How to Select the Right Medical Grade Nitinol Tubing for Your Device
Selecting the right medical grade nitinol tubing affects how well your device works, how safe it is, and how long it lasts. You need to choose tubing that fits what your device will do, like if it helps a stent, heart valve, or surgical tool. Medical grade nitinol tubing is flexible, strong, and remembers its shape, so it is very important for devices used in heart, bone, and surgery care. Studies show nitinol stents work well 97% of the time, which shows they are very reliable for important devices. You help your device work best when you focus on biocompatibility and making sure it is made exactly right. The right medical grade nitinol tubing helps your device follow rules and keeps patients safe.
Key Takeaways
Pick nitinol tubing that matches your device’s job, size, and safety needs. This helps your device work well and last longer.
Look at tubing size, shape memory, flexibility, and biocompatibility. These things help keep devices safe and working inside the body.
Choose tubing with smooth surfaces and high purity. This stops cracks, rust, and device problems.
Work with suppliers who have medical certificates, good quality systems, and clear records. This helps you follow safety rules and get approvals faster.
Use the right sterilization methods like ethylene oxide or hydrogen peroxide vapor. This keeps tubing strong and safe for patients.
Device Requirements
Application and Use
Before picking nitinol tubing, you need to know how your device will be used. If your device goes inside the body, you must pick tubing that is safe and strong.
Devices like neurovascular stents need tubing that is safe for the body, does not rust, and can bend many times. These things help the device work well and last long inside people.
Stents and catheters need tubing with thin walls and strong structure. This makes them bend easily and work with care.
Some tools used outside the body can use cheaper tubing with thicker walls. These tools do not need to bend as much.
Tubing for inside the body must pass strict safety rules like ISO 13485 and ISO 10993. The size must be exact to stop problems and keep the device working.
How the tubing is made and what it can do depends on if it goes inside or outside the body.
Talking to experts helps you choose tubing that works well, keeps people safe, and follows the rules.
The table below shows how different tubing grades fit different medical devices and what they need to do:
Tubing Grade | Common Medical Device Applications | Key Performance Requirements |
|---|---|---|
Standard | Guidewires, Catheters, Needles, Disposables, Sheaths, Snares | Good for grinding and devices that do not touch the body; OD range 0.010"-0.065"; OD/ID ratio 1.11-2.67; OD tolerance ±0.0003" to ±0.001"; used when bending many times is not needed |
Precision | Stents, Cardiovascular Devices, Orthopedic Implants, Temporary and some Permanent Implantables | Needs very even material and good connections; OD range 0.065"-0.197"; OD/ID ratio >1.08; OD tolerance ±0.0005"; roundness over 90% |
Premium | Critical Implantable Devices such as Structural Heart Devices, Neurovascular Stents and Stent Retrievers, Carotid Artery Devices | Needs very exact size, strong against bending, and smooth surface; thin walls with OD >0.198"; OD/ID ratio <1.08; OD tolerance as close as ±0.0005"; roundness over 95%; lasts longer with Standard and Enduro alloys |
Nitinol tubing is used in heart, brain, bone, teeth, and scope devices. Each device needs tubing that fits its job, so you must pick the right grade.
Dimensions and Tolerances
Nitinol tubing must have the right size and be very exact for medical devices. You need to know the outer diameter, inner diameter, wall thickness, and how even the tubing is. If the size is wrong, the device may not work or could be unsafe. For stents and other careful devices, even small mistakes can cause problems.
