How Nitinol Tubing Improves Stent Graft Performance in Vascular Procedures

Stent graft nitinol tubing is changing vascular procedures. It uses special material properties that help keep patients safe. These properties also improve how well treatments work. Nitinol’s shape memory effect helps doctors place stents exactly where needed. This works even in tricky blood vessels. Its superelasticity lets it return to its shape almost every time. This lowers the chance of the stent breaking. Nitinol is safe for the body because of a titanium oxide layer. This layer stops rust and keeps tissue from reacting. Studies show a 97% success rate for these stents. There is only a 4.1% chance of a major problem. This proves nitinol makes stents work better and safer every time.
Key Takeaways
Nitinol tubing can remember its shape. It is also very bendy. This helps stent grafts fit blood vessels well. They can go back to their shape after bending.
The strong titanium oxide layer stops rust. It keeps the tubing safe. It also works well with body tissues.
Nitinol stent grafts last a long time. They do not break easily. They help stop problems like leaks or blockages. They also lower the need for more surgeries.
Using nitinol tubing means smaller cuts in surgery. This makes healing faster. It also means less pain for patients.
Nitinol is better than metals like stainless steel. It is more flexible and lasts longer. It is also safer for vascular treatments.
Nitinol Tubing Basics

What Is Nitinol?
Nitinol is a special metal made from nickel and titanium. These two metals are mixed in almost equal amounts. This mix forms a unique crystal structure. Because of this, nitinol has superelasticity and the shape memory effect. When you bend or stretch nitinol, it can go back to its old shape. It does this when it gets warm or when you stop pressing on it. This makes nitinol very helpful for medical tools.
Nitinol got its name from the Naval Ordnance Laboratory. That is where it was first found by scientists. Making nitinol needs careful control of the nickel and titanium mix. People use vacuum arc melting and powder metallurgy to make good nitinol tubing. This tubing is used for vascular grafts. Nitinol can handle lots of bending and high heat. This makes it great for tough jobs. It is safe for the body and does not rust. That is why it works well inside people. These features help nitinol get used in stents, orthodontic wires, and other medical implants.
Nitinol’s shape memory and superelasticity come from its special atomic structure. This lets it bend and stretch many times without breaking.
Nitinol Tubing for Vascular Grafts
Nitinol tubing for vascular grafts has many benefits over other materials. Doctors like nitinol tubing because it is flexible, strong, and safe. The tubing can bend and twist to fit blood vessels. This helps lower injury during surgery and keeps the graft in place.
The table below shows important facts about nitinol tubing in vascular grafts:
Performance Metric | Outcome/Benefit |
|---|---|
Superelasticity | Goes back to shape and fits tricky vessels, so leaks are less likely and fit is better |
Flexibility | Moves through vessel curves, so there is less injury and fewer problems |
Fatigue Resistance | Handles 10 million bends with no breaks or loss of strength |
Biocompatibility | Works safely with tissue, so bad reactions are rare |
Primary Patency Rate | Up to 86.3% at 12 months |
Stent Fracture Rate | 0% at 12 months |
Clinical Improvement | 88.7% of patients get better at 12 months |
Durability | Lasts a long time even under body stress |
Reduced Complications | Low rates of blood clots, blockages, and repeat surgeries |
Technical Success Rates | 87%–98% in studies |
Nitinol tubing for vascular grafts helps doctors get good results and avoid problems. The tubing lasts a long time and is safe for the body. This helps patients heal faster and lowers the chance of blood clots or blockages. Nitinol tubing for vascular grafts is now the top choice for these uses.
Key Properties of Stent Graft Nitinol Tubing
Shape Memory Effect
Nitinol is special because it remembers its shape. This means nitinol tubing for vascular grafts can go back to its old shape after being bent. Doctors can squeeze the stent graft nitinol tubing to make it small for easy delivery. When it is inside the body, it gets warm and grows to fit the blood vessel. This helps blood flow well and stops leaks.
Nitinol self-expanding stents use this memory to fit the vessel.
Orthodontic archwires made from nitinol gently move teeth into place.
Surgical tools made from nitinol are strong and bendy, so they move through the body without breaking.
Tests show nitinol can handle millions of bends, so it lasts a long time.
The titanium oxide layer on nitinol stops rust and makes it last longer in the body.
Orthopedic devices use nitinol to give steady force, which helps bones heal faster.
Dental tools use nitinol because it can bend a lot and not break.
Studies show nitinol tubing keeps its shape memory at body temperature. This is why it works so well in vascular stents, where a good fit is very important.
Superelasticity
Superelasticity lets nitinol stretch and bend more than most metals. In vascular stents, this helps the device move with the blood vessel. Nitinol tubing for vascular grafts keeps its shape even after lots of bending. This stops breaks and helps it last longer.
