Understanding the Unique Properties of NiTi Tubing in Healthcare

You see NiTi tubing used in many medical devices today, especially when selecting NiTi tubing for medical devices. It has special features like superelasticity and shape memory. It also has high ductility, low corrosion rate, and biocompatibility. These features help devices fit patients’ needs and work well in tough environments. Engineers appreciate these characteristics because they enhance device safety and longevity. When selecting NiTi tubing for medical devices, you gain new benefits, including a 275% increase in fatigue strain limit. The inclusion size is smaller, which contributes to the reliability of the devices. These advancements enable medical devices to perform a wider range of functions.
VAR/EBR Nitinol has a 275% higher fatigue strain limit than regular alloys.
Advanced Nitinol has an inclusion size under 10 µm, much smaller than older types.
These changes help make safer and more advanced heart devices.
Key Takeaways
NiTi tubing is very bendy and snaps back to shape. This helps it work well in things like stents and guidewires. The shape memory effect lets NiTi tubing change shape inside the body. This makes patients feel better and helps treatments work well. Nitinol is very bendy and does not rust easily. This means it lasts a long time in the body and is less likely to break. Using NiTi tubing in medical devices can help patients heal faster. It also lowers the chance of problems and helps people get better results. When picking NiTi tubing, think about how bendy, strong, and safe it is for the body. This helps make medical devices that work well and are safe.
Unique Properties of NiTi Alloy Tubing
Superelasticity in Medical Devices
Superelasticity is what makes nitinol special. This means niti alloy tubing can stretch and bend more than most metals. When used in medical devices, it can recover from strains up to 5.2%. The tubing can move through tight spaces in the body and go back to its original shape. Stents and guidewires use this to move through blood vessels without losing their shape. Niti alloy tubing can handle up to 13% deformation. Stainless steel cannot bend as much. The tubing also resists fatigue, so it lasts longer in busy places.
Property | NiTi Tubing | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility | Very flexible, can recover from strains up to 13% | Strong but not as flexible |
Fatigue Resistance | Good at handling repeated movement | Works well when not moving a lot |
Superelasticity helps in real life. Guidewires made from nitinol tubing work 98% of the time when crossing vessels. Catheters using this tubing have a 92% success rate for delivery. Patients benefit too, with a 30% lower chance of implant rejection than with other metals.

Shape Memory Effect
Shape memory makes niti alloy tubing different from other materials. If you bend or squeeze nitinol when it is cold, it keeps that shape. When you heat it up, it goes back to how it was before. This happens because the metal changes inside. This is useful for medical devices that need to change shape in the body. For example, you can squeeze a stent made from nitinol, put it in a small space, and watch it grow to its full size once inside.
The shape memory effect helps in many ways:
Stents
Guidewires
Orthodontic archwires
Surgical instruments
Niti alloy tubing can get back up to 2.95% of its shape after 600 uses. This is good for devices that need to work many times. Shape memory also helps doctors do less painful treatments for patients.
Property | Description | Impact on Medical Devices |
|---|---|---|
Superelasticity | Lets the tubing stretch and bend a lot and return to shape | Helps devices move through the body easily |
Shape Memory | Tubing can go back to its old shape after bending | Important for gentle surgeries |
Flexibility | Can bend without breaking or folding | Needed for safe use in small blood vessels |
Biocompatibility | Works well with body tissues | Lowers the chance of bad reactions in patients |
High Ductility and Flexibility
Niti alloy tubing is very ductile, so it can stretch and bend without snapping. Its tensile strength is about 500 MPa, so it is strong and dependable. You see this when devices move with the body, like stents that expand and shrink with each heartbeat. The tubing can take a lot of stress and does not wear out fast. This flexibility lets you make medical devices that fit into small or curved places without folding.
Nitinol tubing moves with the body, so it does not hurt tissues.
It can take stress over and over, so it is good for implants that move a lot.
The material stays safe and does not rust, so it lasts a long time.
Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility
Corrosion resistance is important for niti alloy tubing. The titanium in nitinol makes a thin layer on the outside. This layer stops rust and keeps nickel from leaking out. Nitinol will last in the body and not break down. Studies show that niti alloy tubing resists rust better than many other metals used in medical devices.
Study Focus | Findings |
|---|---|
Corrosion Resistance | NiTi alloys resist rust well because of a titanium dioxide layer, which stops nickel from leaking. |
Biocompatibility | Both pre-alloyed NiTi powder and mixed Ni and Ti powders are safe for cells, showing good biocompatibility. |
Comparison of Materials | LPBF-printed parts from pre-alloyed NiTi powder resist rust a bit better than those from mixed powders, but both work well for medical use. |
Biocompatibility means niti alloy tubing works well with body tissues. You do not see allergies or problems with bone growth. Even though nitinol lets out more nickel than titanium, it does not hurt cells or cause rejection. The titanium oxide layer keeps it safe for long use. This makes niti alloy tubing a great choice for implants and other medical devices.
Property | NiTi Alloy Tubing | Comparison to Other Alloys |
|---|---|---|
Superelasticity | Can recover about 5.2% strain | More than many medical alloys |
Shape Memory | Gets back up to 2.95% after 600 uses | Better than many others |
Ductility | Tensile strength near 500 MPa | About the same as other alloys |
Corrosion Resistance | Resists rust better because of titanium oxide | Better than many metals |
Biocompatibility | No allergies, normal bone growth | Like other safe materials |
Tip: If you pick niti alloy tubing for your medical devices, you get superelasticity, shape memory, high ductility, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. These help you make safer, stronger, and longer-lasting devices for patients.
Selecting Nitinol Tubing for Medical Devices

Design Considerations
When picking niti tubing for medical devices, you must think about how it works in the body. The tubing needs to bend and go back to its shape. This helps you make tools that move through small spaces. Nitinol tubing is good for this. It can bend and stretch many times without breaking. This is important for implants that move with the body.
You also need to think about strength. Nitinol tubing is strong and does not break easily. It works well for implants that need to last for years. The tubing can last through over 3.7 × 10^8 cycles in 10 years. This means your devices will keep working, even if they move a lot.
The surface and wall thickness are important too. A smooth surface lowers the chance of cracks. Thicker walls make implants stronger, but you must keep them flexible. Engineers use tests and computer models to find the best design. They check how the tubing bends, stretches, and handles stress. This helps you make safe and dependable medical devices.
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Flexibility | NiTi tubes can return to their original shape after bending, making them ideal for medical tools. |
Strength | They can handle repeated use without breaking, crucial for implants and tools that move inside the body. |
Safety | NiTi tubes are bio-friendly and resist rust, ensuring longevity and reliability in medical applications. |
Tip: When picking niti tubing for medical devices, always check the balance between flexibility, strength, and safety. This helps you make devices that work well and last longer.
Performance Benefits
You want your medical devices to work well and last a long time. Nitinol tubing gives you many good things. It has a high ultimate tensile strength, from 800 to 1500 MPa. This means your implants can take strong forces and not break. Nitinol tubing also resists fatigue. It can bend and stretch millions of times and still work. This is important for implants that move with the body, like heart stents or bone supports.
Nitinol tubing works in many temperatures. It stays stable from -20°C to 80°C. This helps your devices work in many places. The tubing resists rust as well as medical-grade stainless steel. You do not have to worry about it breaking down in the body.
Property | Nitinol Tubing | Conventional Materials |
|---|---|---|
Ultimate Tensile Strength | 800-1500 MPa | Lower than NiTi |
Fatigue Resistance | Millions of cycles without failure | Limited cycles |
Corrosion Resistance | Comparable to medical-grade stainless steel | Varies significantly |
Biocompatibility | ISO13485:2016 certified | Varies, often not certified |
Thermal Stability | -20°C to 80°C | Limited range |
When you use nitinol tubing, you help patients heal faster. Studies show patients recover about 20% faster with nitinol implants. The superelasticity of nitinol tubing lowers the risk of hurting blood vessels. Patients feel less pain and have fewer problems after surgery.