Here are the usual size limits for medical nitinol tubing:
OD Range (mm) | OD Tolerance (mm) | ID Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|---|
≤ 0.3 | ±0.005 | ±0.010 |
0.3 to 0.5 | ±0.007 | ±0.015 |
0.5 to 1.5 | ±0.015 | ±0.020 |
1.5 to 2.5 | ±0.020 | ±0.030 |
2.5 to 3.5 | ±0.020 | ±0.040 |
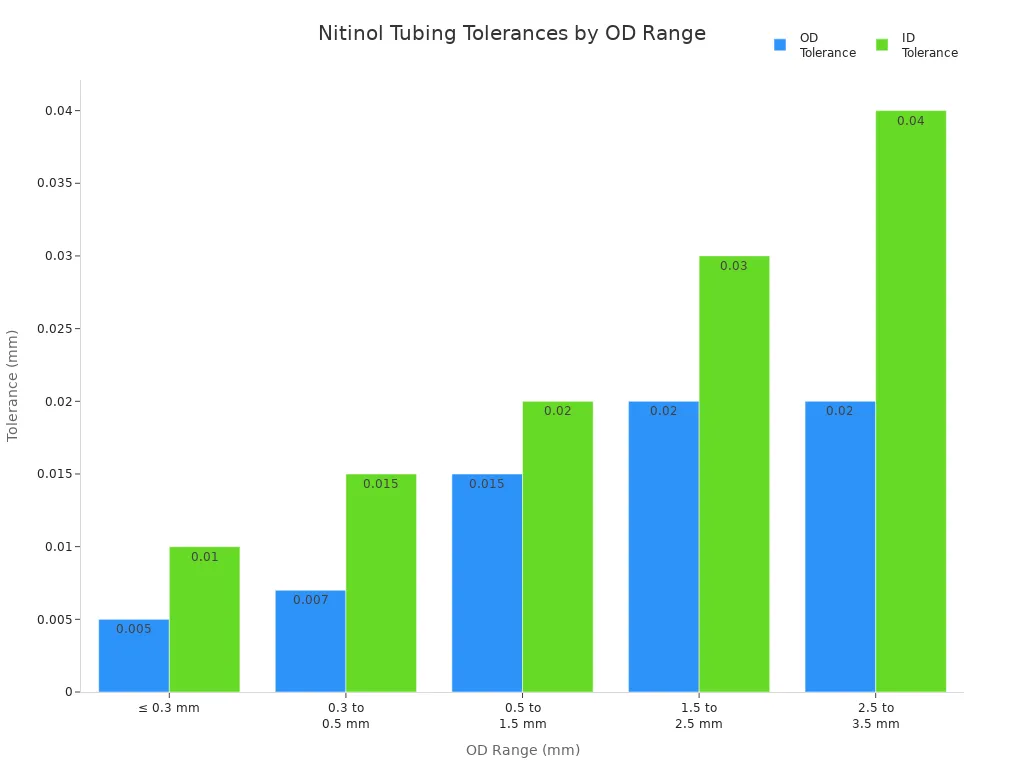
Even wall thickness and roundness make tubing stronger and more flexible. Special ways of making tubing, like electropolishing and laser measuring, help get these exact sizes. You can also change the length and shape to fit your device, which helps it work better and keeps people safe.
Tip: Always check that your supplier uses good quality checks and can track their tubing. This helps make sure the tubing is always good and keeps patients safe.
Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility is very important when picking nitinol tubing, especially for stents and other devices that stay in the body. Good biocompatibility means the tubing is safe with body tissue and does not cause harm.
If nitinol tubing is not safe for the body, it can cause swelling, tissue problems, or bad reactions. These problems can make the device not work and put people at risk. Tubing with less pure nitinol can break more easily, and tiny holes or spots in the metal make breaking more likely. Pure nitinol lasts longer and is less likely to fail.
Nickel can come out of nitinol tubing, but special surface treatments like electropolishing help stop this and make the tubing resist rust. Well-treated tubing causes little swelling and covers well with tissue in tests. Following purity rules like ASTM F2063 and doing careful safety tests help lower risks.
Note: Always ask your supplier for proof of safety tests and certificates. This makes sure your device is safe and follows the rules.
Nitinol Tubing Properties
Superelasticity and Shape Memory
Nitinol tubing has two special features. These are superelasticity and shape memory. Superelasticity lets the tubing bend a lot and snap back. It can stretch up to 8-10% and return to its shape. This is much more than regular metals can do. The tubing changes inside when bent, then goes back to normal. Devices like stents, guidewires, and catheters use this to move through twisty paths. They bend but do not stay bent. This stops kinks and keeps the device working after many uses.
