What You Need to Know About PTCA Balloon Catheters for Stent Delivery
PTCA balloon catheters play a crucial role in percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. These tools help restore blood flow by delivering stents to blocked arteries. Their design includes an inflatable balloon that expands to open narrowed vessels. Recent studies highlight potential complications during angioplasty. For instance, ecchymosis occurs in 18.29% of transradial cases compared to 17.14% of transfemoral. Bruising affects 17.66% in transradial versus 14.27% in transfemoral. The balloon’s precision minimizes risks like vessel permeability loss, which remains at 0% in transfemoral procedures. PTCA Balloon Catheter OEM for Stent Delivery Systems ensures accuracy in stent placement, improving patient outcomes.
Key Takeaways
PTCA balloon catheters help open clogged arteries during angioplasty. This restores blood flow and lowers the chance of heart attacks.
Newer catheters are made with better designs and materials. They bend easily and work more accurately, helping patients recover better.
Balloons with medicine coating reduce artery blockage by releasing drugs. These are great for patients with higher health risks.
Balloons inflate and deflate quickly, making procedures faster. This helps patients recover sooner after treatment.
AccuPath makes catheters that are precise and flexible. This ensures stents are placed correctly and keeps patients safer.
Understanding PTCA Balloon Catheters
Definition and Purpose
PTCA balloon catheters are essential tools in percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. These devices are designed to dilate narrowed or blocked blood vessels during coronary interventions. Each catheter consists of a flexible tube with an inflatable balloon at its tip. Physicians guide the catheter to the site of blockage, where the balloon inflates to compress plaque or obstruction. This process widens the vessel and restores optimal blood flow, reducing the risk of ischemic complications. The balloon’s compliance ensures precise dilation, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
Key Features and Design
Modern PTCA balloon catheters incorporate advanced features that enhance their performance and reliability. Their design includes a hypodermic tube (hypotube) with outer dimensions ranging from 0.59 to 0.69 mm, ensuring flexibility and maneuverability. The balloon itself measures between 0.9 and 1.2 mm in outer dimensions, with elongation capabilities of 0.6 to 2.0 mm. These specifications allow the balloon to adapt to varying vessel sizes and conditions.
Other critical features include tip diameter increases of 1.7–22%, which improve navigation through complex vascular structures. Friction levels range from 0.12 N to 1.07 N, ensuring smooth catheter movement during procedures. The deflation rate, measured at 0.004 to 0.013 µL/s, contributes to rapid deflation times of 10.2–28.1 seconds, enabling efficient stent deployment.
Feature | Measurement Range |
|---|---|
Outer dimensions (hypotube) | 0.59–0.69 mm |
Outer dimensions (balloon) | 0.9–1.2 mm |
Tip diameter increase | 1.7–22% |
Balloon elongation | 0.6 to 2.0 mm |
Friction increase | 0.12 N to 1.07 N |
Deflation rate | 0.004 to 0.013 µL/s |
Estimated deflation time | 10.2–28.1 s |
The material composition of the balloon plays a significant role in its compliance and functionality. Studies show that compliance can be adjusted by altering the material or wall thickness. Mechanical testing highlights that increasing wall thickness reduces compliance, while finite element analysis emphasizes the importance of material behavior in stent expansion.
Types of PTCA Balloon Catheters
PTCA balloon catheters come in various types, each tailored to specific clinical needs. Conventional PTCA catheters, also known as plain old balloon angioplasty (POBA), are widely used for basic vessel dilation. Cutting balloons (CB) feature microblades that score the plaque, facilitating more effective dilation. Drug-coated balloons (DCB) deliver therapeutic agents to the vessel wall, reducing restenosis rates.
