What is Thin Wall Nitinol Tubing for Guidewires
You can see thin wall niti tubing for guidewire used in many medical procedures. This tubing is made from nitinol. Nitinol is known for being very flexible and safe for the body. Nitinol bends easily and does not break. It helps you move devices safely. Thin walls help doctors be more exact and lower risks. Nitinol is picked because it keeps its shape and does not rust. Check the table below to see why nitinol works well:
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Superelasticity | Gives flexibility and strength, so it does not get damaged easily. |
Biocompatibility | Works like other safe implant materials, especially after treatment, so it does not cause bad reactions. |
Thin wall niti tubing for guidewire helps stop kinks, keeps its shape, and is easy to move.
Key Takeaways
Nitinol tubing bends easily and is safe for people. This makes it good for guidewires in medical work. Superelasticity lets nitinol go back to its shape after bending. This helps doctors move through small spaces. Thin walls in nitinol tubing give better control. They also help lower risks during medical work. Nitinol is biocompatible, so it works well with the body. This means there are fewer bad reactions. Using nitinol guidewires makes surgeries safer. It also helps patients get better results.
Thin Wall Niti Tubing for Guidewire: Key Properties
Superelasticity and Shape Memory
Nitinol is used in guidewires because it is superelastic and has shape memory. If you bend nitinol tubing, it goes back to its old shape. This helps guidewires move through small and twisty blood vessels. Shape memory means nitinol can change shape when cold and return to its set shape when warm in the body. This makes nitinol different from stainless steel.
Tip: Nitinol guidewires can go back to their shape after bending or twisting. This helps doctors reach hard spots during procedures.
Here is a table that shows how nitinol tubing and stainless steel tubing are different:
Property | Nitinol Tubing | Stainless Steel Tubing |
|---|---|---|
Superelasticity | Goes back to its shape after bending | Not very stretchy |
Shape Memory Effect | Can return to a set shape | Does not have shape memory |
Flexibility | Very flexible for tricky places | Not as flexible |
Fatigue Resistance | Works well after many bends | Gets tired and weak over time |
Nitinol is used in stents, bone implants, and endoscopic tools. These need to bend and move without breaking. Shape memory lets guidewires go back to their shape at body temperature. This helps guidewires move through tough paths and reach hard places in the body.
Biocompatibility and Corrosion Resistance
Nitinol is made from nickel and titanium. It is safe to use in the body. Medical nitinol lowers the chance of swelling or rejection. Special surface treatments like electropolishing make nitinol even safer. These treatments lower the risk of blood clots and help nitinol fit in with body tissues.
Medical nitinol does not cause cell, nerve, gene, or allergy problems like stainless steel.
Electropolished nitinol helps stop blood clots and helps it join with body tissue.
Nitinol is used in implants that stay in the body for a long time because it does not rust. This keeps guidewires strong and safe, even after many uses. The medical field trusts nitinol because it is safe and works well.
Precision and Thin Wall Design
Guidewires need thin walls for better control and less risk. Nitinol tubing can be made with very thin walls and exact sizes. Factories use special methods like alloy control, mandrel drawing, and heat treatment to make thin wall nitinol tubing. Cameras check the wall thickness, and workers fix problems fast.
Here is a table that shows how factories make nitinol tubing and keep it the right size:
Manufacturing Technique | Tolerance Range |
|---|---|
Outer Diameter (OD) | +0.0003" to +0.001" (10.2 µm to 25.4 µm) |
Precision Tubing Tolerance | ±0.0005" (12.7 µm) |
Concentricity Tolerance | > 90% |
You can see that thin wall nitinol tubing meets strict size rules. Factories keep the wall thickness the same so guidewires are safe. Even a small change in nickel can change nitinol’s shape memory and superelasticity. Workers use heat and special tools to keep tubing exact.
Here is a chart that shows OD and wall tolerances for different nitinol tubing sizes:

Nitinol tubing comes in different grades. Standard grades have tolerances as small as 10.2 µm. Precision and premium grades can be as close as ±12.7 µm or better. These tight sizes help doctors use guidewires in careful procedures.
Note: Keeping thin walls and exact sizes helps stop kinks and makes guidewires work better in medical procedures.
Guidewire Performance with Nitinol Tubing
Flexibility and Kink Resistance
You need a guide that bends but does not snap. Nitinol makes this happen. When you use a nitinol guide, it moves through tight spots easily. It does not get stuck. Superelasticity lets the guide bend and twist. It always goes back to its shape. You can push the guide through curves and loops. You do not have to worry about kinks.
Nitinol tubing makes your guide very flexible.
Nitinol keeps your guide strong during long use.
Superelasticity lets your guide bend in tight places.