Shape memory is also very important. It lets the tubing change shape at body temperature. This helps doctors use small cuts for surgery. For example:
Nitinol tubing lets doctors put in stents or other devices small, then make them bigger inside the body.
Shape memory helps the device fit better and hurt less tissue.
Smaller cuts mean less damage and faster healing.
Stents and catheters can reach hard spots and open up where needed.
Superelasticity and shape memory together make devices flexible and strong.
A study showed nitinol leads could go in small and then get bigger inside the body. This helped the device stay in place and cover more area. It also made surgery easier and safer. Using nitinol tubing with these features helps devices work better and keeps patients safe.
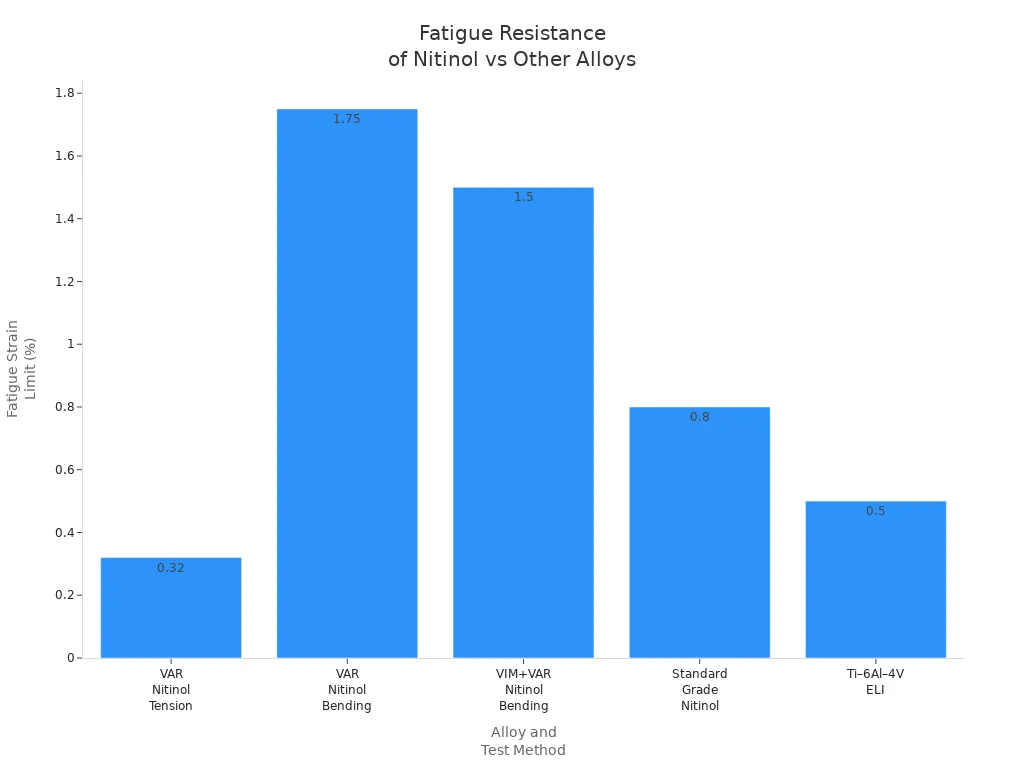
Fatigue and Corrosion Resistance
Fatigue resistance means the tubing can bend many times without breaking. This is important for stents and implants that move a lot. Nitinol tubing can last through millions of bends. High-purity nitinol is even better. It can bend about 1.75% before breaking in tests. This is almost twice as good as regular nitinol. Devices last longer and stay safe in the body.
Material Type | Fatigue Strain Limit (Tension-Tension) | Fatigue Strain Limit (Bending) |
|---|---|---|
High-purity VAR Nitinol | 0.32% | 1.75% |
VIM+VAR Nitinol | — | 1.5% |
Standard Nitinol | Lower | Lower |
Ti–6Al–4V ELI (for reference) | — | — |
Corrosion resistance means the tubing does not rust or break down in the body. This is very important for implants that stay in for a long time. ASTM F2129 is the rule for testing how well tubing resists rust. The test checks if the tubing stays strong in a liquid like blood at body heat. If the tubing has a high breakdown point, it resists rust better. How smooth and pure the tubing is also matters. For stents and implants, you must also check ISO 10993-1 for safety. Using both rules helps keep devices safe and patients protected.
