How to Select the Right PET Heat Shrink Tubing for Endoscope Sheaths
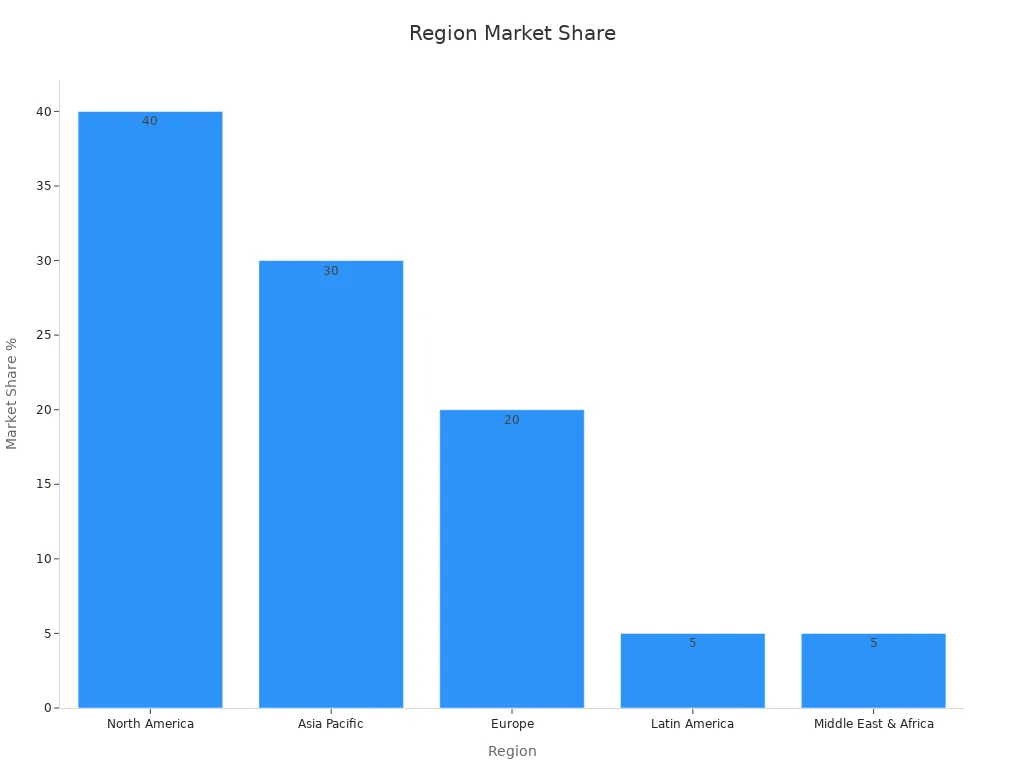
Selecting the right endoscope sheath pet heat shrink tubing is hard. Even experts can find it tricky. You need to think about the exact size and material. This helps protect delicate medical tools. Pet heat shrink tubing is used a lot in medical equipment. It has about 60% of the market. This is because pet heat shrink tubing is safe for the body. It also meets strict rules. This tubing can handle tough cleaning. It helps devices work well every time. More people want heat shrink tubing for medical tools now. The chart below shows how much each region uses it in 2023.
Key Takeaways
Measure with care and pick tubing that fits snugly. Make sure there are no wrinkles. This helps protect endoscope sheaths and wires. - Choose the right shrink ratio, often 2:1. This makes sure the tubing fits well and covers everything. There should be no open spaces. - Find a good wall thickness. The tubing should be strong but also bend easily. This helps when you use and clean it. - Use PET heat shrink tubing that meets medical rules. It should pass safety and cleaning tests. - Work with skilled suppliers who give certifications. They should let you test samples to check quality.
Key Criteria for Endoscope Sheath PET Heat Shrink Tubing
Sizing and Fit
When picking endoscope sheath pet heat shrink tubing, you must measure carefully. The tubing size and shrink ratio are important for safety and how well it works. Pick tubing that is not more than 15% bigger than your sheath. This makes sure the tubing fits tightly and does not slip. If the tubing is too big, it can get loose or wrinkle. Wrinkles can trap dirt and germs. Many people use the 25% rule. This means the tubing should shrink by about one-fourth to fit well. A tight fit keeps endoscope wires safe and the sheath smooth. This makes it easy to put in and take out.
Tip: Try the tubing on a sample sheath first. This lets you see if there are any gaps or bunching that could cause problems.
A good fit also stops the tubing from moving during cleaning. You want the tubing to stay put after many uses. This is very important when endoscope wires need to be safe and steady.
Shrink Ratio
The shrink ratio shows how much the tubing gets smaller with heat. For endoscope sheath pet heat shrink tubing, common ratios are 1.1:1, 2:1, and 3:1. The best ratio depends on your sheath and the wires you need to cover. A 2:1 ratio means the tubing shrinks to half its size. This works for most medical wires and endoscopes. If you need to cover odd shapes or connectors, a 3:1 ratio is better.
Fatigue life, tensile strength, and residual elongation show how well pet heat shrink tubing handles stress and cleaning.
