Comparing the Pros and Cons of Nitinol Tubing and Stainless Steel Tubes

Choosing the best material for medical applications often comes down to the comparison between Nitinol Tubing vs. Stainless Steel Tube. Each has unique properties that suit different needs. Nitinol tubing stands out for its exceptional flexibility and fatigue resistance, making it ideal for devices that require bending without breaking. It also offers better biocompatibility, reducing the risk of rejection by the body. On the other hand, stainless steel tubing is known for its strength, lower cost, and ease of fabrication, which makes it a popular choice for many medical instruments. Below is a quick comparison highlighting the key differences between Nitinol Tubing vs. Stainless Steel Tube:
Feature | Nitinol Tubing | Stainless Steel Tubing |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility | Superior | Less flexible |
Fatigue Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
Medical Suitability | Higher in some devices | Widely used |
Cost | Higher | Lower |
Key Takeaways
Nitinol tubing bends easily and goes back to its shape. This makes it great for medical devices that move in the body. Stainless steel tubes are very strong and cost less money. They are also easier to make. But they do not bend as well as nitinol tubing. Seamless nitinol tubing lasts longer and is best for implants. Welded tubing costs less and is good for simple uses. Nitinol tubing does not rust and helps stop blood clots. This makes it safer for implants that stay in the body. You should pick the right tubing based on how flexible it needs to be. You should also think about cost and how the device will be used.
Which Is Better?
Nitinol Tubing
Nitinol tubing is used in many new medical tools. It has a special superelasticity. This means it can bend and then go back to its shape. Doctors pick seamless nitinol tubing for things that move inside the body, like stents or guidewires. Seamless nitinol tubing has smooth surfaces. These smooth surfaces help stop blood clots from forming. Welded nitinol tubing is also used in medical tools. But seamless nitinol tubing is more common for implants.
Nitinol tubing is very good at handling bending over and over. Devices made from seamless nitinol tubing can bend many times and not break. This makes nitinol tubing great for things that move a lot. Welded nitinol tubing works well too. But seamless nitinol tubing usually lasts longer when things get tough. Nitinol tubing does not rust easily. This is important for implants that stay in the body for a long time. The body also accepts nitinol tubing well.
Tip: Engineers should use nitinol tubing when they need flexibility, superelasticity, and long-lasting parts.
Stainless Steel Tube
Stainless steel tube is strong and used in many places. It has higher tensile strength than nitinol tubing. This makes it good for things that need to be very tough. Welded stainless steel tube is found in surgical tools and support parts. Seamless stainless steel tube is also used in some medical devices. But it cannot bend like nitinol tubing can.
Stainless steel tube costs less than nitinol tubing. It is easier to cut and weld. This makes it cheaper to make. Welded stainless steel tube is good for things that do not need to bend much. Seamless stainless steel tube does not rust easily. But nitinol tubing still works better in harsh places. Stainless steel tube is used a lot in hospitals. But it may not be best for implants that stay in the body for a long time.
When picking between nitinol tubing and stainless steel tube, engineers should think about:
If they need superelasticity
How much bending the part will do
The cost and how easy it is to make
If it is good for medical use
Nitinol Tubing vs. Stainless Steel Tube
Key Differences
When you compare nitinol tubing vs. stainless steel tube, you first look at what they are made of. Nitinol tubing has about 55% nickel and 45% titanium. This mix gives nitinol tubing its special features. Stainless steel tubes are made from iron, chromium, and nickel. Nitinol tubing can switch between two phases called austenite and martensite. This lets nitinol tubing bend and go back to its shape. Stainless steel tubes cannot do this. They stay stiff and only bend a little before they change shape for good.
Aspect | Nitinol Tubing | Stainless Steel Tubes |
|---|---|---|
Material Composition | ~55% Nickel, 45% Titanium | Iron, Chromium, Nickel (varies) |
Crystalline Structure | Austenite/Martensite phases (reversible) | Traditional alloy, no phase change |
Unique Properties | Shape memory, superelasticity | Rigid, lacks shape memory |
Mechanical Behavior | Reversible deformation | Permanent deformation under stress |
Biocompatibility & Corrosion Resistance | High | Good, but less than nitinol |
Nitinol tubing is very flexible and can return to its shape. This is called the shape memory effect. Stainless steel tubes do not have this. Nitinol tubing also does not rust easily, which is good for medical tools. Stainless steel tubes are easier to make and cost less money. Nitinol tubing needs special care and costs more to make. Both seamless nitinol tubing and welded nitinol tubing have these special features. Seamless nitinol tubing usually works better when things get hard. Welded nitinol tubing is still helpful, especially if you want to save money.
