strength for tough electrical jobs
Resistance to chemicals and heat, even after cleaning
Meets ISO 13485, RoHS, and other safety rules
PET tubing keeps blocking electricity after being cleaned with gas, heat, or radiation. The tubing is tough and shrinks well, so it is good for covering wires in medical tools. Factories use very clean rooms to make PET tubing. This keeps it free from dirt and safe for the body.
Tip: PET tubing is trusted for electrical safety because it shrinks well, is safe for the body, and can be cleaned many times.
PET tubing is used in many medical tools. Its thin walls, strong shrinking, and safety help make good devices. The tubing can be cleaned many times and still work well. This keeps medical devices safe and working for a long time. PET tubing is still a top choice for shrinking, sealing, holding, and electrical jobs in medical tools.
Ultra-thin wall PET tubing is special because of its material science. The way it is made gives it strong walls and smooth surfaces. It can also be cleaned many times without problems. The table below shows how making changes in the process can change how PET tubing works:
Fermentation Run | pH | Induction Strength (µmol IPTG/g CDW) | PET Degradation (%) in 72h |
|---|---|---|---|
A | 6.5 | 0.8 | 100 |
B | 6.5 | 0.8 | 71 |
C | 6.5 | 0.8 | 54 |
D | 6.0 | 0.4 | 43 |
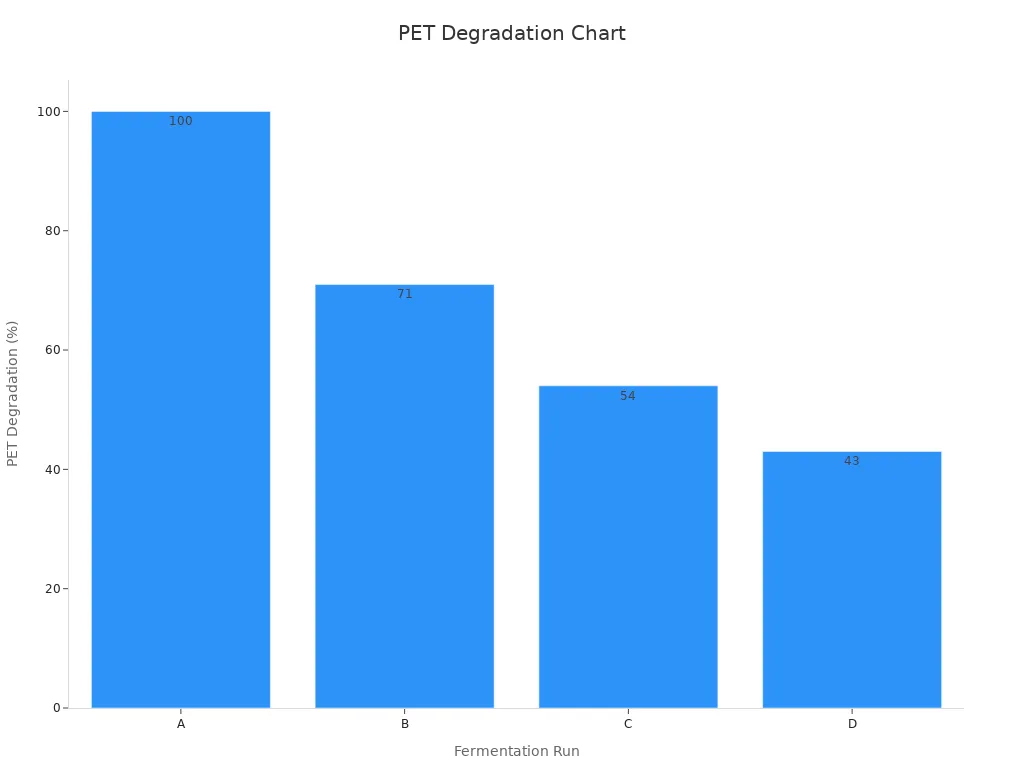
PET tubing is used in many things, especially medical devices. These devices need to be safe for the body and cleaned often. When picking tubing, engineers should think about material science. This helps them get the best results for their projects.
FAQ
What makes ultra-thin wall PET tubing different from regular tubing?
Ultra-thin wall PET tubing has much thinner walls than normal tubing. This lets it bend more and fit tightly around small parts. Medical device makers like this tubing because it is strong and smooth. It can also handle being cleaned many times.
How does sterilization affect PET tubing in medical devices?
Sterilization is very important for medical tools. PET tubing can handle steam, gas, and radiation cleaning. The tubing keeps its shape and strength after being cleaned. This means it is safe to use again in hospitals and clinics.
Can PET tubing be used after multiple sterilization cycles?
Yes, PET tubing stays strong and bendy after many cleanings. Hospitals use autoclaves or chemicals to clean tools. The tubing does not break or lose its protection, even after many cleanings.
Why do medical devices need tubing that resists sterilization damage?
Medical devices must stay safe and clean for patients. Tubing that does not get damaged by cleaning helps stop germs. PET tubing keeps its smooth surface and strength after being cleaned. This helps devices last longer and work better in hospitals.
What types of sterilization work best with PET tubing?
PET tubing works well with steam, ethylene oxide gas, and gamma radiation. Each way kills germs but does not hurt the tubing. Makers test the tubing to make sure it stays strong and safe after every cleaning.
See Also
Top Uses Of Ultrathin PET Heat Shrink Tubing In Medicine
Importance Of Ultra-Thin PET Heat Shrink Tubing In Healthcare
Selecting The Ideal Ultra-Thin PET Heat Shrink Tubing Guide
Essential Facts About PET Heat Shrink Tubing For Electronics