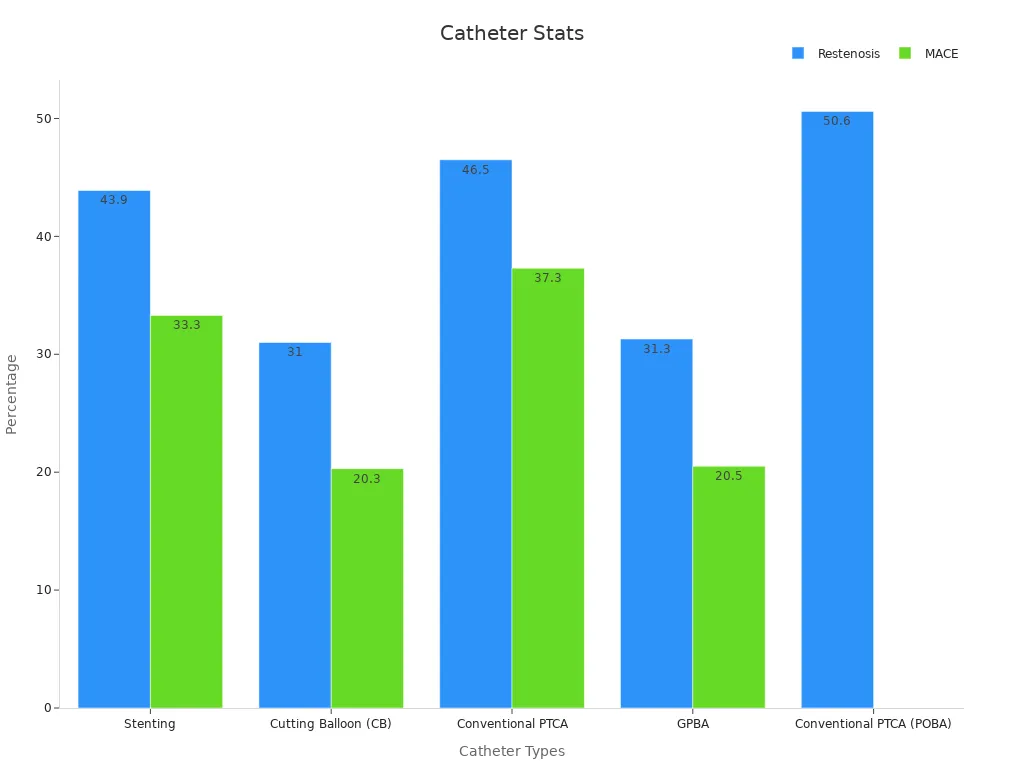
Comparative studies highlight the performance differences among these types. For example, cutting balloons show lower angiographic restenosis rates (31%) compared to conventional PTCA (46.5%). Drug-coated balloons demonstrate superiority in reducing lumen loss and target lesion revascularization compared to plain old balloon angioplasty.
Type of Balloon Catheter | Angiographic Restenosis Rate | Major Adverse Coronary Events (MACE) | Target Lesion Revascularization (TLR) |
|---|---|---|---|
Stenting | 43.9% | 33.3% | N/A |
Cutting Balloon (CB) | 31% | 20.3% | 20.0% |
Conventional PTCA | 46.5% | 37.3% | 37.6% |
GPBA | 31.3% | 20.5% | 20.5% |
Conventional PTCA (POBA) | 50.6% | N/A | N/A |
Drug-coated balloons have also shown promising results in clinical trials. A nine-month follow-up study revealed that paclitaxel-coated balloons are noninferior to drug-eluting stents (DES) in terms of fractional flow reserve, with low clinical event rates. However, randomized controlled trials indicate that DCB-PCI may not achieve non-inferiority compared to DES due to higher rates of target lesion revascularization.
How PTCA Balloon Catheters Work in Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
Mechanism of Action
PTCA balloon catheters operate as essential tools in coronary angioplasty procedures. Physicians use these devices to open blocked coronary arteries and restore blood flow. The catheter is guided to the site of the blockage, where the balloon inflates to compress the obstruction against the artery wall. This process widens the passage, allowing blood to flow more freely. In many cases, the balloon is inflated multiple times to achieve optimal dilation. This minimally invasive approach reduces the risk of complications and improves patient outcomes.