Advantages and Disadvantages
To compare nitinol tubing vs. stainless steel tube, it helps to see what is good and bad about each one. Each material has things it does well and things it does not do as well. This affects how they are used in medicine and industry.
Nitinol Tubing:
Advantages:
Has shape memory and superelasticity, so it bends and goes back to its shape.
Is strong and stiff.
Does not rust easily.
Works well with lubricants.
Both seamless nitinol tubing and welded nitinol tubing can handle lots of bending.
Is safe for implants because it works well with the body.
Disadvantages:
Costs more because the materials and making process are expensive.
Is hard to cut because it can change shape while cutting.
Needs careful handling to keep its special features.
Welded nitinol tubing may not last as long as seamless nitinol tubing in tough places.
Stainless Steel Tubes:
Advantages:
Costs less and is easier to cut.
Is strong for many uses.
Both welded and seamless stainless steel tubes are easy to find.
Does not rust in most places.
Disadvantages:
Weighs more than nitinol tubing.
Can be hard to weld and shape.
May rust in salty or very hot places.
Is not as flexible and does not have shape memory.
Welded stainless steel tubes may need special tools to join.
Note: Both seamless nitinol tubing and welded nitinol tubing have their own good points, but seamless nitinol tubing often works better in hard medical jobs. Welded nitinol tubing can save money for less important uses.
The main differences between nitinol tubing vs. stainless steel tube are in how flexible they are, how long they last, how much they cost, and how easy they are to make. Nitinol tubing, especially seamless nitinol tubing, is the most flexible and lasts the longest. Welded nitinol tubing is still strong but may not last as long in hard places. Stainless steel tubes, both seamless and welded, are strong and cost less but are not as flexible as nitinol tubing. The best choice depends on what the device needs, how important flexibility is, and how much money you can spend.
Mechanical Properties

Flexibility and Fatigue
Nitinol is very flexible and can bend a lot. It can go back to its shape even after many bends. Doctors use nitinol in stents and guidewires because it moves well inside the body. Stainless steel is strong but not as flexible as nitinol. It does not bend as much and can break if bent too often.
Nitinol tubing is very elastic and resists breaking. It can bend a lot without getting damaged.
Nitinol stents can bend millions of times and still work. Stainless steel stents can crack if bent too much.
Nitinol’s superelasticity helps it spread out stress. This makes it last longer when things move a lot.
Studies show nitinol lasts longer if made carefully. Clean materials and good processing help it work better. Stainless steel’s life changes with test speed and where it is used. Both react to stress in different ways, but nitinol is better for things that need to bend and last a long time.
Note: Nitinol’s flexibility helps it fit tricky shapes in the body. This lowers the chance of hurting blood vessels.
Strength and Durability
Stainless steel is usually stronger than nitinol. It can take more force before it breaks. But nitinol’s superelasticity and shape memory make it last longer when bent many times. Nitinol tubing can bend over and over and not break. This is good for medical tools that move a lot.
Nitinol’s strength depends on how it is made. Good nitinol tubing does not crack and lasts longer. Stainless steel is strong but does not have shape memory or superelasticity. Nitinol’s flexibility and strength make it great for implants that move all the time.
Nitinol can lose some features if it gets too hot or is heated many times.
Making nitinol tubing needs careful control to keep it strong.
Special coatings and alloy changes can make nitinol work better.
Stainless steel is still a good choice if you need strength but not much bending. Nitinol is special because it is strong and can bend a lot, which is important for things that move again and again.
Biocompatibility and Corrosion
Medical Applications
Nitinol and stainless steel are used in many medical devices. They are important for implants and surgical tools. Nitinol is chosen for implants because it bends easily and remembers its shape. It also does not rust much. These features help nitinol stents and implants last longer in the body. Stainless steel is strong and does not rust easily. It is used for surgical tools and implants that do not stay in the body for a long time.
