Top Reasons Nitinol Tubing Leads in Medical Device Innovation
Nitinol tubing medical device components are the top choice for medical devices due to their exceptional flexibility, usefulness, and safety for the body. Surgeons rely on nitinol tubing medical device components in critical surgeries, especially for self-expanding stents that strengthen blood vessels and enhance patient safety. Hospitals also use nitinol tubing medical device components in Simon vena cava filters, which trap blood clots and reduce the risk of embolism. These nitinol tubing medical device components feature superelasticity and shape memory, allowing devices to conform inside the body without wearing out or rusting easily. Additionally, nitinol tubing medical device components are compatible with MRI tools, enabling doctors to obtain clearer images and perform procedures with greater precision.
Key Takeaways
Nitinol tubing has special superelasticity and shape memory. This lets medical devices bend and twist. They can go back to their original shape inside the body.
Nitinol tubing is very safe for long-term implants. It does not cause many allergic reactions. It does not break down easily.
Nitinol tubing helps with minimally invasive surgeries. It allows smaller and flexible devices. These devices move easily in tight spaces. Patients recover faster and have less harm.
Advanced manufacturing lets nitinol tubing fit each patient. This helps make smarter and more exact medical devices. It leads to better treatment results.
Nitinol tubing is strong and lasts a long time. It helps medical implants work well for years. This is good for heart, brain, and bone care. There are fewer problems for patients.
Nitinol Tubing Medical Device Components
Superelasticity
Superelasticity makes nitinol tubing different from other materials. This special property lets nitinol tubing bend and twist much more than stainless steel or cobalt-chromium alloys. Doctors use superelastic nitinol tubing in catheters and guidewires. These devices can move through tight, curvy blood vessels without breaking or folding. The tubing goes back to its original shape after each use. This helps doctors reach hard-to-get places in the body safely.
A table below shows how nitinol tubing compares to other materials:
Material | Key Mechanical Properties | Unique Advantages in Medical Devices |
|---|---|---|
Nitinol | Shape memory effect; superelasticity (pseudoelasticity); phase transformation between austenite and martensite phases | Can undergo large deformation and return to original shape without permanent deformation; excellent flexibility and kink resistance; ideal for self-expanding stents and dynamic anatomical environments |
Stainless Steel | High tensile strength; corrosion resistance | Good mechanical strength; limited flexibility; may induce more inflammatory response |
Cobalt-Chromium | Superior tensile strength; fatigue resistance; radiopacity | Allows thinner strut designs; better flexibility than stainless steel; lacks superelastic and shape memory properties |
Superelastic nitinol tubing can stretch and bend a lot before it gets damaged. It can handle more strain than most metals. This means nitinol tubing medical device components can be bent and stretched many times during use. The special phase change between austenite and martensite gives nitinol tubing its superelasticity. This makes it great for use inside the moving human body.
Shape Memory
Shape memory helps nitinol tubing medical device components work well in hospitals. When nitinol tubing gets warm from the body, it goes back to its original shape. This is important for devices like self-expanding stents and vena cava filters. These devices need to change shape when placed in the body, then return to their set shape to work right.
Nitinol tubing can recover a lot of strain, up to about 4.16%. Superelastic strains can reach almost 7%. Usually, nitinol tubing medical device components recover about 70-75% of strain after being bent. This high recovery rate means devices made from medical grade nitinol tubing work safely and reliably inside the body. The shape memory comes from phase changes between martensite and austenite, which happen near body temperature. This makes nitinol tubing a top choice for devices that must move with the body and return to their shape.
Tip: Shape memory lets nitinol tubing remember complex shapes. This helps doctors use advanced medical devices that open up exactly where needed.
Biocompatibility & Corrosion Resistance
Biocompatibility and corrosion resistance are very important for medical devices. Nitinol tubing medical device components meet strict safety rules. Medical grade nitinol tubing does not rust from body fluids. This helps stop device failure and lowers the chance of bad reactions. The smooth surface of superelastic nitinol tubing also makes it easier to put in and take out devices without hurting tissue.
Nitinol tubing can be bent many times without breaking. Studies show nitinol tubing medical device components can handle up to 8% recoverable strain because of martensitic transformations. Special processing, like Electron Beam Refining, makes medical grade nitinol tubing last longer inside the body. Microstructural analysis shows stable grain structures and low dislocation densities even after millions of uses. This proves nitinol tubing is strong enough for tough medical jobs.
Nitinol tubing medical device components stay safe inside the body for a long time.
Superelastic nitinol tubing resists fatigue, so it works well for implants that move a lot.
Medical grade nitinol tubing helps make safer and better medical devices for people everywhere.
Device Performance
Flexibility & Strength
Nitinol tubing is very flexible and strong. Doctors and engineers pick nitinol tubing for tools that need to bend and twist. These tools move through small spaces in the body. Superelasticity lets nitinol tubing bend many times without breaking. This stops kinks and helps the tubing keep its shape. The stress-strain curve for nitinol shows a flat part. This means the tubing pushes with the same force, even when stretched. Nitinol tubing works well for catheters and guidewires. These must travel through tricky blood vessels.