Tip: Always ask your tubing supplier for proof they follow ASTM F2129 and ISO 10993-1 for rust and safety.
Surface Finish and Purity
How smooth and pure the tubing is affects how well it works. Smooth tubing with no flaws is less likely to crack or rust. You should pick tubing that is polished or finished very well. This is extra important for stents, where small flaws can cause problems.
Purity is also key. Tiny bits stuck in the metal can start cracks and make rust worse. ASTM F2063 says the biggest allowed bit is 39.0 μm. This rule helps stop early breaks and keeps the device safe. High-purity nitinol, like Redox or Enduro, is even better. It has fewer bits and resists cracks and rust more.
Note: Always get a paper from your supplier that shows the tubing meets ASTM F2063 for purity and bit size. This is very important for stents and other important medical devices.
Choosing nitinol tubing with the right finish and purity helps your device last longer, work better, and keep patients safe.
Compliance and Standards
ASTM F2063 and Certifications
You need to make sure your nitinol tubing follows strict rules. ASTM F2063 gives the main rules for what is in the tubing, how pure it is, and how strong it is. If your tubing meets this rule, your device can pass safety checks. This also helps keep patients safe. Always ask your supplier to show proof that their nitinol tubing meets ASTM F2063.
Regulators want more than just ASTM F2063. You must check for the right papers and certificates. Most medical device makers look for these:
ISO 13485:2016 for quality systems
FDA registration for factories to meet fda rules
Cleanroom certificate (ISO 14644 Class 7/8) for clean making
Risk checks using ISO 14971
Computer systems to track document versions
You also need to keep good records. These include the Design History File, Device Master Record, and Device History Record. Electronic DHR helps you track each piece of nitinol tubing from start to end. This tracking helps with fda rules and audits. When you get ready for things like 510(k), PMA, or CE Mark, these records show your tubing meets all the rules.
Tip: Always ask your supplier for the latest certificates and proof of fda rules. This keeps your device and patients safe.
Sterilization and Processing
Sterilization is very important for nitinol tubing in medical devices. You must pick a way that keeps the tubing safe and strong. Not every sterilization method is good for nitinol tubing. Some can hurt the shape memory or cause rust.
The table below shows which sterilization ways work best for nitinol tubing:
Sterilization Method | Compatibility with Nitinol Tubing | Temperature Impact | Residue Presence | Effect on Shape Memory and Flexibility | Cycle Time | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Ethylene Oxide (EO) | High | Low temperature | Toxic residues present | Keeps shape memory and flexibility | 12-24 hours | Works well, but needs care because of toxicity |
Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor (VHP) | High | Low temperature | No toxic residues | Keeps tubing properties | 1-3 hours | Fast and lowers infection risk |
Steam Autoclaving | Not recommended | High temperature | None | Hurts shape memory and flexibility | N/A | Can make tubing fail early |
Radiation (Gamma, Electron Beam) | Not recommended | N/A | N/A | Changes surface, raises corrosion | N/A | May not be safe for patients |
Ethylene oxide and hydrogen peroxide vapor are best for nitinol tubing. They use low heat, so they do not hurt the tubing’s shape memory or flexibility. These ways also help keep the surface smooth and safe. Before sterilizing, you should use ultrasonic cleaning to remove oils and dirt. This step helps stop contamination.
You must follow ISO and FDA rules for sterilization, like ISO 13485, AAMI TIR12, and ISO 17665. Keep records of your sterilization steps, surface treatments, and test reports. These records show your nitinol tubing stays strong and safe after many sterilizations. Always check that your sterilization matches your surface treatments to keep corrosion resistance and biocompatibility.
Note: Good records and the right sterilization help you meet fda rules and keep your nitinol tubing safe for every patient.