Nitinol can release nickel ions, which may cause allergies. Some people are sensitive to nickel. About 17.5% of people tested have this problem.
Special treatments on nitinol stents can lower nickel release. These treatments also help stop rust.
Porous nitinol is as safe as porous stainless steel and titanium. It is good for bone implants and tissue supports.
Both nitinol and stainless steel need careful testing and surface treatments. This makes sure they are safe for medical use.
Note: Safety rules require tests and labels for nitinol and stainless steel in medical devices.
Performance in Medical Applications
Nitinol tubing does not rust easily in the body. Surface treatments make a smooth layer that keeps nickel from coming out. This layer helps keep the implant safe. Nitinol stents do not break down and keep working well for a long time. Stainless steel also resists rust, but nitinol works better in tough body conditions.
Nitinol’s smooth surface helps stop blood clots from forming. It also causes less damage to blood vessels than stainless steel. Animal tests show nitinol stents make fewer clots and hurt vessels less. The chart below shows how nitinol and stainless steel stents compare in rabbits:
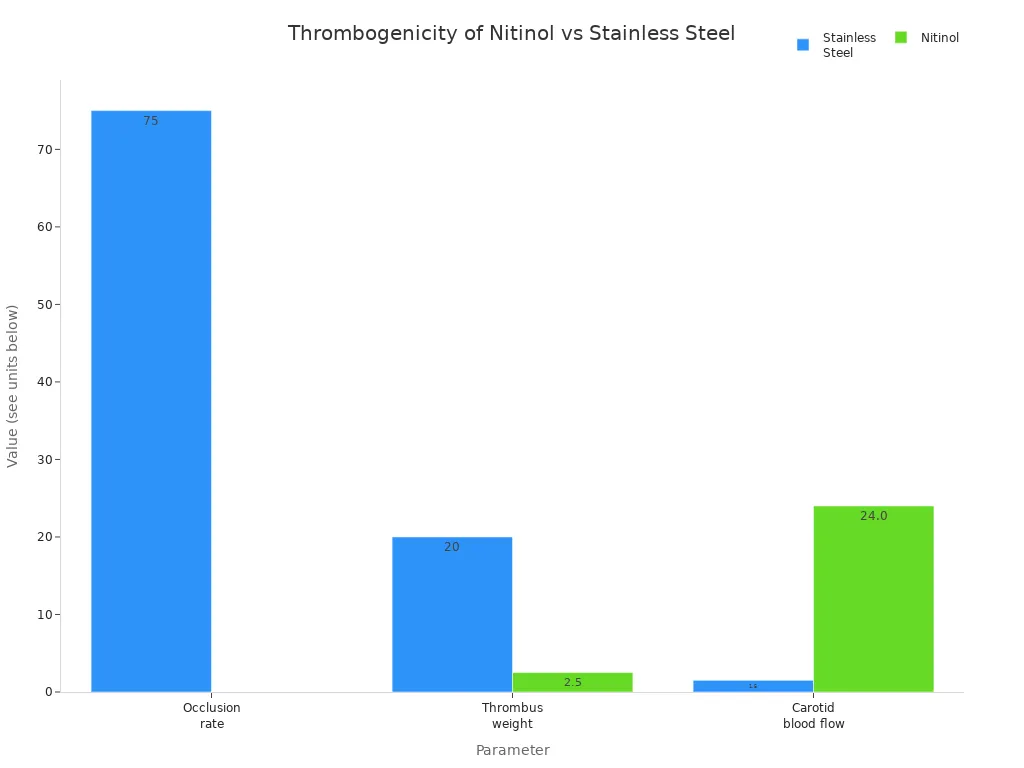
Parameter | Stainless Steel | Nitinol |
|---|---|---|
Occlusion rate | 75% | 0% |
Thrombus grade | III (subocclusive) | I (no lumen encroachment) |
Thrombus weight | 20 mg | 2.5 mg |
Carotid blood flow | 1.5 ml/min | 24.0 ml/min |
Scientists are working to make nitinol even safer. They want to lower nickel release and help the body accept implants better. They also try to make nitinol implants fit each person. Both nitinol and stainless steel meet strict safety rules. But nitinol is better at not rusting and works well with the body. This makes it a top choice for long-term implants and surgical stents.