Inflation and Deflation Process
The inflation and deflation process of PTCA balloon catheters is a critical aspect of their functionality. During inflation, the balloon expands to exert pressure on the plaque or blockage, compressing it against the arterial wall. The inflation process is carefully controlled to ensure precise dilation without damaging surrounding tissues. Once the desired vessel diameter is achieved, the balloon deflates rapidly, allowing the catheter to be repositioned or removed. Modern PTCA balloon catheters feature advanced deflation mechanisms, with rates ranging from 0.004 to 0.013 µL/s. This rapid deflation capability minimizes procedural time and enhances efficiency during coronary angioplasty.
Interaction with Blocked Arteries
PTCA balloon catheters interact directly with blocked arteries to restore blood flow. The balloon’s compliance and material composition play a vital role in this interaction. When inflated, the balloon adapts to the shape and size of the artery, ensuring uniform pressure distribution. This adaptability reduces the risk of arterial damage while effectively compressing the blockage. The catheter’s tip design further aids navigation through complex vascular structures, allowing precise placement at the site of obstruction. By combining mechanical precision with advanced materials, PTCA balloon catheters optimize the treatment of blocked arteries during percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty.
PTCA Balloon Catheter OEM for Stent Delivery Systems
Role in Stent Positioning
PTCA balloon catheter OEM for stent delivery systems plays a critical role in ensuring accurate stent positioning during angioplasty. The materials used in these catheters are engineered to expand uniformly under high pressure. This uniform expansion is essential for placing stents precisely at the site of arterial blockage. The mechanical properties of the balloon, such as compliance and elasticity, directly influence the success of the procedure.
Design optimization of PTCA balloon catheters focuses on their shapes, sizes, and mechanical characteristics. These factors ensure that the stent remains stable during deployment. Advanced engineering principles applied in manufacturing these catheters enhance their ability to navigate complex vascular structures. This precision minimizes the risk of stent misplacement, which could lead to complications or the need for repeat procedures.
AccuPath’s PTCA balloon catheter OEM services prioritize these design elements. Their products are tailored to meet the demands of modern cardiovascular interventions, ensuring that stents are positioned with unparalleled accuracy.
Deployment and Expansion of Stents
The deployment and expansion of stents rely heavily on the performance of PTCA balloon catheters. During angioplasty, the balloon inflates to expand the stent, pressing it against the arterial walls. This process restores blood flow and stabilizes the vessel. The balloon’s ability to expand uniformly ensures that the stent achieves its intended shape and size, reducing the risk of restenosis.
Statistical outcomes highlight the impact of PTCA balloon catheter OEM for stent delivery systems on procedural success:
The Metricath system improved vessel sizing accuracy, increasing the minimal lumen diameter (MLD) from 4.4±0.77 mm to 5.17±0.82 mm (P<.001).
The ratio of MLD to reference vessel diameter improved from 77.4±15.2% to 91.2±17.5% (P<.001).
The ratio of MLD to nominal stent diameter increased from 76.2±7.1% to 90±9.4% (P<.001).
These advancements demonstrate the importance of precise balloon catheter design in achieving optimal stent expansion. AccuPath’s OEM solutions incorporate cutting-edge technology to enhance stent deployment outcomes, ensuring patient safety and procedural efficiency.
Ensuring Precision and Stability
Precision and stability are paramount in PTCA balloon catheter OEM for stent delivery systems. The interaction between the balloon and the stent must be carefully controlled to avoid complications. Advanced simulations have validated the effectiveness of these catheters in various scenarios.
Evidence Description | Details |
|---|---|
Simulation Approach | Simulated the stent life-cycle, including balloon folding and expansion. |
Comparison Method | Compared detailed simulation with standard expansion methods. |
Stent Designs | Validated two stent designs with different stiffness levels. |
Asymmetrical Positioning | Demonstrated effectiveness with asymmetrically positioned stents. |
These simulations highlight the versatility of PTCA balloon catheters in handling diverse clinical challenges. The ability to maintain stability during stent deployment reduces the risk of complications, such as stent migration or vessel damage.