Evidence Aspect | Superelastic Nitinol Stent Grafts | Non-Superelastic Stent Grafts (Explanted) |
|---|---|---|
Compliance Increase | Up to ~6 times more flexible with radial compression | Flexibility as low as 1.7 × 10⁻⁵ mmHg⁻¹ (much lower) |
Distensibility Loss | Keeps stretching ability in the body | Loses stretching ability by 25% to 88% |
Pulse Wave Velocity Reduction | 22% lower (1.6 times more stretch) | Not as good as superelastic grafts |
Fatigue Life (Stress and Strain at 80–120 mmHg) | Stress: 60 MPa, Strain: 0.038% (safe levels) | N/A |
Operating Temperature Range | Works at body temperature | N/A |
This table shows nitinol stents work better than others in flexibility, stretching, and lasting a long time. Superelasticity helps the stent change with the vessel, so it lasts longer and has fewer problems.
Biocompatibility and Corrosion Resistance
Nitinol tubing is safe for the body in vascular procedures. It makes a strong titanium oxide layer on its surface. This layer keeps the metal from rusting and stops bad reactions with body tissues. Because nitinol tubing is biocompatible, the body accepts it and there is less swelling or rejection.
Doctors trust nitinol because it is safe and works well. Its biocompatibility and rust resistance help the device stay safe and useful for many years. This makes vascular implants last longer and helps patients avoid more surgeries.
Performance Advantages in Vascular Procedures
Self-Expanding Stent Grafts
Self-expanding stent graft nitinol tubing has changed how doctors treat blood vessels. These devices use nitinol’s shape memory and superelasticity to open up by themselves inside the vessel. This helps the stent fit tightly, even in bent or oddly shaped vessels. Doctors can put these grafts in using small catheters. This means less harm to the body and faster healing.
Scientists have tested self-expanding nitinol stents in animals and people. In pigs, making the stents too big caused more tissue to grow inside the vessel. But picking the right size made results better. Studies like the Pulsar-18 nitinol stent showed these stents work well and are safe for patients with femoropopliteal artery disease. The SENS-FP and SUPER-SL trials looked at different stent types. They found that newer nitinol stents bend better, break less, and last longer.
Animal tests showed stents with low friction hurt vessels less.
Clinical studies found that sizing the stent less than 20% bigger at the end improved patency rates to 88%.
Newer nitinol stents broke less often, so vessels stayed open.
The table below shows important facts about nitinol endovascular devices:
Property/Metric | Result/Value |
|---|---|
Elastic Modulus | 28 GPa |
Poisson’s Ratio | 0.3 |
Tensile Strength | 100 MPa |
Flexibility (Solitaire FR) | 0.38 ± 0.11 N |
Flexibility (Trevo XP ProVue) | 0.91 ± 0.11 N |
Flexibility (Stent D) | 0.59 ± 0.05 N |
Fatigue Resistance | Up to 400 million cycles |
Heart Valve Frame Endurance | 600 million heartbeats |
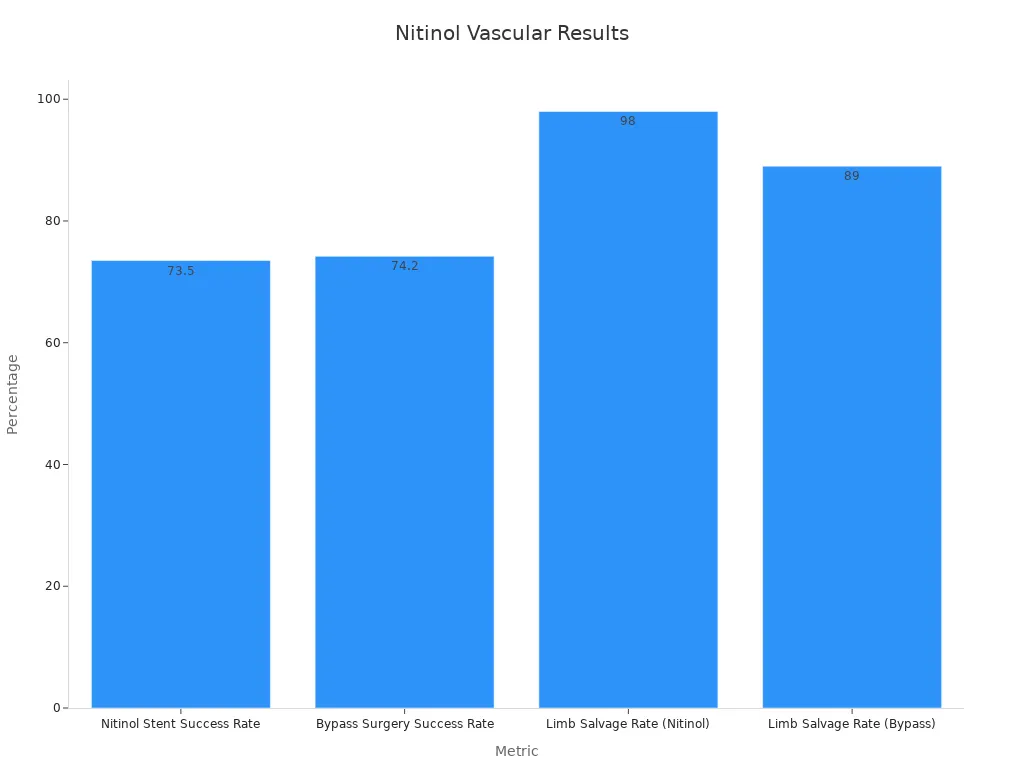
Nitinol Stent Success Rate | 73.5% |
Bypass Surgery Success Rate | 74.2% |
Limb Salvage Rate (Nitinol) | 98% |
Limb Salvage Rate (Bypass) | 89% |
These numbers show nitinol devices are very flexible and strong. They last a long time and help patients stay safe. Using stent graft nitinol tubing helps grafts keep their shape and work well for years.