Cost and Processing
Material Cost
Nitinol tubing costs more than stainless steel tubing. This is because nitinol uses nickel and titanium. These metals are expensive. Stainless steel tubing uses iron, chromium, and nickel. These are cheaper metals. Both seamless nitinol tubing and welded nitinol tubing cost more. They need special steps to make them.
Manufacturers pick seamless stainless steel tubing for cheaper projects. Seamless nitinol tubing is chosen when flexibility matters more than price. Nitinol tubing is costly, so companies sometimes mix it with stainless steel tubing. This helps save money and still get the right features.
Tip: Using nitinol tubing only where needed can help save money in medical devices.
Machinability and Joining
It is much harder to machine nitinol tubing than stainless steel tubing. Nitinol needs special tools and skilled workers. When heated, nitinol tubing faces high stress. It must be held in strong, heat-resistant holders. These steps make it cost more and take longer. Both seamless nitinol tubing and welded nitinol tubing need careful handling. This keeps their shape memory and superelasticity.
Stainless steel tubing is easier to cut, weld, and join. Welded stainless steel tubing does not need special heat treatments. This makes it faster and cheaper to work with. Seamless stainless steel tubing is also easy to machine and join. This helps lower the cost.
Joining nitinol tubing to itself or other materials is hard. Nitinol reacts to heat and can form oxide layers. This can hurt weld quality. Laser welding, glue, and special cleaning are often needed. Welded nitinol tubing may need extra steps to stay strong and safe. Stainless steel tubing can be joined with normal welding or soldering.
New ideas help fix some of these problems. For example, new laser cutting and 3D printing help make custom seamless nitinol tubing. This gives better results. Some companies use puzzle-cut joining to connect nitinol and stainless steel tubing. This does not need welding or glue. It saves time and money and keeps the tubing strong.
Tubing Type | Machinability | Joining Methods | Processing Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
Seamless nitinol tubing | Difficult | Laser, adhesive, puzzle | High |
Welded nitinol tubing | Difficult | Laser, adhesive | High |
Seamless stainless steel | Easy | Standard welding | Low |
Welded stainless steel | Easy | Standard welding | Low |
Note: Both seamless nitinol tubing and welded nitinol tubing need careful work to keep their special features. Stainless steel tubing is easier and cheaper to use, but it is not as flexible or tough.
Typical Uses

Medical
Doctors and engineers use nitinol and stainless steel tubing in many medical devices. Nitinol tubing is found in catheters, guidewires, and stents. Its superelasticity and shape memory help these tools move through blood vessels. They do not kink or get stuck. Seamless nitinol tubing is best for implants that must bend and return to shape. Welded nitinol tubing is used in some tools too. But seamless nitinol tubing works better for implants that stay in the body a long time.
Stainless steel tubing is common in tools like needles and surgical instruments. Welded stainless steel tubing is strong and easy to shape. Seamless stainless steel tubing is used when smooth surfaces are needed. Stainless steel tubing is not as flexible as nitinol tubing. Doctors often pick nitinol stents for arteries because they do not kink and last longer. Welded nitinol tubing is good for parts that are not as important. Seamless nitinol tubing is picked for stents and implants that stay in the body.
Note: Nitinol tubing, especially seamless types, helps lower blood clot risks in stents. Welded tubing costs less for single-use or short-term medical tools.
Industrial
Nitinol tubing is also used outside of medicine. Engineers use seamless nitinol tubing in planes for fuel and hydraulic systems. It absorbs vibration and does not rust easily. This makes it good for tough places. Welded nitinol tubing is used in robots and machines that need to bend a lot. Seamless nitinol tubing is picked for connectors that must go back to shape after bending.
Stainless steel tubing is used in many industries. Welded stainless steel tubing is found in building, cars, and food factories. Seamless stainless steel tubing is chosen for high-pressure jobs and places where leaks are bad. Welded stainless steel tubing is easier and cheaper to make. This makes it good for big projects.
