How Superelastic Nitinol Tubing Enables Flexible and Durable Medical Solutions
You see superelastic nitinol tubing changing how medical devices work. This tubing can bend and twist, then go back to its shape. It does this even after strong force is used. Nitinol has special properties like superelasticity and shape memory. These help devices reach hard places in your body. Nitinol does not rust and lasts longer than many other metals. Doctors use this tubing for things like stents, catheters, and surgical tools. Hospitals pick nitinol because it makes devices flexible, strong, and safe for patients. The market for superelastic tubing in medical devices keeps growing as more people need better care.
Key Takeaways
Superelastic nitinol tubing can bend and twist easily. It always goes back to its first shape. This makes medical devices both flexible and strong.
Nitinol tubing does not rust or wear out fast. It lasts longer than stainless steel or plastic in medical tools.
Doctors use nitinol tubing in stents, catheters, and surgery tools. These tools help doctors reach hard places in the body safely.
Nitinol tubing is safe for the body and does not cause many allergies. It helps patients get better more quickly.
Careful making and testing make sure nitinol tubing is strong and safe. It meets tough medical rules for safety and strength.
What Is Superelastic Nitinol Tubing?
Material Properties
You may ask why superelastic nitinol tubing is so special. This tubing is made from a nickel-titanium alloy. The mix of these two metals is almost equal. Nitinol is very pure, which gives it special qualities. Other materials do not have these qualities. The tubing can bend, twist, and stretch. It always goes back to its original shape. This happens because of the way atoms are arranged inside nitinol.
Superelastic nitinol tubes are flexible and strong. They work well in medical devices that move through small or curved spaces. The tubing does not kink or crush easily. It keeps working even when under pressure. It also does not rust, so it lasts longer in the body. Doctors trust nitinol tubing because it is safe for patients.
Tip: Superelastic nitinol tubes come in many shapes and sizes. This helps match the tubing to each medical device’s needs.
Making superelastic nitinol tubing takes careful steps. Makers melt the metals in a vacuum to keep them clean. They shape the alloy into blocks called ingots. Then they heat and work the metal to get the right grain structure. After that, they pull the tubing through dies and heat it again. This removes stress from the metal. These steps give you tubing with the best superelastic behavior and strength.
Shape Memory and Superelasticity
The real magic of nitinol is in its shape memory and superelasticity. When you bend or stretch the tubing, it changes shape. But it goes back to normal when you let go. This is because nitinol can switch between two crystal forms. These are called martensite and austenite. At low temperatures or under stress, nitinol becomes martensite. Martensite is easy to shape. When you heat it or remove stress, it turns back to austenite. Then it snaps back to its original shape.
Superelastic nitinol tubing can handle large strains, sometimes over 5%. It still goes back to its shape. Most metals cannot do this. The tubing acts almost like rubber but is as strong as metal. Studies show superelastic nitinol tubes are better than other shape memory alloys. They are more flexible and recover better. You can trust this tubing for devices that need to bend and twist. It will not break or lose its shape.
Superelastic behavior makes nitinol tubing great for medical tools. These tools must go through blood vessels or tight spaces. You get both shape memory and superelasticity. This means your devices stay safe and reliable during use.
Performance Benefits of Nitinol Tubing
Flexibility and Kink Resistance
Superelastic nitinol tubes are very flexible in medical devices. You can bend, twist, or stretch them. They always go back to their original shape. This helps devices move through tight or curved places in the body. You do not have to worry about kinks or bends that stay. Superelastic nitinol tubing lets you make devices for hard-to-reach spots. This makes less invasive surgeries safer and better.
Note: Superelastic nitinol tubes can bounce back after big bends. Your device keeps its shape, even after many uses.
Studies show nitinol tubing helps guidewires and catheters move in small blood vessels. The tubing’s superelasticity lets it fit the shape of the vessel. This lowers the chance of hurting the vessel. You get better control and more accurate placement. Devices with superelastic nitinol tubes help patients feel better and heal faster.