Vessel Conformability and Apposition
Nitinol endovascular devices are great at fitting the shape of blood vessels. Nitinol lets stent grafts bend and change to match the vessel’s curves and size. This helps stop gaps between the graft and the vessel wall, which can cause problems.
Studies back this up. The STENTYS nitinol stent study used ultrasound to check vessel size after the stent was put in. Three days later, the vessel got 19% bigger. No stents moved out of place after six months. This shows nitinol stent grafts can change with the vessel and stay close to the wall. The CASPER dual-layer nitinol stent also fit the vessel well and had only a 1.4% rate of big problems. Its two-layer design helped stop small clots and made it safer.
Doctors pick nitinol for vascular grafts because it gives:
Automatic fit to vessel size and shape
Strong contact with the vessel wall
Lower chance of vessel injury and clots
Good results in tough cases
These things make nitinol devices the best choice for hard vascular procedures. Being able to fit and stay in place helps them last longer and lowers the need for more surgeries.
Reduced Migration and Endoleaks
Migration and endoleaks are big worries in vascular grafts. Nitinol tubing helps stop these problems by holding tight and staying flexible. Studies using ultrasound checked how well nitinol stent grafts stay put. They found that making the graft bigger made it stiffer, with a 5.9% drop in strain for every 10% more oversizing. This means nitinol grafts can hold on better and move less.
Looking at AneuRx stent grafts with nitinol struts, there were very few breaks or holes. Most problems were not near where the graft was fixed, and there was no clear link to movement or leaks. This means nitinol devices hold well and stay strong over time.
Clinical trials like MISAGO 1 and ORION showed nitinol stents work better than angioplasty to keep vessels open and lower problems. The high fatigue strain limit of 0.4–0.8% and cleaner material make these grafts last longer. Patients with nitinol devices feel better faster and have fewer problems.
Nitinol’s mix of flexibility, strength, and safety gives vascular grafts the boost they need for long-term success.
Using stent graft nitinol tubing in these devices helps grafts stay in place and lowers the risk of leaks. This leads to better results for patients and helps vascular treatments last longer.
Patient Safety and Outcomes
Minimally Invasive Delivery
Nitinol tubing helps doctors do less invasive surgeries. Surgeons can make smaller cuts when using nitinol devices. These devices bend and move easily inside blood vessels. Their flexibility and superelasticity help them slide without hurting tissue. Nitinol stents and guidewires fit the shape of each vessel. This lowers the chance of tissue getting hurt. Smaller cuts mean patients feel less pain and have smaller scars. Doctors finish surgeries faster, so patients leave the hospital sooner. Nitinol’s shape memory lets devices open up only when needed. This makes it easier to put them in the right spot. This way, patients heal faster and have less trauma.
Improved Outcomes
Nitinol helps patients get better results in many ways. Its biocompatibility means the body does not react badly. Stents made from nitinol press tightly against vessel walls. This helps blood flow and stops leaks. Nitinol is strong, so devices last a long time and rarely need to be replaced. Studies show nitinol implants lower rejection by 30% compared to other metals. Guidewires made from nitinol cross vessels 98% of the time. Catheters with nitinol tubing work 92% of the time with no big problems. These facts show nitinol devices help people heal faster and need fewer repeat surgeries.