Nitinol tubing helps your devices last longer.
Implants made with nitinol tubing move with the body and do not break easily.
You can trust nitinol tubing to keep working, even after years of use.
Safety and Reliability
Safety is the most important thing when picking niti tubing for medical devices. Nitinol tubing is safe to use in the body. It forms a thin titanium oxide layer on the outside. This layer stops nickel from leaking out, which keeps your implants safe and bio-friendly. The tubing meets strict rules, like ISO 10993 and ASTM F2063. These rules make sure your implants are tested for safety and reliability.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Biocompatibility | Nickel-Titanium Strand materials undergo specialized surface treatments that create a protective titanium oxide layer, preventing nickel ion leaching and enhancing biocompatibility. |
Regulatory Compliance | The materials meet stringent international standards, including ISO 10993, ensuring thorough testing for cytotoxicity and other safety parameters. |
Clinical Evidence | Long-term studies show excellent biocompatibility profiles for Nitinol implants, with successful applications in millions of patients since the 1980s, demonstrating a strong safety record. |
Regulatory groups check nitinol tubing for chemical, mechanical, and performance needs. They make sure every piece is safe before you use it in medical devices. Polished nitinol tubing lowers the risk of protein sticking and bacteria growing. This helps your implants stay clean and safe for a long time.
Medical-grade nitinol tubing forms a stable titanium dioxide layer, stopping nickel ion release.
Special surface treatments make nitinol tubing even safer for long-term implants.
Polished nitinol tubing lowers the chance of infection.
When you pick nitinol tubing, you give your patients safe, reliable, and long-lasting implants. You can trust nitinol tubing to meet the needs of modern medical devices.
Applications of NiTi Tubing in Healthcare

Stents and Vascular Devices
Nitinol tubing is used in many stents and vascular devices. These devices help keep blood vessels open. They also support blood flow in the body. Nitinol can change shape to fit arteries. This helps lower the chance of vessel damage. Its superelasticity lets it bend and go back to its shape. This works even in twisty blood vessels. You get better results and fewer problems with these devices.
Nitinol tubing helps blood flow in heart arteries and keeps them open.
The tubing fits vessel shapes, so there are fewer risks.
Nitinol is in many heart devices, which helps patients do better.
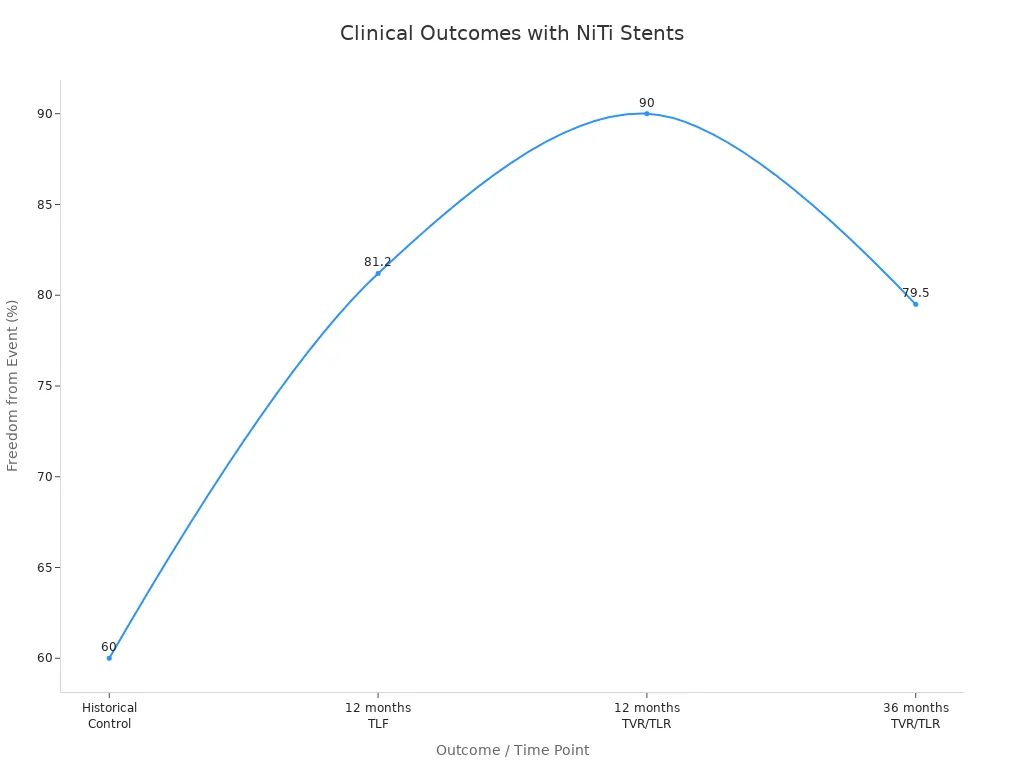
A study called the RELIABLE Study showed good results for nitinol stents. Patients had 81.2% freedom from target lesion failure after 12 months. This was better than the 60% in an older group. After three years, 79.5% of patients did not need another procedure.