Durability and Fatigue Resistance
You want medical devices to last a long time. Superelastic nitinol tubes are very strong and resist breaking. They can bend millions of times and not break. The table below shows how nitinol tubing compares to stainless steel:
Property / Material | Nitinol Tubing (Superelastic NiTi Alloy) | Stainless Steel (Medical Grade) |
|---|---|---|
Fatigue Resistance | Can endure 10 million to 1 billion bends without failure | Less flexible, prone to fatigue failure |
Elastic Deformation Capacity | Up to 8% elastic strain with full shape recovery | No superelastic strain capacity |
Tensile Strength | Typically 500–900 MPa, >800 MPa when welded | Typically 600–1100+ MPa |
Corrosion Resistance | High, especially with electropolishing | Good, but less durable under bending stress |
Flexibility | High, suitable for bending in tight or curved anatomical sites | Lower, less suitable for repeated bending |
Nitinol tubing is better than polymers too. Superelastic nitinol tubes keep their shape and strength after many uses. Polymers can break or get weak under stress. Nitinol tubing stays strong and works well. You can trust your device to work every time, even in tough surgeries.
Superelastic nitinol tubes do not rust and are safe for the body.
Devices with nitinol tubing last longer and are less likely to fail.
Patients have fewer problems and get better results.
Superelasticity and shape memory make nitinol the best for flexible, strong medical devices. You get tools that work well, even after many uses. This helps doctors give safer and better care.
Applications of Superelastic Nitinol Tubing in Medical Devices
Superelastic nitinol tubes have changed how doctors use medical devices. These tubes help make tools that bend and twist, but always go back to their shape. You can find them in many devices, like stents, catheters, and surgical tools. More doctors use superelastic nitinol tubing because they want safer and easier ways to treat people.
Note: The market for nitinol medical devices is growing quickly. Experts think it will reach $38.6 billion by 2031. North America is growing the fastest because more people need less invasive surgeries.
Stents and Vascular Implants
Superelastic nitinol tubes are important in self-expanding stents and vascular implants. These stents can squeeze small for delivery. When inside the body, they open up to fit the blood vessel. Shape memory helps the stent keep the vessel open and lets blood flow. Superelasticity lets the stent bend with the vessel, so it does not kink or break.
Studies show nitinol stents work very well. For example, patency rates can be as high as 86.3% after 12 months. Stent fracture rates are 0% in many tests. Most patients have better blood flow and fewer problems. Nitinol stents last longer because they do not rust or wear out. Doctors trust these devices for hard vascular procedures.
Clinical Outcome Aspect | Evidence Summary |
|---|---|
Primary Patency Rate | 58% to over 90% at 12 months; e.g., 86.3% at 12 months |
Stent Fracture Rate | 0% at 12 months; no fractures in long-term tests |
Clinical Improvement | 88.7% of patients improved by at least one category |
Procedural Success | Above 85% in aneurysm treatments |
Mortality and Complications | Perioperative mortality as low as 0.6% |
Doctors use self-expanding stents for many things, like treating artery disease and aneurysms. Superelastic nitinol parts help stents fit twisted vessels. This makes surgeries safer and helps patients get better results.
Tip: Studies like RESILIENT and MISAGO show nitinol stents work well for real patients.
Catheters and Guidewires
Catheters and guidewires with superelastic nitinol tubes give doctors more control and safety. These tools must move through tiny, winding blood vessels. Superelasticity lets the catheter bend and twist without kinking. Doctors can reach hard places in the body with less risk.
Success rates are high with nitinol guidewires. For example, vessel crossing works 98% of the time. Catheter delivery works about 92% of the time. Nitinol’s biocompatibility lowers implant rejection by 30% compared to other metals. This means fewer problems for patients and better results.
Evidence Aspect | Metric / Result | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Vessel Crossing Success Rate (Guidewires) | 98% | High reliability in navigating blood vessels |
Catheter Delivery Success Rate | 92% | Most catheters are placed successfully |
Implant Rejection Reduction | 30% lower | Nitinol reduces tissue reactions |
Device Durability | Millions of cycles | Less risk of device failure |
Superelastic nitinol tubes also help in brain surgeries. Some brain vessel procedures have a 100% success rate. Catheters made with nitinol are flexible and last a long time. This means fewer repeat surgeries and faster healing for patients.
