How to Identify Quality 0.2 mm OD Nitinol Tubing for Your Needs

When you choose small-diameter nitinol tubing 0.2 mm OD, you have many options. Nitinol is special because it has unique features. Many companies use nitinol for its strength and bendiness. You need good nitinol tubing for your work. Nitinol does not rust and can handle pressure. Doctors use nitinol in medical tools to keep people safe. Engineers pick nitinol when they need things to be exact. As a small-diameter nitinol tubing 0.2 mm OD supplier, it's important to ensure that the quality meets your standards. You should look at nitinol to see if it is even. Picking nitinol tubing means finding what fits your needs. Good nitinol tubing helps you do better work. Nitinol is always dependable.
Tip: Always ask your small-diameter nitinol tubing 0.2 mm OD supplier if they have nitinol certificates before you buy.
Key Takeaways
Check what material and grade the nitinol tubing is. Make sure it has good strain recovery and resists rust. This helps the tubing last longer.
Make sure the wall thickness is very exact for 0.2 mm OD tubing. This keeps the tubing strong and bendy for medical use.
Look at the surface of the nitinol tubing. A smooth surface stops weak spots from forming. Weak spots can make the tubing break.
Pick suppliers who have the right certificates. Look for ISO 13485 and ISO 9001. These show the tubing is safe and high quality.
Ask suppliers if they can make custom tubing. Custom tubing can fit special medical or work needs better.
Quality Indicators

Material and Grade
When you pick small diameter tubing, check the material and grade. Nitinol tubing is special because of its properties. It is made from nickel and titanium. This mix gives nitinol shape memory and superelasticity. These features let nitinol tubing bend and go back to its shape. You want tubing that bends many times without breaking. Fatigue resistance and durability are important for medical and industrial jobs. Nitinol can last through up to 10 million bends. This is much better than other metals.
Look for nitinol that meets top standards. ASTM F2082 and ASTM F2004 are two main standards. These standards show the tubing is safe and strong. The Af temperature range for nitinol is usually 0 to 20°C. This range lets nitinol stay superelastic at body temperature. The right alloy mix and heat treatment control these features.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Typical Af Temperature Range | 0 to 20°C |
Purpose | Superelasticity at body temperature |
Control Factors | Alloy composition, heat treatment |
Standards | ASTM F2082, ASTM F2004 |
Check the grade for reliability. Good nitinol grades have high strain recovery. They have a recovery ratio of about 98%. This means the tubing works well after many uses. High corrosion resistance keeps the tubing safe in harsh places. The titanium oxide layer on nitinol helps protect it. This makes it safe for medical use.
Property | Value | Impact on Reliability and Longevity |
|---|---|---|
Strain Recovery | 5.62% | Makes biomedical devices work well. |
Recovery Ratio | 98% | Lowers risk of breaking under stress. |
Corrosion Resistance | High | Stops damage in tough places. |
Fatigue Resistance | High | Lets tubing handle many bends. |
Fatigue resistance and durability make nitinol a great choice. It works well for small diameter metal tubing in medical tools and other tough jobs.
Note: Biocompatibility is important for neurovascular stents. Nitinol is safe for the body and does not rust. This lowers the risk of swelling or rejection.
Wall Thickness and Size
Wall thickness and size are very important for small diameter tubing. You need tubing with tight tolerances so it works well. If the wall is too thin or thick, it might not fit or could break. Dimensional accuracy is very important for medical devices like stents. It helps the tubing stay strong and flexible.