Studies show nitinol guides are more flexible than steel ones. This helps you move the guide through tricky body parts. Shape memory means your guide can bend many times and still work. Your guide lasts longer and works better.
Navigation in Complex Anatomy
You often need to move a guide through twisty, narrow vessels. Nitinol helps you do this easily. Shape memory and superelasticity let your guide fit vessel curves. The guide can change shape as it moves. It goes back to normal when needed. This helps you reach hard spots.
Nitinol helps your guide move through tough places.
Your guide fits vessel curves and causes less harm.
New tech, like hybrid designs and coatings, makes guides better.
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Superelasticity | Gives your guide more flexibility and kink resistance, perfect for delicate vessels. |
Shape Memory | Lets your guide adapt to complex pathways, improving navigation. |
Technological Advances | Hybrid designs and coatings help your guide perform in challenging scenarios. |
Nitinol guides have changed how you do surgery. You can use tools that are flexible and work well. These guides help you reach hard places and stay in control. In one study, a nitinol guide called Fielder XT worked 87.8% of the time in tough cases. Regular guides only worked 79.0% of the time. You get better results and fewer problems.
Tip: With a nitinol guide, you can reach places that were too hard before. This means safer procedures and better results for patients.
Safety and Reliability
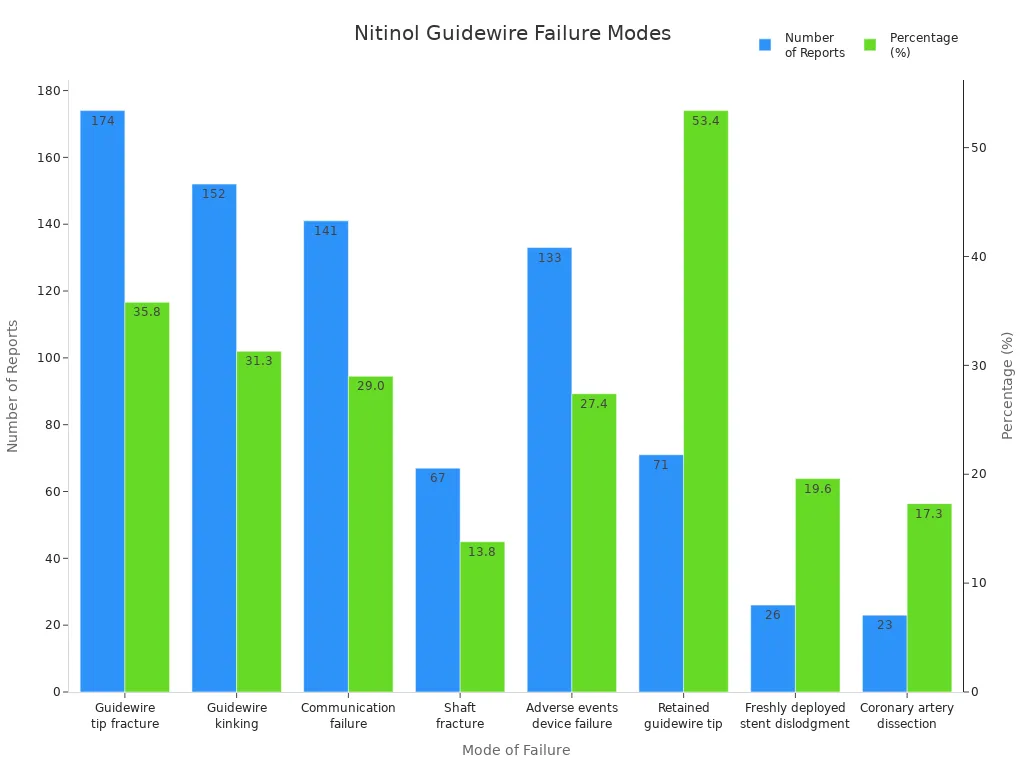
You want a guide that keeps patients safe. Nitinol guides help lower the risk of problems. Nitinol is strong and flexible. Your guide is less likely to break or kink. You can trust your guide to work well, even in long or hard cases.
Mode of Failure | Number of Reports | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
Guidewire tip fracture | 174 | 35.8 |
Guidewire kinking | 152 | 31.3 |
Communication failure | 141 | 29.0 |
Shaft fracture | 67 | 13.8 |
Adverse events due to device failure | 133 | 27.4 |
Retained guidewire tip | 71 | 53.4 |
Freshly deployed stent dislodgment | 26 | 19.6 |
Coronary artery dissection | 23 | 17.3 |
Deaths reported | 7 | N/A |
Nitinol guides are used the most in the market. You see them more because they are flexible and strong. These guides help you place catheters more easily and with care. As you do more simple surgeries, you need guides that work every time. Nitinol guides meet this need.
Nitinol guides help you do hard surgeries.
You get guides that last longer and work better.