Retrieval Baskets and Hingeless Instruments
Doctors use superelastic nitinol tubes in retrieval baskets and hingeless surgical tools. These tools must bend and flex many times during surgery. Superelasticity lets baskets open and close smoothly. The tubes do not kink, so doctors can move them through tight spaces.
Retrieval baskets with nitinol tubing help remove stones or objects from the body. Hingeless tools use nitinol to grab and hold tissue without breaking. Superelastic nitinol tubes give a steady force, so these tools are easy to use and reliable.
Callout: Nitinol’s special phase change lets these tools recover from up to 8% strain. This means you can use them again and again in advanced medical devices.
You see superelastic nitinol used in many surgeries, like laparoscopy and endoscopy. Doctors can make complex device shapes for less invasive surgeries. This helps patients heal faster and with less pain.
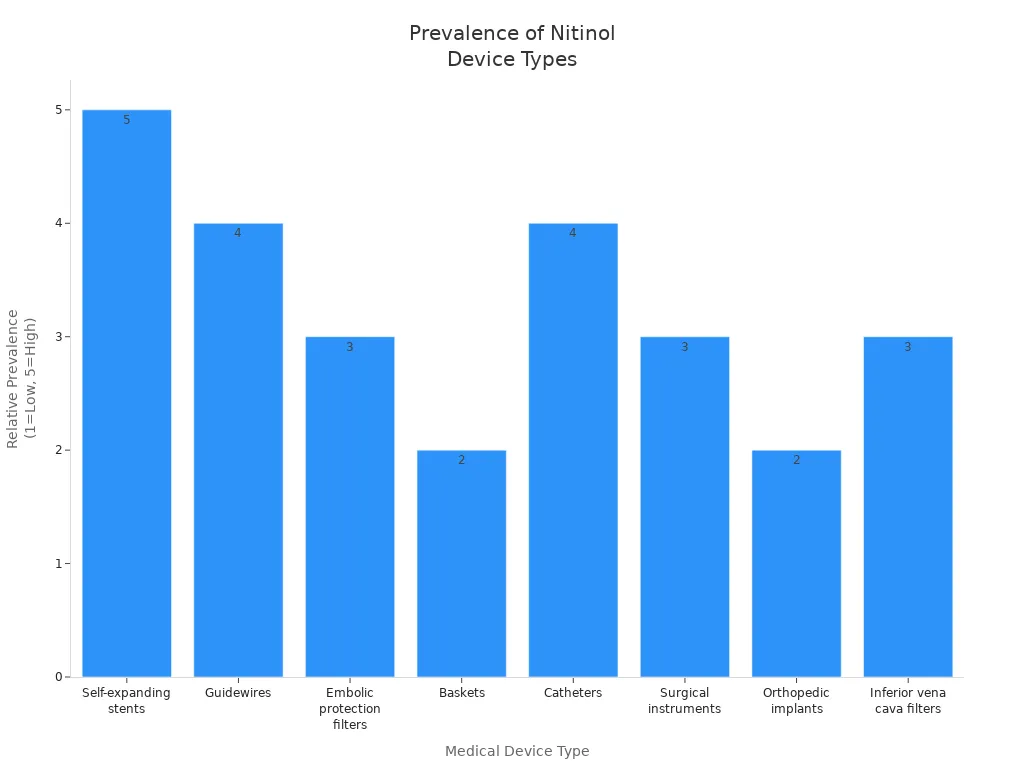
Table: Medical Devices Utilizing Superelastic Nitinol Tubing and Market Trends
Medical Devices Utilizing Superelastic Nitinol Tubing | Supporting Market Data and Trends |
|---|---|
Self-expanding stents (especially peripheral vascular) | Dominance in nitinol medical device market; key for improving blood flow in peripheral artery disease |
Guidewires | Widely used in minimally invasive procedures; part of peripheral vascular products segment |
Embolic protection filters | Commercially successful products in recent years |
Baskets | Used in minimally invasive interventional procedures |
Catheters | Growth driven by minimally invasive surgeries; improved maneuverability and reduced trauma |
Surgical instruments | Increasing demand due to minimally invasive techniques |
Orthopedic implants (rods, screws) | Development spurred by success in peripheral vascular space; used in spinal surgeries |
Inferior vena cava filters | Significant commercial success in recent years |
Superelastic nitinol tubes help doctors make advanced medical devices with special shapes. These devices can go through small cuts, so surgeries are less invasive. Shape memory, superelasticity, and biocompatibility make nitinol tubing a top choice for many medical uses.