Evidence Type | Details |
|---|---|
Study Name | RELIABLE Study |
Patient Population | Japanese patients with blocked SFA arteries |
Freedom from TLF at 12 months | 81.2% (56/69 patients) |
Historical Control | 60% from RESILIENT trial |
Freedom from TVR/TLR at 36 months | 79.5% |
Guidewires and Catheters
Nitinol tubing is used in guidewires and catheters for many medical needs. These devices must move through tight and twisty body paths. Nitinol’s superelasticity lets guidewires bend without breaking. Catheters need to be both flexible and strong. Nitinol tubing gives them these features. The tubing goes back to its shape after bending, so it does not hurt tissues.
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Superelasticity | Lets guidewires and catheters bend without lasting damage. |
Biocompatibility | Lowers immune reactions by 95% compared to other metals. |
Corrosion Resistance | Keeps catheters safe and strong in body fluids. |
Flexibility | Helps catheters move through tricky body parts. |
Strength | Gives catheters the power to work in tough jobs. |
You find nitinol tubing in catheters for the heart, brain, and other organs. Catheters with nitinol tubing last longer because they do not rust. You can trust these catheters to work well in many medical jobs.
Tip: If you pick nitinol tubing for catheters, you get flexibility, strength, and rust resistance. This helps you do safer and better procedures.
Orthopedic and Dental Uses
Nitinol tubing is also used in orthopedic and dental devices. Its shape memory and pseudoelasticity help in many ways. In orthodontics, nitinol tubing helps move teeth gently and safely. Dental prostheses use nitinol tubing to lower stress on implants. This means less wear and fewer repairs.
A study showed that reverse curve nitinol wires could move lower front teeth by 20 degrees. This made bite correction work better. Another study found dental prostheses with nitinol tubing lowered reaction forces. This helps protect the implants that hold them.
Nitinol tubing is used in orthopedic devices for bone repair and joint support. The tubing bends and goes back to its shape, which helps bones heal in the right spot. Nitinol tubing does not rust, so these devices last longer in the body.
Note: Nitinol tubing’s special features make it a great choice for many medical uses, from catheters to dental and bone devices. You help patients heal faster and safer with these advanced devices.
Advantages and Challenges of Nitinol Tubing
Benefits for Minimally Invasive Procedures
Nickel-titanium alloy tubing gives many benefits for less invasive surgeries. Patients heal faster and feel less pain when doctors use this material. Superelastic niti tubing lets devices bend and move easily in the body. These devices do not lose their shape. Doctors can make smaller cuts, so scars are smaller and healing is quicker. Nickel titanium alloy is safe for the body, so patients have fewer bad reactions. Flexible devices made from medical-grade nitinol move through tight spaces. This lowers the risk of hurting tissues. The tools are strong and last a long time.
Biocompatibility lowers the chance of allergies.
Durability means devices work well for many years.
Superelasticity and shape memory help devices go back to their shape.
Smaller cuts mean less scarring and faster healing.