Common shrink ratios like 2:1 and 4:1 help you get a tight fit. This stops gaps and keeps the tubing from being too tight. This is important for safety and how well the device works.
Pet heat shrink tubing keeps over 88% of its strength after 50 hydrogen peroxide cleanings. This means it is very strong.
The tubing works with autoclaving, gamma rays, and hydrogen peroxide. It keeps its shape and is safe for the body.
Studies show the right shrink ratio keeps the tubing in place. This protects endoscope wires and stops the tubing from moving.
Always test your tubing size and shrink ratio first. This helps you check if it fits, lasts, and works well in real use.
You should pick the shrink ratio that fits your sheath and wires. This makes sure the tubing covers everything tightly and leaves no gaps. For thin-wall pet heat shrink, the right ratio keeps it flexible and easy to use in medical tools.
Wall Thickness
Wall thickness is also important for endoscope sheath pet heat shrink tubing. Thin-wall pet heat shrink is flexible and low profile. This is good for delicate endoscope wires. But you still need enough thickness to protect against pressure and damage. If the wall is too thin, the tubing can break or tear. If it is too thick, it gets stiff and hard to fit over bends.
Research shows wall thickness changes strength and how well the tubing works. The table below shows how different things change with wall thickness:
Parameter | Impact on Tubing Performance |
|---|---|
Mechanical Strength | Thicker walls make tubing stronger and better at handling pressure |
Flexibility | Gets lower as wall thickness goes up |
Heat Transfer Coefficient (HTC) | Thinner walls help heat move through better |
Pressure Drop (PD) | Wall thickness changes flow and how well tubing holds up |
You should balance wall thickness for the best strength and use. Thin-wall pet heat shrink works for most endoscope wires, but always test it in real life. This helps you avoid problems during cleaning or many uses.
Note: For high-pressure or rough use, pick a little thicker wall. This gives more protection but still keeps some flexibility.
Thin-wall pet heat shrink is used a lot in many places. It gives good protection and stays flexible. This makes it great for endoscope sheaths and other medical wires. Always match wall thickness to what you need for the best results.
Material Properties of PET Heat Shrink Tubing
Mechanical and Chemical Resistance
Endoscope sheath applications need strong protection. They also need chemical resistance. PET heat shrink tubing gives both of these. This material does not wear out easily. It keeps its shape even when pulled or bent. You can count on it in tough places like hospitals. The tubing does not get damaged by many cleaning chemicals. This means it works well with disinfectants. Because it resists chemicals, it does not get ruined during cleaning.
Here is a table that lists important mechanical properties:
Property | Specification Requirement | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
Tensile strength | ≥ 107 N/m² | ASTM D2671 |
Shrink ratio | 2:1 | N/A |
Dielectric Strength | > 4,000 V/mil | N/A |
Long-term Temp. | -196°C to 135°C | N/A |
Short-term Temp. | Up to 200°C | N/A |
PET heat shrink tubing still works well after many cleanings. Tests show it lasts longer than Nylon 6.6. Nylon 6.6 can break down faster. You get strong and safe tubing even after lots of cleaning. This helps keep your medical tools safe and working.
Temperature and Sterilization Resistance
You need tubing that can take high heat and many cleanings. PET heat shrink tubing has a glass transition temperature over 85°C. This means it can go through steam cleaning at 121–135°C. It does not lose its shape. It also works with gamma rays and ethylene oxide cleaning. Even after 50 hydrogen peroxide cleanings, it stays strong. This makes it good for long-term use in hospitals.
Here are some important facts about temperature and cleaning:
Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
Shrinking temperature range | Approximately 70°C to 190°C |
Typical shrinking temperature | 150°C |
Long-term temperature use | -196°C to 135°C |
Short-term temperature use | Up to 200°C |
Melting point | 235°C |
Sterilization methods | Ethylene oxide, Gamma radiation, Autoclaving |
You can trust PET heat shrink tubing to work well during cleaning. It stays strong and does not break down, even in harsh conditions.
Additional Features (UV, Flame Retardancy)
Sometimes you need more features for special jobs. PET heat shrink tubing can block UV light. This keeps devices safe from the sun. It helps the tubing last longer and work better. Flame retardancy is another safety feature. It is important in places where fire is a risk. Some PET heat shrink tubing is black. This helps stop extra light from getting in. It is good for optical tools and makes them work better.
Tip: Always check if the tubing has the features you need. Make sure it matches your device and use. This helps your medical tools stay strong, safe, and clean.
Compliance with Medical Standards

Importance of Compliance
You need to follow rules when picking PET heat shrink tubing for medical tools. Groups like the FDA, EMA, and ISO make these rules. These rules help keep patients safe. They also make sure the tools work well. If you follow the rules, you will not have recalls or legal trouble. Hospitals and clinics only use products that meet these rules. As more people use medical tools, following the rules gets even more important. Getting approval from these groups helps people trust your product.
FDA Title 21 CFR Part 820 tells how to make and test products.
ISO 13485 checks if you have good quality systems.