Nitinol Tubing vs. Traditional Materials
Stainless Steel and Polymers
When you look at nitinol tubing and compare it to stainless steel and polymers, you notice big differences in how they work in medical devices. Nitinol is special because it bends and then goes back to its shape. Stainless steel is hard and can bend out of shape. Polymers are soft but can break or wear out quickly. Nitinol gives more flexibility and superelasticity. This means devices can move through tight places without getting stuck or breaking.
Performance Aspect | Nitinol Tubing | Stainless Steel / Polymers |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility & Superelasticity | High; bends and returns to shape easily | Stainless steel is stiffer; polymers flexible but less durable |
Fatigue Resistance | Excellent; withstands millions of bends | Stainless steel less flexible; polymers prone to cracking and wear |
MRI Safety | Non-ferromagnetic; safe for MRI procedures | Stainless steel is ferromagnetic and unsafe for MRI; polymers are MRI-safe but weaker |
Clinical Recovery | 20% faster patient recovery; fewer complications | Generally slower recovery and higher complication risk |
Allergic Reactions | Lower incidence due to biocompatibility | Higher risk with stainless steel; polymers generally biocompatible but less durable |
Vessel Patency | High long-term patency rates in vascular interventions | Lower patency and more repeat procedures reported |
Device Durability | High; advanced surface treatments improve lifespan | Stainless steel durable but less flexible; polymers less durable |
Device Customization | Advanced heat treatments allow tailored properties | Limited customization compared to nitinol |
You should also think about price. Nitinol tubing costs more than stainless steel or polymers. This is because making nitinol is harder. The price is higher, but you get special things like shape memory, superelasticity, and no rust. These features help you make devices that last longer and work better. This is very important for things like stents.
Tip: Even though nitinol costs more, it can save money later. You need fewer repeat surgeries because the devices last longer.
Patient Outcomes and Device Longevity
Nitinol tubing helps patients get better results. Devices made from nitinol can bend and fit inside tricky blood vessels. This lowers the chance of hurting the vessel and helps people heal faster. You see this in stents and guidewires. Nitinol’s superelasticity lets these tools move smoothly and cause less harm. Patients heal about 20% faster and feel less pain when doctors use nitinol instead of other materials.
Nitinol’s shape memory lets devices go back to their shape after bending.
Its biocompatibility means fewer allergies and less rejection.
Devices last longer because nitinol does not get tired or rusty.
You find nitinol in many new heart devices, like transcatheter heart valves and leadless pacemakers. These devices keep working for a long time because nitinol can bend millions of times without breaking. Special coatings on nitinol tubing also stop nickel from leaking out, so implants are safer for long use.
Nitinol’s special features help make devices smaller, more bendy, and stronger. This means fewer problems and more comfort for patients.
Nitinol tubing helps doctors do less invasive surgeries. This means less pain and faster healing for patients. You can count on nitinol to be safe and work well in tough medical jobs.