Tubing Outer Diameter Range (mm) | Wall Thickness Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|
Up to 0.3 | ±0.010 |
0.3 to 0.5 | ±0.015 |
0.5 to 1.5 | ±0.020 |
1.5 to 2.5 | ±0.030 |
2.5 to 3.5 | ±0.040 |
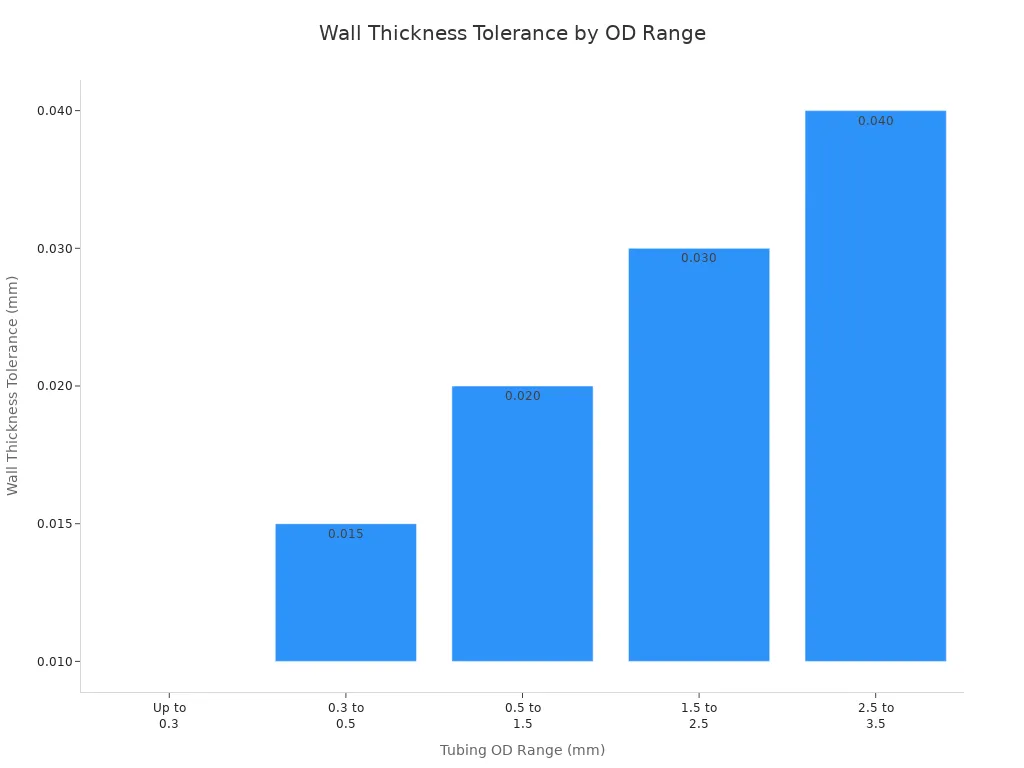
For 0.2 mm OD, you want a wall thickness tolerance of ±0.010 mm. This tight control helps the tubing last longer and work better. Dimensional inspections check the wall thickness and size. These checks make sure the tubing is even and meets strict needs.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Dimensional precision | Makes tubing work well in important jobs. |
Tight tolerances | Keep tubing even for medical devices. |
Accurate dimensions | Needed for tubing in medical uses. |
Dimensional inspections | Check wall thickness for strength and flexibility. |
Making small diameter tubes needs high accuracy. Both the outer and inner diameters must meet tough standards. This accuracy helps the tubing work well in medical and industrial jobs.
Surface and Consistency
Surface quality is another sign of good small diameter tubing. You want a smooth and even surface. A rough or uneven surface can cause weak spots. These weak spots can make the tubing break or fail. Surface finish types like AO, MP, and CE help you judge the quality.
Surface Finish | Threshold Surface Area (cm²) | Breakdown Potential Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
AO | ~0.5 | More likely to break, normal flaws |
MP | ~5.0 | Flatter flaws, less likely to break |
CE | ~5.0 | Like MP, but flaws are more even |
Special tools can check the surface. These include scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and x-ray diffraction. These tools help you find tiny flaws or weak spots. You can also use a simple chemical test with sodium hypochlorite. This test shows if there are inclusions in the nitinol. If the tubing has inclusions, it may corrode or fail.
Transition electron microscopy
Auger electron spectroscopy with back scatter electron detection
Scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy
Atomic force microscopy
X-ray diffraction (XRD)
A good surface finish helps the tubing stay strong and safe. It also helps patients heal faster when used in medical devices. Always check for a smooth, even surface when you pick small diameter tubing. This step helps you avoid weak spots and makes sure you get top quality.