Aspect | Nitinol Tubing Characteristics | Stainless Steel Tubes Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Initial Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
Durability | Longer lifespan, fewer replacements needed | Shorter lifespan, more frequent repairs required |
Maintenance Needs | Lower maintenance due to strength and flexibility | Higher maintenance due to frequent checks |
Long-term Cost | More cost-effective over time due to reduced upkeep | More expensive over time due to ongoing repairs |
Customization | Available, enhancing performance and reducing failures | Limited customization options |
Seamless nitinol tubing and welded nitinol tubing both have special uses in industry and medicine. Seamless tubing is best for important jobs. Welded tubing is picked when saving money matters or the job is not as hard.
Summary Table
Picking the best tubing means looking at many details. Engineers and doctors compare nitinol tubing and stainless steel tubes by checking their main features. The table below lists important facts for both types. These facts help people choose which tubing works best for them.
Specification | Nitinol Tubing | Stainless Steel Tubes |
|---|---|---|
Recovered Elongation | ~8% | ~0.8% |
Biocompatibility | Excellent | Fair |
Effective Modulus | Approx. 48 GPa | 193 GPa |
Torqueability | Excellent | Poor |
Density | 6.45 g/cm³ | 8.03 g/cm³ |
Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic | Magnetic |
Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) | Approx. 1,240 MPa | Approx. 760 MPa |
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) - Martensite | 6.6 x 10⁻⁶ cm/cm/°C | 17.3 x 10⁻⁶ cm/cm/°C |
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) - Austenite | 11.0 x 10⁻⁶ cm/cm/°C | N/A |
Resistivity | 80 to 100 micro-ohm·cm | 72 micro-ohm·cm |
Tip: Nitinol tubing bends easily and remembers its shape. Stainless steel tubing is stiffer and easier to work with.
When picking stainless steel tubing, people should check rules like ASTM A500, ASTM A1085, ASTM A1065, ASTM A847, and CSA G40.21. These rules tell how strong, big, and exact the tubing should be. Following these rules makes sure the tubing is safe and good quality.
Here are some things to remember when comparing tubing:
Nitinol tubing bends and goes back to its shape. Stainless steel tubing stays stiff and does not bend much.
Nitinol tubing does not rust easily. Stainless steel tubing can rust in tough places.
Nitinol tubing costs more but lasts longer if it moves a lot.
Stainless steel tubing is easier to cut and put together.
Engineers and doctors should pick tubing that fits the job. Choosing the right tubing helps keep things safe and working well.
Nitinol tubing and stainless steel tubing are both helpful for medical devices. Nitinol tubing can bend, remember its shape, and last a long time. This makes it good for tough medical jobs. Stainless steel tubing is strong and costs less. It works well for many regular medical tools. New ways let people use both types together. Nitinol tubing is used when bending is important. Stainless steel tubing is picked when strength and saving money matter. The best tubing depends on what the device needs and how much money there is. For hard medical projects, talking to experts helps get the best results.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing popular in medical devices?
Nitinol tubing can bend and then go back to its shape. Many engineers use it for stents and guidewires. Its flexibility helps doctors reach tricky spots in the body. This tubing does not rust, so it is safe for implants that stay in the body.
Can stainless steel tubes be used for all medical applications?
Stainless steel tubes are strong and easy to shape. They work well for many medical tools. But they are not as flexible as nitinol tubing. Some implants need to bend more, so nitinol tubing is a better pick.
How do seamless and welded tubes differ in medical use?
Seamless tubes have no joints, so they are smooth. This smoothness helps stop blood clots in implants. Welded tubes cost less and work for many tools. But seamless tubes usually last longer inside the body.
Why does nitinol tubing cost more for medical devices?
Nitinol tubing uses pricey metals and needs special steps to make. It takes more time and skill to produce. The higher price comes from its special features. These features help medical devices work better and last longer.
Are there safety concerns with nitinol or stainless steel in medical implants?
Both materials follow strict safety rules for implants. Nitinol tubing can let out nickel, which may cause allergies for some people. Special surface treatments help lower this risk. Stainless steel is also safe for most medical tools.
See Also
Evaluating Tensile Strength Differences Between Nitinol And Stainless Steel
Tips For Choosing The Ideal Nitinol Tubing Supplier
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Modern Medical Uses
Discovering Various Uses Of Nitinol Tubing In Healthcare Equipment
A Guide To Manufacturing Nitinol Tubing For Medical Purposes