AccuPath leverages these advancements to deliver OEM solutions that prioritize precision and stability. Their PTCA balloon catheters are designed to meet the highest standards, ensuring successful outcomes in even the most complex cases.
Applications in Cardiovascular Interventions
Treating Coronary Artery Disease
PTCA plays a vital role in treating coronary artery disease, a condition caused by plaque buildup in the arteries. Physicians use a balloon to compress the plaque and widen the artery. This process restores blood flow and reduces the risk of heart attacks. PTCA often involves the placement of stents to keep the artery open. Drug-eluting stents are particularly effective in preventing restenosis by releasing medication that inhibits tissue growth. These advancements have made PTCA a cornerstone of modern cardiovascular interventions.
Emergency Use in Acute Conditions
PTCA is a lifesaving procedure in emergencies such as acute myocardial infarction. In these situations, time is critical. Physicians use a balloon catheter to quickly open blocked arteries and restore blood flow to the heart. This rapid intervention minimizes heart muscle damage and improves survival rates. The ability to deploy stents during the procedure further enhances its effectiveness. Drug-eluting stents are often used to ensure long-term artery patency, reducing the likelihood of future complications.
Compatibility with Advanced Stent Technologies
Modern PTCA techniques are compatible with advanced stent technologies, including bioresorbable and drug-eluting stents. These stents offer improved outcomes by adapting to the artery's natural healing process. The balloon used in PTCA ensures precise stent placement and expansion. This compatibility allows physicians to tailor treatments to individual patient needs. As a result, PTCA continues to evolve as a key component of cardiovascular interventions, addressing complex cases with greater precision and success.
Benefits and Advancements in PTCA Balloon Catheter Technology
Advantages of Modern PTCA Balloon Catheters
Modern PTCA balloon catheters offer significant advantages over earlier models, improving both procedural efficiency and patient outcomes. These catheters feature advanced materials and designs that enhance flexibility and durability, allowing physicians to navigate complex vascular structures with ease. Hydrophilic coatings reduce friction, enabling smoother catheter movement during angioplasty. Additionally, modern balloons demonstrate superior precision in stent placement, minimizing the risk of complications such as restenosis.
Comparative studies highlight the clinical benefits of these advancements. For instance, Paccocath-coated catheters show a dramatic reduction in in-segment late luminal loss (0.03 ± 0.48 mm) compared to uncoated catheters (0.74 ± 0.86 mm, p=0.002). Patients also benefit from shorter antiplatelet therapy durations, with modern catheters requiring only one month compared to twelve months for earlier models. These improvements underscore the transformative impact of modern PTCA balloon catheters on clinical outcomes.
Metric | Paccocath (Modern) | Uncoated Catheters (Earlier) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
In-segment late luminal loss | 0.03 ± 0.48 mm | 0.74 ± 0.86 mm | 0.002 |
Antiplatelet therapy duration | 1 month | 12 months | N/A |
Follow-up period | 2 years | N/A | N/A |
Innovations in Materials and Design
Recent innovations in PTCA balloon catheter technology have revolutionized their performance and reliability. Advanced materials like nitinol and specialized polymers enhance flexibility and durability, ensuring the balloon can withstand the mechanical stresses of angioplasty. Hydrophilic coatings improve maneuverability, reducing friction during navigation. Cutting-edge imaging technologies, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and intracardiac echocardiography (ICE), provide real-time visualization, enabling precise catheter placement.
Other advancements include the integration of pressure-sensitive electrodes for high-resolution cardiac mapping and the use of 3D mapping systems for detailed anatomical models. Artificial intelligence (AI) further enhances these systems by improving image interpretation and offering real-time decision support. These innovations collectively elevate the accuracy and efficiency of PTCA procedures, contributing to better clinical outcomes.
Key Material and Design Innovations:
Nitinol and polymer construction for flexibility and durability.
Hydrophilic coatings for reduced friction.
Real-time imaging via OCT and ICE.