Shape memory is also important for nitinol tubing. When nitinol tubing gets warm, it goes back to its first shape. This happens even after bending or stretching. Medical-grade nitinol tubing can recover over 90% of its shape. It can handle up to 10% strain. Stainless steel only handles about 1% strain. Devices made from nitinol tubing stay flexible and strong. They work well during tough procedures.
Nitinol tubing’s flexibility helps doctors reach hard places in the body. This makes treatments safer and better for patients.
Minimally Invasive Compatibility
Nitinol tubing changed how doctors do minimally invasive surgery. Its special features help make smaller and more exact medical devices. Surgeons use nitinol tubing in stents, guidewires, and robot tools. These can move through tricky body paths with little harm. This means less injury and faster healing.
Nitinol tubing’s flexibility lets devices move through tight curves safely.
Superelasticity keeps devices from losing shape or kinking.
Nitinol guidewires and catheters work better than old materials.
Fatigue resistance means nitinol tubing lasts longer with lots of use.
Biocompatibility lowers the chance of bad reactions for patients.
Custom nitinol tubing helps make devices that fit different body shapes.
A table shows how nitinol tubing beats old materials in surgery:
Metric / Outcome | Nitinol Tubing Data | Relevance to Minimally Invasive Procedures |
|---|---|---|
Technical Success Rate | 97% success in 70 of 72 patients | High reliability in clinical use |
Shape Recovery Strain | Approximately 4.16% | Tools return to original shape after bending |
Superelastic Strain | About 7% | Significant bending without permanent damage |
Aneurysm Occlusion at 12 Months | 96.7% (29 of 30 patients) | Long-term effectiveness |
Lower Rejection Rate | 30% less than traditional materials | Improved biocompatibility and safety |
Reduced Operative Time | ~19.6 min vs. ~48.8 min for traditional | Faster procedures, less patient exposure |
Smaller Incision Size | ~3.8 cm vs. ~8.7 cm for traditional | Enables minimally invasive techniques |
Fatigue Life and Durability | 2-3x longer at 10^7 cycles | Greater longevity and reliability |
Patient Recovery Improvement | 20% faster recovery times | Faster healing and reduced hospital stays |
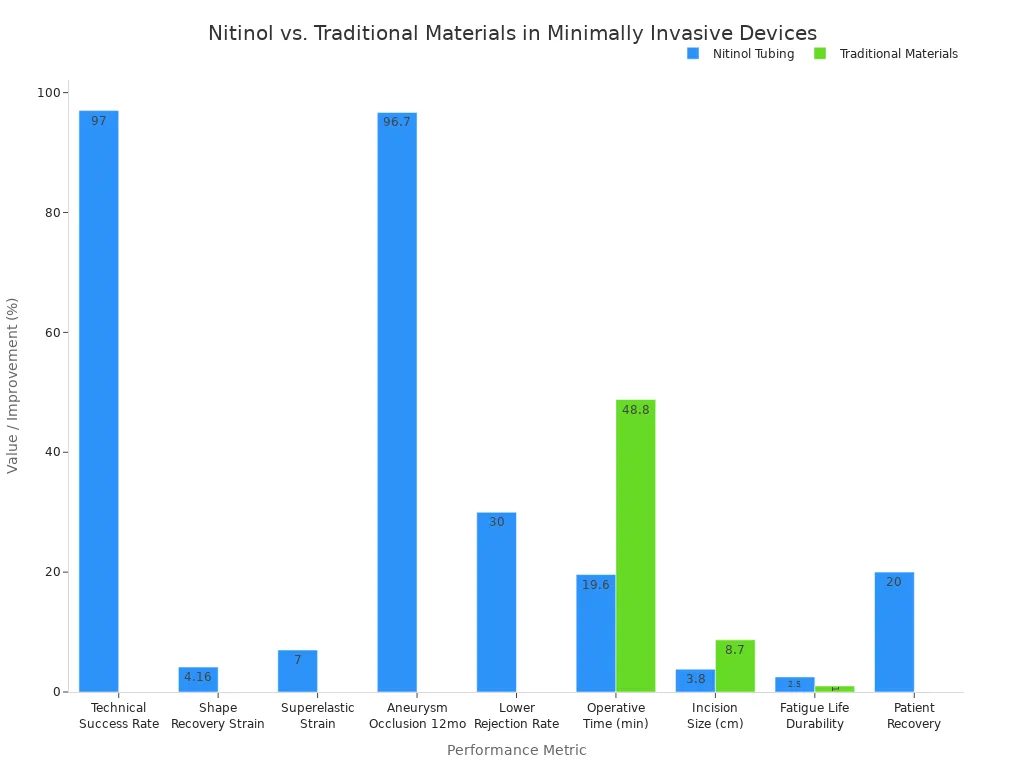
Nitinol tubing lets doctors make smaller cuts and finish surgery faster. Patients heal quicker and have less risk. Devices made from nitinol tubing help doctors do hard jobs with more accuracy.