Inspection Methods

Visual and Microscopic Checks
You should check nitinol tubing for problems before using it. Start by looking at the tubing with your eyes. You might see cracks, bends, or marks on the surface. Sometimes, you need to see even smaller problems. Industrial microscopes help you find tiny defects. Automated cameras can scan the tubing and spot issues quickly. Borescopes let you look inside small tubes. Each way of checking has good and bad points.
Inspection Method | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
Direct visual inspection | Easy to use, no equipment needed, depends on inspector skill | Quality changes with inspector, hard to see in dark spots |
Inspection using industrial microscopes | Finds tiny problems without damage, can use with software | Sample size may not fit, depends on operator skill |
Automated inspection using cameras | Reduces mistakes, improves quality, saves time | Costs a lot, needs regular care |
Inspection using borescopes | Lets you see hard-to-reach places, low upkeep | Must pick the right tool for good results |
Microscopes help you find micro-cracks and inclusions in nitinol. These small flaws can make tubing break. Studies show inclusions are a big reason for nitinol wire failure. Small cracks at inclusions can make the tubing wear out faster. If you find where cracks start, you can guess how long the tubing will last.
Study Title | Key Findings |
|---|---|
Inclusions Size-based Fatigue Life Prediction Model of NiTi Alloy for Biomedical Applications | Shows inclusions are a main cause of nitinol wire failure. |
Observation and modeling of potential sub-threshold damage growth mechanism for nitinol in ultra-high cycle fatigue | Says it is important to know how small cracks grow at inclusions for device life. |
In vitro fatigue–crack growth and fracture toughness behavior of thin-walled superelastic Nitinol tube for endovascular stents | Points out that finding crack starting spots helps guess device life. |
Inclusions Size-based Fatigue Life Prediction Model of NiTi Alloy for Biomedical Applications | Talks about how inclusions and surface problems matter for nitinol failure. |
Observation and modeling of potential sub-threshold damage growth mechanism for nitinol in ultra-high cycle fatigue | Explains that small cracks at non-metallic inclusions affect fatigue. |
Tip: Always use both your eyes and microscopes to find weak spots in nitinol tubing.
Precision Measurement Tools
You need to measure nitinol tubing very carefully. Use special tools to check the outside size and wall thickness. These tools help you meet strict rules for medical and industrial jobs. For 0.2 mm OD nitinol tubing, even tiny mistakes can cause big trouble.
Measurement Tool | Outer Diameter Range (OD) | Wall Thickness Range |
|---|---|---|
UG412 | 0.25-11.4 mm | 0.0762-5.08 mm |
UG430 | 0.51-29.2 mm | 0.0762-12.7 mm |
UG460 | 6.35-60 mm | 0.102-25.4 mm |
High Frequency | 0.25-7.62 mm | 0.0255-1.27 mm |
Dimensional tolerances are important for nitinol tubing. Tubing smaller than 0.3 mm needs a tolerance of ±0.005 mm. This tight control keeps nitinol tubing safe and strong.
Dimensional Tolerances | Specification |
|---|---|
±0.005 mm | Tubing below 0.3 mm |
You should use these tools to check every batch of tubing. Good measurements help you avoid weak spots and make sure the tubing fits well.
Non-Destructive Testing
Non-destructive testing lets you check nitinol tubing without breaking it. You can use special lights to look for cracks or rust. Leak testing checks if the tubing is airtight. Liquid penetrant testing helps you find cracks on the surface. You put on a liquid, then use a powder to see the flaws.
Testing Method | Description |
|---|---|
Visual Testing (VT) | Uses your eyes and special lights to look for cracks, rust, and wrong shapes. |
Leak Testing (LT) | Checks if parts are airtight using bubbles, special gas, pressure, or a mass spectrometer. |
Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT) | Puts a liquid on the tubing to find cracks that do not go all the way through, then uses a powder to show them. The tubing must be clean for this to work well. |
Eddy current testing works well for nitinol tubing. This test finds inside problems, cracks near the surface, and changes in metal thickness. Probes touch the tubing and show problems by changes in the electric current. You can find issues early and stop failures. Picking the right probe, keeping the tube clean, and using different settings help get better results. Ultrasonic testing also helps you find hidden problems inside the tubing.