AI-driven mapping systems for enhanced precision.
Contributions of AccuPath to PTCA Technology
AccuPath has emerged as a leader in advancing PTCA balloon catheter technology. The company focuses on developing catheters with superior precision and stability, ensuring optimal stent deployment. Their products incorporate advanced composites that offer high durability and excellent performance, leading to enhanced patient outcomes.
AccuPath also integrates adaptive learning algorithms into its catheter systems, enabling real-time adjustments tailored to patient-specific anatomies. This innovation improves procedural accuracy and reduces the likelihood of complications. By prioritizing cutting-edge materials and intelligent design, AccuPath continues to set new benchmarks in PTCA balloon catheter technology, solidifying its role as a key contributor to modern cardiovascular interventions.
Material Type | Durability | Performance | Patient Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
Metal-Plated Catheters | High | Excellent | Improved |
Traditional Materials | Moderate | Good | Standard |
Advanced Composites | High | Very Good | Enhanced |
PTCA balloon catheters remain indispensable in percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, offering advanced solutions for treating blocked arteries. Their innovative designs ensure precise stent placement and effective vessel dilation, minimizing complications and improving procedural success.
The adoption of PTCA balloon catheter technology has grown significantly across global markets:
North America leads with its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high prevalence of cardiovascular diseases.
Europe shows steady growth due to an aging population and improved healthcare systems.
Asia-Pacific exhibits the highest growth rate, driven by increased healthcare investments and rising awareness of cardiovascular health.
Clinical advancements further highlight their benefits:
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Restenosis Rate Reduction | Drug-coated balloons reduce restenosis rates by 60% compared to traditional balloons. |
Procedural Success Rate | A clinical trial in Germany showed DCBs achieving 89% target lesion revascularization-free survival at 24 months. |
Increase in Procedures | Japan reported a 21% increase in PTCA procedures using next-generation balloons from 2021 to 2023. |
Market Growth | North America experienced a 7% annual increase in PCI procedures from 2020 to 2023. |
Innovations by companies like AccuPath continue to drive progress in PTCA balloon catheter technology. Their focus on precision and adaptability ensures better patient outcomes and procedural efficiency, solidifying their role in modern cardiovascular interventions.
FAQ
What is the primary purpose of a PTCA balloon catheter?
A PTCA balloon catheter helps open blocked coronary arteries during angioplasty. It compresses plaque against the artery walls, restoring blood flow. Physicians often use it to deliver stents, ensuring the artery remains open and reducing the risk of restenosis.
How does a drug-coated balloon differ from a conventional balloon?
Drug-coated balloons release medication to prevent tissue growth, reducing restenosis rates. Conventional balloons only dilate the artery without delivering therapeutic agents. Studies show drug-coated balloons achieve better long-term outcomes in certain cases.
Tip: Drug-coated balloons are ideal for patients at high risk of restenosis.
Are PTCA balloon catheters reusable?
No, PTCA balloon catheters are single-use devices. Reusing them could compromise sterility and performance, increasing the risk of complications. Manufacturers design these catheters for one-time use to ensure patient safety.
What advancements have improved PTCA balloon catheter technology?
Modern PTCA balloon catheters feature advanced materials like nitinol and hydrophilic coatings. These innovations enhance flexibility, durability, and maneuverability. Real-time imaging technologies, such as OCT, also improve procedural accuracy.
Can PTCA balloon catheters treat all types of arterial blockages?
PTCA balloon catheters effectively treat many blockages, especially in coronary arteries. However, heavily calcified or complex lesions may require additional tools, such as cutting balloons or atherectomy devices, for optimal results.
Note: Physicians assess each case individually to determine the best treatment approach.
See Also
A Comprehensive Overview of PTCA Balloon Catheter Production
Essential Tips for Selecting the Perfect PKP Balloon Catheter
The Role of Self-Expanding Stents in Vascular Procedures
Latest Innovations in Etched PTFE for Catheter Production
Evaluating Top Kyphoplasty Balloon Makers and Their Advancements