Choosing the Right Medical Grade Nitinol Tubing Supplier
Experience and Quality Systems
You need a supplier who knows a lot about medical nitinol tubing. Not every metal company understands what neurovascular stents need. When you look at suppliers, check if they have made medical nitinol tubing before. This is very important for neurovascular stents and other special devices.
Make sure the supplier is registered with the FDA and follows 21 CFR Part 820. This means they use a good quality system, train workers, check equipment, and do audits.
Check if they have ISO 13485 certification. This shows they follow world rules for medical devices and safety.
Look at their quality records, like device master records and device history records. These records help you see how your device was made.
Ask if they use cleanrooms that meet ISO 14644. Cleanrooms keep stents and other devices clean and safe.
Make sure they test for biocompatibility and surface finish. This is very important for stents and implants.
See if they know how to process nitinol, including tests for strength, bending, and shape memory.
Ask if they can track every piece and are ready for audits. You want a supplier who can show all needed papers.
Check if the supplier has had any legal or FDA problems. Stay away from suppliers with recalls or warnings.
Pick a supplier who always tries to get better by doing audits and updating their ways.
Choosing a supplier with experience in neurovascular stents helps you avoid mistakes. It also helps your device meet all safety rules.
Support and Documentation
A good supplier gives you more than just nitinol tubing. You should get full help and clear papers for every device, especially for neurovascular stents.
Certifications like ISO 13485 and ASTM F2063 show the tubing is safe and high quality.
Detailed batch papers let you track each piece of tubing in your device.
Quality test reports, like DSC, BFR, and strength tests, show the tubing works well for stents and other devices.
The paperwork should clearly show they follow FDA and ASTM rules.
Good suppliers give 24/7 help, training, and support for custom device designs.
Tools like order tracking help you plan for making and getting your devices.
Tip: Pick suppliers who use the best raw materials and control every step. This keeps your nitinol tubing for stents and other devices safe, steady, and ready for checks.
A supplier with strong papers and help lets you get your device to market faster and safer. You can focus on new ideas, knowing your stents and other devices use the best medical nitinol tubing.
You can pick the right medical grade nitinol tubing by using simple steps. First, know what your device needs and make sure the tubing fits its job. Check that the tubing follows all rules and pick a supplier who has done this before.
Figure out what your device will do and what it must handle.
Look at the tubing’s size, how exact it is, and if it is safe for the body.
Make sure it has shape memory, can bend many times, and can be cleaned safely.
Choose a supplier with the right certificates and keep good records for every device.
Tip: Talk to suppliers early and use a checklist so you do not miss anything important. For more help, visit hznitinol.com or ask experts at Tegra Medical.
FAQ
What is the difference between standard and premium medical grade nitinol tubing?
Standard tubing is used for tools that do not stay inside people. Premium tubing is made for important implants like stents. Premium tubing is made with more care and is cleaner. It also has a smoother surface. Using premium tubing makes devices safer and last longer.
How do you check if nitinol tubing is biocompatible?
You need to get test reports from your supplier. Look for papers that show ISO 10993 and ASTM F2063. These papers mean the tubing passed safety tests for the body. Always read these papers before picking tubing for implants.
Can you cut or shape nitinol tubing after you buy it?
Yes, you can cut or shape nitinol tubing. The best way is to use laser cutting or careful grinding. Always ask your supplier which way is best. If you cut it wrong, the tubing can get damaged or lose its smooth finish.
What is the best way to sterilize nitinol tubing?
Ethylene oxide and hydrogen peroxide vapor are the best ways. These keep the tubing’s shape memory and let it bend. Do not use steam or radiation. High heat or strong rays can hurt nitinol tubing and make it less safe.
How do you make sure your supplier meets medical standards?
Check if your supplier has ISO 13485 and FDA papers. Ask for their quality records and audit reports. Good suppliers give you all the right papers and can track every piece. This helps you follow medical rules and keeps your devices safe.
See Also
Choosing The Ideal Nitinol Tubing Supplier For You
The Manufacturing Process Of Nitinol Tubing For Medicine
A Detailed Guide To Selecting Proper Nitinol Tubing