More people need nitinol guides as treatments get better.
When you use a nitinol guide, you keep patients safe and lower device problems. You can trust your guide to help you get the best results.
Medical Uses of Nitinol Guide Wires
Nitinol guide wires are used in many areas of medicine. You find these wires in heart, brain, and blood vessel procedures. Doctors like nitinol guide wires because they bend and fit in small spaces. These wires help make surgeries safer and give better results.
Cardiovascular Procedures
Doctors use nitinol guide wires for heart procedures every day. These wires help with angioplasty, stent placement, and blocking blood flow. Nitinol guide wires make these treatments hurt less and help patients heal faster. You can move the wires through tricky arteries with care.
Angioplasty: Nitinol guide wires open blocked arteries. The wires bend and twist, so the surgery is less invasive.
Stent Placement: Nitinol guide wires help place stents. The wires reach hard spots and help finish the job quickly.
Embolization: Nitinol guide wires block blood flow in certain places. The wires help lower risks and give better results.
Procedure | Advantages |
|---|---|
Coronary Angioplasty | Easier to move through tough blood vessels. |
Stent Placement | Safer and faster for hard-to-treat arteries. |
Nitinol guide wires bend more and do not kink like stainless steel wires. You see more success in heart procedures with these wires.
Neurovascular Applications
Doctors use nitinol guide wires for brain and nerve procedures. These wires help treat strokes, tangled blood vessels, and block blood flow. Nitinol guide wires move through twisty brain vessels without kinking. Surgeries are safer and patients heal better.
Application Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
Embolization Procedures | Flexible, do not kink, work with other tools, easier to move, safer surgeries. |
Arteriovenous Malformations | Bend to fit tricky paths, do not kink, work with small tubes. |
Stroke Treatment | Move quickly in vessels, shape memory helps guide, safer for patients. |
General Neurovascular Use | Block blood flow well, fewer problems after surgery, patients heal faster. |
Nitinol guide wires help doctors do better in brain procedures by 25%. There are fewer problems and patients get better faster.
Peripheral Vascular Interventions
Doctors use nitinol guide wires to reach blocked blood vessels and give treatment. These wires bend and move through hard blood vessel paths. You can cross blockages and reach the right spot easily.
Nitinol guide wires help cross blockages, even when fully blocked.
You can use devices more easily.
You save money and lower the chance of hurting blood vessels.
Guidewire Material | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
Nitinol | Bends, does not kink | Reaching target vessels, crossing blockages, giving treatment |
Stainless Steel | Stiff, supports well | General blood vessel procedures |
Cobalt Chromium | Pushes well | Crossing blockages near the start of vessels |
Nitinol guide wires help you move through blood vessels with control. You can steer the wires and avoid hurting the vessel. These wires stay strong and keep their shape even when pushed.
Tip: Nitinol guide wires are good for surgeries with small cuts. These wires help you reach tough spots and help patients get better.
Thin wall nitinol tubing helps guidewires work better. You get wires that bend easily and do not kink. These wires are strong and last a long time. Factories make guidewires with care and check them for quality. This keeps patients safe during procedures.
Attribute | Benefit |
|---|---|
Precision Manufacturing | Makes sure medical devices work well |
Durability and Flexibility | Helps doctors do smoother procedures |
Quality Control Measures | Makes devices safe and meet rules |
New guidewires will have cool features soon. Some will use tiny sensors, fiber optics, and robots. Nitinol tubing has made stents and catheters better. Patients heal faster and have fewer problems.
Nitinol fits in small places and bends without breaking.
You use guidewires that last longer and work in hard cases.
Future guidewires will help you control them better and keep patients safe.
Thin wall nitinol tubing helps doctors and patients. It makes healthcare safer and works better for everyone.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing better for guidewires than stainless steel?
Nitinol tubing bends more than stainless steel. It does not break or kink as easily. Nitinol goes back to its shape after bending. Stainless steel can get stuck or snap. Nitinol lasts longer during use.
How thin can nitinol tubing walls be for medical guidewires?
Nitinol tubing walls can be as thin as 0.001 inches. This is about 25 microns. Factories use special tools to make thin, strong walls. Thin walls help you steer the guidewire better.
Is nitinol safe for your body?
Nitinol is safe for your body. Doctors use it in many implants. Special surface treatments make it even safer. These treatments help stop allergies or blood clots.
Where do you use nitinol guidewires most often?
Doctors use nitinol guidewires in the heart, brain, and blood vessels. These wires help reach blocked arteries and treat strokes. They also help with surgeries that need small cuts.
See Also
The Manufacturing Process of Nitinol Tubing for Medicine
The Importance of Nitinol Tubing in Minimally Invasive Surgery
The Significance of Nitinol Tubing in Modern Healthcare