Lower Complication Rates
Nitinol devices help lower problems during vascular procedures. Their flexibility and superelasticity let them move with the vessel. This makes them less likely to break or move out of place. Nitinol’s biocompatibility means fewer people get swelling or infections. Doctors see fewer cases of restenosis and thrombosis after using nitinol stents. Using nitinol in less invasive surgeries means less tissue gets hurt and healing is quicker. Patients feel less pain and can go back to normal life sooner. Robotic surgeries with nitinol tubing also have fewer mistakes and safer healing. These reasons make nitinol a top pick for keeping patients safe.
Nitinol’s special features—shape memory, superelasticity, and biocompatibility—help keep patients safe and improve results in vascular care.
Nitinol vs. Other Stent Materials
Stainless Steel Comparison
Stainless steel was used for stents in the past. Now, nitinol is the top pick for many devices. These two metals act very differently in the body. The table below shows how they compare:
Performance Aspect | Nitinol Stents | Stainless Steel Stents |
|---|---|---|
Time to First Corrosion | Average 908 minutes | Average 325 minutes |
Durability | About 1880 minutes (some with no defect) | About 893 minutes |
Corrosion Damage Type | Mostly complete lysis, some fractures | Often break into several pieces |
Mechanical Properties | Superelastic, compliant, crush-resistant | Stiff, prone to recoil |
MRI Compatibility | Non-ferromagnetic, fewer artifacts | Ferromagnetic, more artifacts |
Fatigue Resistance | Superior under cyclic loading | Inferior fatigue resistance |
Nitinol stents do not rust as fast as stainless steel. They last longer and break less often. Nitinol can bend and move with the vessel. Stainless steel stents are stiff and can snap back after opening. This can make them fit poorly and cause more problems. Nitinol is safer for MRI scans because it does not react to magnets. It also causes fewer problems in pictures. Nitinol stents can handle lots of movement without breaking. This helps them last longer inside the body.
Nitinol’s special features help it work better with the body than stainless steel.
Why Choose Nitinol?
Nitinol gives many good things for vascular devices. These come from both how it works and how it helps patients:
Technical Advantages:
Nitinol stents open up by themselves. They push out to keep vessels open and fight outside pressure.
Bigger nitinol stents stay in place better. This stops them from moving and helps them work well.
Clinical Benefits:
Studies show nitinol stents work better than balloon angioplasty for some vessel problems.
Nitinol stents keep vessels open longer and lower the chance of them closing again.
Patients with nitinol stents get better faster and need fewer repeat surgeries.
In one study, nitinol stents worked 96% of the time and only 23.3% closed again in a year. These numbers are better than other stents.
Ongoing Research:
Scientists are still learning how nitinol’s forces can help even more.
Long-term checks show nitinol stents stay strong, even in hard cases.
Nitinol’s superelasticity, shape memory, and biocompatibility make it different from other metals. These things help devices fit vessel curves and stay in place. Studies prove nitinol is the best choice for today’s vascular treatments.
Nitinol is important in vascular procedures. Its shape memory and superelasticity help stent grafts work better. Nitinol tubing lets doctors press stent grafts against vessel walls. This helps patients get better results. Nitinol does not rust and helps devices last longer. Studies show nitinol devices work for a long time and lower risks. Nitinol also lets doctors do less invasive surgeries, which helps patients heal better. Experts think nitinol will be used even more in the future. New nitinol designs could help patients even more. Nitinol will probably stay the best choice for stent grafts.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing ideal for stent grafts?
Nitinol tubing has shape memory and superelasticity. These features help stent grafts fit blood vessels better. The tubing does not rust and is safe inside the body. Doctors use nitinol because it works well for a long time in vascular procedures.
How does nitinol improve vascular wall apposition?
Nitinol stents push softly against vessel walls. This helps the stent fit closely to the vessel. The tight fit stops leaks and keeps the stent in place. Patients get better blood flow and have fewer problems.
Are nitinol stent grafts safe for MRI scans?
Nitinol stent grafts do not react to magnets. They make fewer problems in MRI pictures. Most patients with nitinol devices can have MRI scans safely. Doctors still check each patient before doing the scan.
How long do nitinol stent grafts last?
Nitinol stent grafts can last for many years in the body. They can bend millions of times without breaking. Most patients do not need another surgery. Regular doctor visits help make sure the stent keeps working.
Can nitinol stent grafts reduce recovery time?
Nitinol stent grafts let doctors do less invasive surgeries. Patients usually heal faster and get back to normal sooner. Smaller cuts and less damage mean shorter hospital stays and less pain.
See Also
How Nitinol Tubing Drives Progress In Medical Innovations
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Minimally Invasive Care
Ways Nitinol Tubing Is Transforming Modern Medical Equipment
The Critical Role Of Nitinol Tubing In Medical Advancements
Nickel-Titanium Tubing Boosts Catheter And Implant Effectiveness