USP Class VI and ISO 10993 look at safety and if the tubing is safe for the body.
If you meet these rules, your PET heat shrink tubing will work well in medical tools.
Biocompatibility
You must make sure PET heat shrink tubing is safe for the body. Biocompatibility means the tubing will not hurt people or cause bad reactions. Important rules for this are ISO 10993 and USP Class VI. These rules say you must test for safety and if it is toxic. The tubing must stay safe after cleaning and not be harmful. Hospitals use these rules to pick safe tubing for patients.
A table below shows the main rules for biocompatibility:
Standard | Focus Area | Application in Medical Equipment |
|---|---|---|
ISO 10993 | Biocompatibility | Testing for safe contact with tissue |
USP Class VI | Toxicity/Safety | Certification for non-toxic materials |
You should always check if your tubing meets these rules before using it in medical tools.
Certifications and Documentation
You need paperwork to show you follow the rules. You must keep certificates and test results for each batch of PET heat shrink tubing. You need this paperwork to get approval. The FDA wants you to keep records to show you follow Title 21 rules. ISO 13485 helps you keep good quality and safe products. Companies often give certificates for ISO 10993, USP Class VI, and FDA rules. These papers help hospitals and clinics trust your tools.
Tip: Always ask for and check certificates before using PET heat shrink tubing in medical tools.
The world market for PET heat shrink tubing was USD 350 million in 2024. This shows that following the rules is very important for medical tools. You can only do well in this market if you meet all the main rules for medical tools.
Supplier Verification and Product Quality
Supplier Experience
Always check if your supplier has lots of experience. A supplier who has worked in the medical field for many years knows the rules. They also know what hospitals and clinics need. Ask how long they have sold heat shrink tubing for medical devices. Pick suppliers who have helped hospitals or clinics before. This makes it easier to trust them.
Tip: Pick suppliers who can show you stories or feedback from other medical customers.
Product Certification
Make sure your pet heat shrink tubing comes with the right papers. Good suppliers give you documents that show their tubing meets FDA, ISO, and USP rules. These papers prove the tubing is safe and works well in hospitals. Always ask for these papers before you buy. You can use a table to keep track of what each supplier gives you:
Supplier Name | FDA Certificate | ISO 13485 | USP Class VI | Years in Business |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Supplier A | Yes | Yes | Yes | 15 |
Supplier B | Yes | No | Yes | 8 |
This table helps you compare suppliers and choose the best one for good tubing.
Sample Testing
Always test samples before you buy a lot of pet heat shrink tubing. Testing helps you see if the tubing fits, is strong, and works well. Try the tubing on your endoscope sheaths and clean it a few times. Look for cracks, shrinking, or color changes. Good testing helps you feel sure about your final product.
Note: Testing samples can help you save money and avoid problems later. You can find issues early and stop delays in your project.
If you follow these steps, you are more likely to get good pet heat shrink tubing. You keep your devices safe and help protect your patients.
When you select pet heat shrink tubing for endoscope sheaths, you need to focus on precise sizing, material performance, and compliance. Always check that your pet heat shrink tubing meets all medical standards. Use a checklist to confirm that the tubing fits your sheath, matches sterilization needs, and follows standards for safety. Pet heat shrink tubing must pass strict standards for hospitals. You should ask suppliers for proof that their pet heat shrink tubing meets these standards. Pet heat shrink tubing works best when you follow standards and test samples. Pet heat shrink tubing protects your devices and meets all standards. Pet heat shrink tubing gives you confidence in your work. Pet heat shrink tubing supports patient safety and meets standards. Pet heat shrink tubing helps you meet every standard. Pet heat shrink tubing ensures your tools meet all standards. For best results, talk with suppliers and regulatory experts about pet heat shrink tubing and standards.
FAQ
What is the best shrink ratio for endoscope sheaths?
You should use a 2:1 shrink ratio for most endoscope sheaths. This ratio gives a tight fit and covers wires well. If you need to cover connectors or odd shapes, try a 3:1 ratio.
How do you test PET heat shrink tubing before full use?
Always test a sample on your actual sheath. Heat the tubing, check for gaps, wrinkles, or cracks. Clean it several times. If the tubing stays strong and fits well, you can use it for your devices.
Can PET heat shrink tubing handle repeated sterilization?
Yes, PET heat shrink tubing resists many sterilization methods. You can use steam, gamma rays, or hydrogen peroxide. The tubing keeps its shape and strength after many cleaning cycles.
What certifications should you ask your supplier for?
You should ask for FDA, ISO 13485, and USP Class VI certificates. These documents show the tubing is safe, high quality, and meets medical standards.
Why does wall thickness matter for endoscope sheaths?
Wall thickness affects strength and flexibility. Thin walls keep the tubing flexible and easy to use. Thicker walls give more protection. You should balance both for the best results.
See Also
How To Pick The Right FEP Autoclavable Tubing
Selecting The Ideal Ultra-Thin PET Heat Shrink Tubing
A Complete Guide To Finding The Perfect Tubing Size