Flexibility helps protect tissues from harm.
Durability and Precision
Medical-grade nitinol is strong and accurate for tough jobs. Nickel-titanium alloy tubing bends and twists many times. It does not break easily. This helps medical tools and implants last longer. Superelastic niti tubing goes back to its shape after bending. This lets doctors guide devices through small or curved spaces. Special ways of making these devices, like heat treatment and extrusion, make them even better. You can trust these tools to work well and stay accurate.
Devices keep their shape and work after many uses.
Precision helps doctors reach hard places in the body.
Long-lasting tools mean you do not need to replace them often.
Manufacturing and Cost Challenges
Making nickel-titanium alloy tubing is not easy. You must control the nickel and titanium mix very carefully. Special machines are needed to cast and shape the tubing. The process uses long heat treatments and tricky machining steps. Quality checks are strict to stop tiny defects. These steps make it harder and more costly to make than other metals. Titanium is expensive, and making the tubing costs more too. Even though medical-grade nitinol is pricey, its special features make it a good choice for many implants and flexible devices.
Note: Think about the higher cost and the benefits of durability, flexibility, and safety when you pick nickel-titanium alloy tubing for your devices.
You can see how niti tubing has made medical tools better. Its superelasticity and shape memory help devices last longer. The biocompatible surface keeps patients safe. In heart care, niti stents fit blood vessels well. This helps patients get better results. Niti tubing is also used in bone, brain, and surgery devices.
Medical Field | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Surgical Instruments | Nitinol memory alloy capillary tubes in endoscopic and laparoscopic devices | Easier to move, less harm to tissues, and more precise work. |
Cardiovascular Medicine | Self-expanding stents made from nitinol capillary tubes | Stents fit vessels better, lower injury risk, and work well for a long time. |
Orthopedic Surgery | Dynamic stabilization systems utilizing nitinol | Acts like real joints, slows down damage, and helps patients for years. |
Neurovascular Intervention | Flow diverters and aneurysm occlusion devices | Uses gentle force, good for sensitive areas, and may allow smart implants. |
Niti tubing keeps changing how doctors treat patients. New research looks at mixing niti with other materials. Scientists want to make properties better and lower costs. They also try to adjust shape memory and superelasticity for special uses. Niti may help send medicine to certain body parts.
Research Direction | Description |
|---|---|
Hybrid Materials | Mixing NiTi with other metals or plastics to make it better or cheaper. |
Fine-tuning Properties | Changing shape memory and superelasticity for different jobs. |
Integration with Nanotechnology and Biotechnology | Using NiTi’s shape memory to send drugs to the right place. |
You will see more new ideas for medical devices with niti. These changes will help doctors give better care and help patients live healthier lives.
FAQ
What makes NiTi tubing different from other metals in medical devices?
NiTi tubing is special because it bends and goes back to its shape. It does not rust and works well with the body. These things help make safer and longer-lasting medical devices.
Can you use NiTi tubing for implants that move a lot?
Yes, you can use NiTi tubing for moving implants. It can bend and stretch many times without breaking. This makes it good for stents and bone supports that move with the body.
Is medical nitinol tubing safe for patients with metal allergies?
Most people can use medical nitinol tubing safely. The titanium oxide layer stops nickel from leaking out. This layer helps lower the chance of allergic reactions.
How do you clean and sterilize NiTi tubing?
You can clean NiTi tubing with normal hospital cleaning methods. Use steam, chemicals, or plasma to sterilize it. The tubing does not rust, so it stays safe after cleaning.
Where do you see NiTi tubing used most in healthcare?
Doctors use NiTi tubing in stents, guidewires, catheters, and dental devices. Its strength and flexibility help doctors do less invasive procedures and help patients heal faster.
See Also
Unveiling Nitinol Tubing's Role in Healthcare Innovations
The Importance of Nitinol Tubing in Modern Medicine
Nitinol Tubing's Impact on the Future of Medical Devices
The Manufacturing Process of Nitinol Tubing for Healthcare
Nitinol Tubing's Contribution to Progress in Medical Technology