Manufacturing and Quality for Superelastic Nitinol Tubes
Medical-Grade Processing
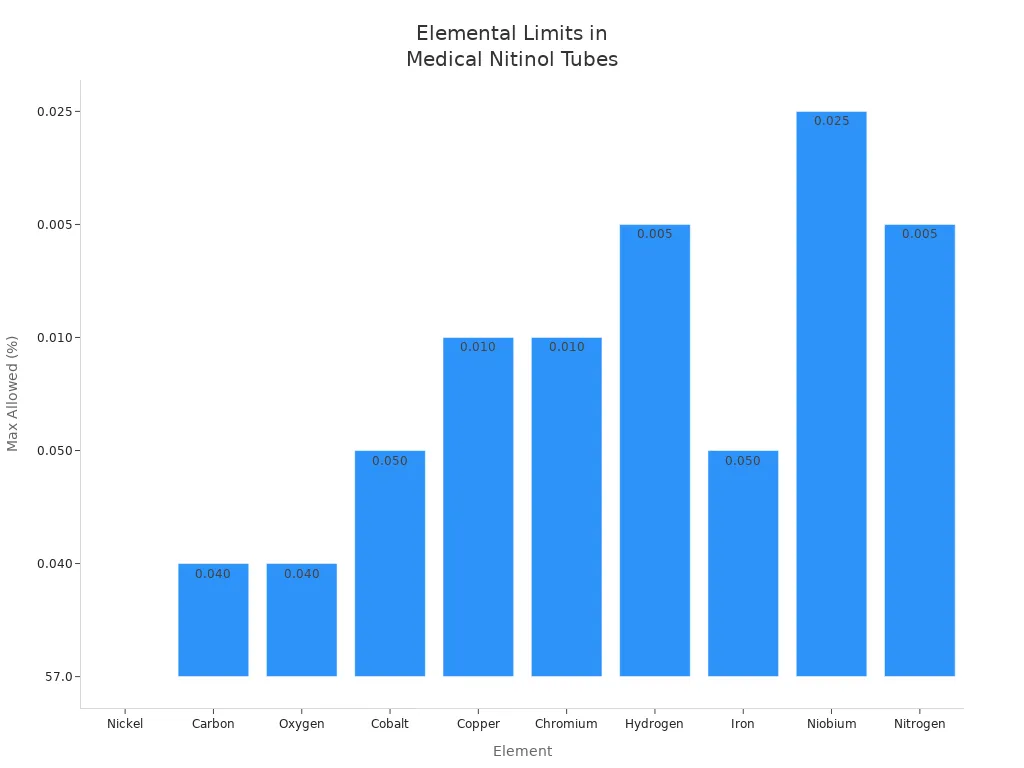
Nitinol tubing for medical devices must meet strict rules. Makers follow careful steps to keep each tube safe and strong. First, they mix nickel and titanium in exact amounts. The table below shows how much of each element is allowed in medical-grade nitinol:
Element | Allowed Range or Maximum (%) |
|---|---|
Nickel | 54.5 - 57.0 |
Titanium | Balance |
Carbon | ≤ 0.040 |
Oxygen | ≤ 0.040 |
Cobalt | ≤ 0.050 |
Copper | ≤ 0.010 |
Chromium | ≤ 0.010 |
Hydrogen | ≤ 0.005 |
Iron | ≤ 0.050 |
Niobium | ≤ 0.025 |
Nitrogen | ≤ 0.005 |
Keeping these elements under control helps nitinol stay strong and flexible. You can see how little of each impurity is allowed in the chart below:
Makers use many steps to shape and finish nitinol tubing:
They heat the alloy to set its shape and superelasticity.
They polish the surface to make it smooth and stop rust.
They test each batch for strength, size, and surface quality.
They use special tools like ultrasound and X-rays to find hidden problems.
They follow rules like ASTM F2063 and ISO 13485 to make sure every tube is safe for medical use.
These steps help nitinol tubing work well in devices that bend and flex many times.
Biocompatibility and Safety
Nitinol tubing must be safe to use in the body for a long time. Experts test nitinol to make sure it is safe before using it in any device. Tests show that nickel from nitinol stays far below FDA safety limits. The chart below shows how nickel release gets lower over time:
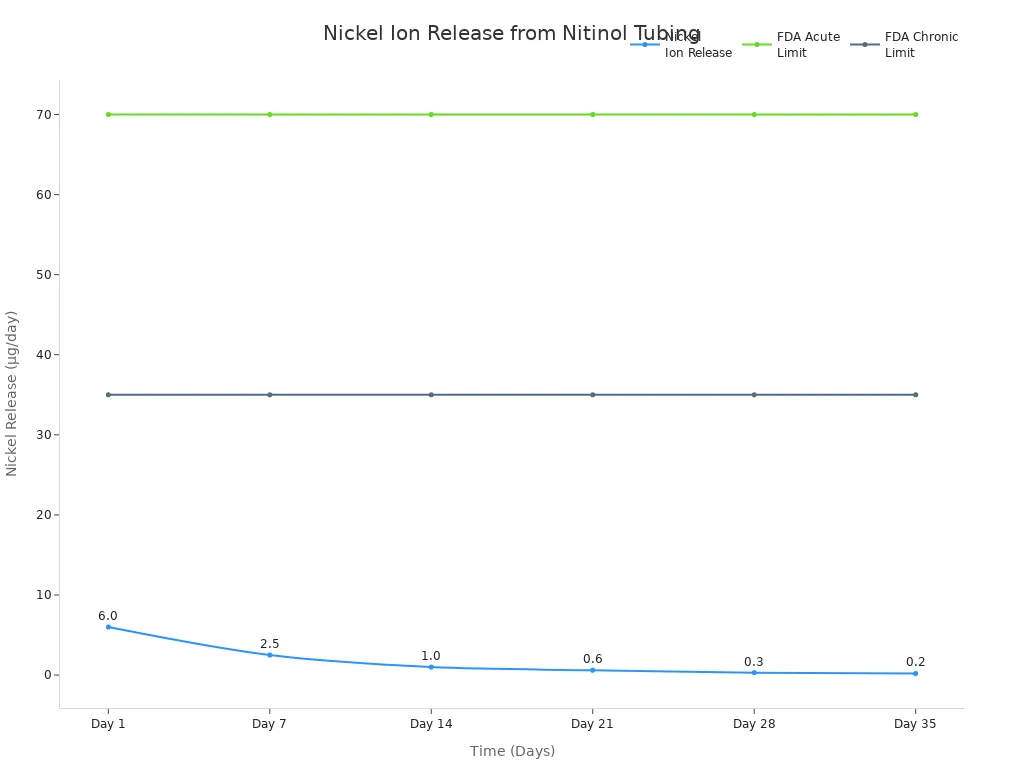
Nitinol makes a strong oxide layer on its surface. This layer stops rust and keeps nickel from leaking out. Doctors see that tissue near nitinol stays healthy, with little swelling even after months. Tests also show nitinol tubing does not cause allergies or toxic reactions.
To keep nitinol safe, makers use:
Electropolishing to smooth the surface and lower nickel release.
Passivation to add a protective layer.
Regular testing for rust resistance and strength.
You can trust that nitinol tubing meets tough safety rules. It passes tests for safety, strength, and performance. This makes it a good choice for medical implants and devices that stay in the body for years.