Note: Non-destructive testing helps keep nitinol tubing safe for medical and industrial jobs.
Application Needs
Nitinol Tubing for Neurovascular Stents
Picking nitinol tubing for neurovascular stents is important. These stents must travel through very small blood vessels in the brain. Nitinol gives both strength and flexibility for these jobs. The tubing needs to bend but not break. This helps doctors reach the right place in the brain. You can get nitinol tubing in special shapes and sizes. This makes sure it fits your device well.
Custom sizes help match the tubing to the stent.
Flexible tubing moves through tricky blood vessels.
Durable tubing lasts through many uses.
Good tubing works well in surgery.
Wall thickness and diameter change how strong and bendy the stent is.
Nitinol tubing for neurovascular stents must meet tough rules. The tubing should keep its shape and give steady support. Superelasticity helps the stent stay in place. This lowers the risk of the stent moving during surgery. The tubing’s flexibility protects brain tissue and keeps people safe.
Property | Nitinol Tubing | Cobalt-Chrome Alloys |
|---|---|---|
Elastic Modulus | Lower than cobalt-chrome alloys | 200 - 240 GPa |
Yield Strength | Lower than cobalt-chrome alloys | Exceeds 2000 MPa |
Elastic Strain | Can exceed 8% | On the order of 1% |
Superelasticity | Yes | No |
Adaptability | High flexibility for complex structures | Limited adaptability |
Nitinol tubing gives a good mix of flexibility, strength, and safety for these uses.
Medical Biocompatibility
You must use nitinol tubing that is safe for people. Biocompatibility is very important for stents and other medical tools. Nitinol tubing for neurovascular stents must follow ISO 10993-1 and ASTM F2063 rules. These rules help keep patients safe during surgery. You should pick tubing that passes all safety tests.
Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|
ISO 10993-1 | Biocompatibility testing |
ASTM F2063 | Material quality |
FDA Guidance | Regulatory compliance |
Special surface treatments make nitinol tubing better for stents. Electropolishing makes the tubing smooth and lowers nickel release. This helps stop allergic reactions in people. New coatings also make stents safer and help stop blood clots.
Evidence Description | Findings |
|---|---|
Electropolishing effects | Thinner oxide layer means less nickel release and better safety. |
In vitro evaluation | Electropolished samples show less protein sticking, which is good for medical use. |
Thrombotic response | Electropolished tubing causes fewer blood clots in neurovascular stents. |
Ni-rich layer removal | Surface treatments remove nickel-rich layers, making tubing safer for neurovascular applications. |
Advanced coating technologies | Lower nickel ion release and help healing in neurovascular stents. |
Always check that your nitinol tubing meets all medical rules for best safety and performance.
Industrial Performance
Nitinol tubing is not just for medical tools. You can use it in many tough jobs in factories. Nitinol’s superelasticity and shape memory help it work well. The tubing stays strong even after bending many times. This makes nitinol tubing a great pick for hard jobs.
Property | Austenite | Martensite |
|---|---|---|
Thermal conductivity | 0.18 W/cm * deg. C | 0.086 W/cm * deg. C |
Coefficient of thermal expansion | 11.0E-6/deg. C | 6.6E-6/deg. C |
Young's modulus | approx. 83 GPa | approx. 28 to 41 GPa |
Yield strength | 195 to 690 MPa | 70 to 140 MPa |
Ultimate tensile strength | 895 MPa | 1900 MPa |
Elongation at failure | 25 to 50% | 5 to 10% |
Nitinol tubing for neurovascular stents also works well in factories. It resists rust and lasts a long time. The tubing’s special features help meet strict factory rules. Nitinol tubing gives safe and steady results in every job.
Supplier Selection
Small-Diameter Nitinol Tubing 0.2 mm OD Supplier
When you need a small-diameter nitinol tubing 0.2 mm OD supplier, you want someone who knows what you need. Not every supplier gives the same service or quality. You should see if the supplier has worked with nitinol and medical jobs before. Good suppliers tell you their prices and do not hide extra costs. They let you buy small amounts and send orders fast. This helps your project stay on time.