You can see superelastic nitinol tubing making big changes in medical devices. This tubing helps make devices that are flexible, strong, and work well for patients. New improvements include thin film nitinol, smoother surfaces, and tubing that lasts longer. The table below shows how these help medical devices:
Innovation Aspect | Impact on Medical Devices |
|---|---|
Thin Film Nitinol | More precise and reliable tools for small surgeries |
Fatigue Durability | Devices last two times longer |
Surface Finishes | Safer for the body and work better |
You will also see new trends in medical devices. These include making devices smaller, using bioresorbable nitinol, and adding smart wearable features. These trends help make devices safer, last longer, and work better. Nitinol tubing will keep leading new ideas in medical care.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing different from other metals?
You can bend nitinol tubing, and it goes back to its shape. Most other metals will stay bent or might break. Nitinol has superelasticity and shape memory. These features let you use it in devices that need to flex many times. The tubing keeps its strength even after lots of bending.
Can nitinol tubing be used inside your body for a long time?
Yes, you can use nitinol tubing in your body for a long time. It makes a strong oxide layer that protects it. This layer stops nickel from leaking out. Doctors pick nitinol for implants because it stays safe and strong for years.
How does nitinol help in less invasive surgeries?
Nitinol tubing bends and twists without breaking. You can move devices through small or curved spaces. This lets doctors use smaller cuts on patients. People heal faster and feel less pain. Nitinol helps doctors do these advanced surgeries.
Is nitinol safe for people with metal allergies?
You do not need to worry much about allergies with nitinol. It lets out only a tiny bit of nickel. Special coatings make it even safer for people. Most people do not have a reaction to nitinol. Doctors often use it for safe, long-lasting implants.
Tip: Always talk to your doctor if you have questions about nitinol or any implant material.
See Also
Transforming Medical Devices Through Innovative Nitinol Tubing
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Modern Medical Uses
Nitinol Tubing’s Impact On Progress In Medical Technology
Discovering How Nitinol Tubing Enhances Healthcare Equipment
The Process Behind Manufacturing Nitinol Tubing For Medicine