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Price and Transparency | Suppliers must show prices and explain all costs. |
Quality and Certifications | Look for ISO 13485 and ISO 9001:2015 for medical safety. |
Customization Options | Suppliers should give custom sizes and finishes for your project. |
Order Flexibility | Pick suppliers who allow small orders and quick shipping. |
Picking a nitinol tubing supplier means checking these things. You want a supplier who answers your questions and helps you choose the right tubing for your job.
Certifications and Support
Certifications are important when picking a supplier for medical nitinol tubing. You should look for these:
ISO 9001 and ASTM F2063 show the supplier cares about quality and follows rules.
ISO 13485 is needed for medical devices and proves the supplier meets safety rules.
Medical-grade skills and certifications help you trust the tubing for important jobs.
Suppliers with good technical support make your work easier. They help you pick the right nitinol tubing and make sure it fits medical needs. Good support means you get help after you buy. If you have problems, the supplier can help fix them fast. This keeps your project moving and your tubing safe.
Tip: Choose suppliers who answer fast and keep you updated about your order.
Customization Options
You might need special nitinol tubing for your medical job. The best suppliers let you change your order in many ways. You can pick superelastic or shape memory nitinol. You can choose the transformation temperature, wall thickness, and even the shape. Suppliers can make tubing for stents, needles, or other medical tools. They also offer different surface finishes, lengths, and patterns.
Customization Feature | Details |
|---|---|
Types of Nitinol | Superelastic, Shape Memory |
Transformation Temperatures | -25°C to 120°C |
Wall Thickness | Down to less than 0.05 mm |
Shapes and Patterns | Stents, needles, spiral cuts, custom shapes |
You can also ask for special packaging, logos, or colors. Some suppliers let you order as little as 50 kilograms. Custom nitinol tubing for neurovascular jobs is possible with the right supplier. Fast lead times and clear delivery dates help you avoid waiting. Good suppliers keep you updated and help you plan your medical projects.
You can find good 0.2 mm OD nitinol tubing by using simple steps. First, check the nitinol material, grade, and wall thickness. Use easy checklists to make sure the tubing is tested and safe. Make sure your supplier is reliable and follows the rules.
Custom nitinol tubing lets you pick what fits your medical job.
Strong quality checks and ISO rules help keep tubing safe.
Good suppliers give support and send nitinol on time.
Look at these resources to help you pick nitinol with confidence:
Resource Type | Benefit |
|---|---|
Quality Standards | ISO 13485 means nitinol is safe and works well. |
Clinical Benefits | Top nitinol tubing lasts long and works in real cases. |
Customization | Custom tubing helps devices work better for patients. |
Cost Efficiency | Good nitinol saves money and needs less fixing. |
Supplier Reliability | Trustworthy suppliers help and deliver nitinol when you need it. |
Tip: Use nitinol checklists and talk to experts to get the best tubing.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing different from other metals?
Nitinol tubing can bend and then go back to its shape. It is both strong and flexible. This is why nitinol is used in many jobs. Other metals cannot do this. They do not have shape memory or superelasticity.
How do you check the quality of 0.2 mm OD nitinol tubing?
You can look at the tubing with your eyes. You can use microscopes and tools to measure it. Non-destructive tests help find cracks or weak spots. Always ask your supplier for test results and certificates.
Why is wall thickness important for small-diameter tubing?
Wall thickness changes how strong and bendy the tubing is. If the wall is too thin, it might break. If it is too thick, it may not fit right. You need tight tolerances to keep things safe and working well.
Can you use nitinol tubing for medical devices?
Yes, nitinol tubing can be used for medical devices. The tubing must meet ISO 10993-1 and ASTM F2063 rules. Biocompatibility and safety are very important for people’s health.
What should you look for in a nitinol tubing supplier?
Pick a supplier who has experience and clear certificates.
Look for custom choices and quick delivery.
Good suppliers help you get the tubing you need for your project.
See Also
Choosing The Ideal Nitinol Tubing Supplier For You
Best Nitinol Tubing OD 2mm Supplier For Savings
A Comprehensive Guide To Choosing Nitinol Tubing