Durability in Implants
Durability matters for implants that stay in the body for years. Nitinol tubing is very strong and lasts a long time. Studies show nitinol tubing implants last two to three times longer than other materials. Superelasticity lets nitinol tubing handle millions of bends without breaking. This is why doctors use it for stents, heart valves, and other permanent devices.
Clinical studies prove nitinol tubing is good for implants:
Trials show a 98% success rate and 12% fewer problems than old materials.
Patients heal about 20% faster with nitinol tubing implants.
Special surface treatments make nitinol tubing safer for long-term use.
Nitinol implants cause 30% fewer rejection cases, so patients feel better.
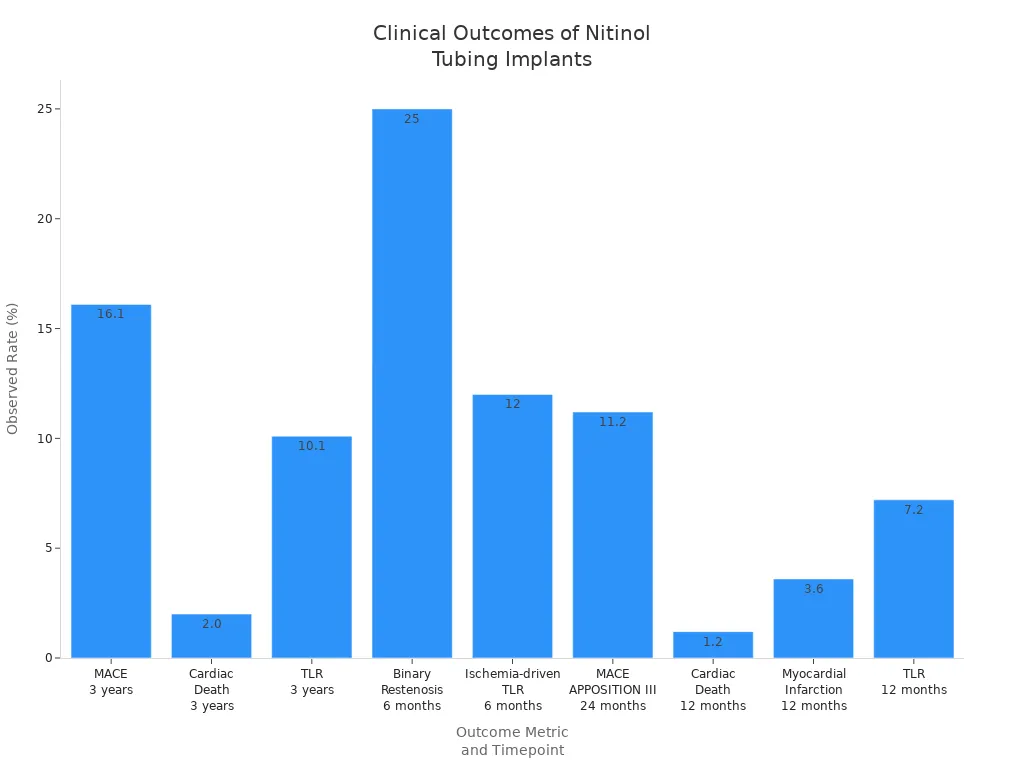
A table shows the good results of nitinol tubing:
Clinical Outcome Metric | Observed Result / Description |
|---|---|
Major Adverse Cardiac Event (MACE) Rate | 16.1% at 3 years follow-up |
Cardiac Death Rate | 2.0% at 3 years follow-up |
Target Lesion Revascularization (TLR) | 10.1% at 3 years follow-up |
In-stent Late Loss (12 months) | 0.21 mm (main branch), 0.58 mm (side branch) |
Cardiac Death (Sideguard I & II studies) | 1.2% at 12 months |
Myocardial Infarction (Sideguard I & II) | 3.6% at 12 months |
TLR (Sideguard I & II studies) | 7.2% at 12 months |
Endothelialization | Complete within 7 days in animal studies |
Procedural Success Rates (APPOSITION I) | Technical: 100%, Device: 96%, Procedural: 96% |
Stent Expansion (3 days post-implant) | 18% increase, complete apposition to vessel wall |
In-stent Late Lumen Loss (6 months) | 0.71 ± 0.71 mm |
Binary Restenosis (6 months) | 25% |
Ischemia-driven TLR (6 months) | 12% |
Malapposed Struts (APPOSITION II) | 0.58% with nitinol stent vs. 5.46% with conventional BMS (p<.001) |
MACE Rate (APPOSITION III) | 11.2% at 24 months |
Late Lumen Loss (APPOSITION IV) | Lower with nitinol stent compared to R-ZES at 4 and 9 months |
Nitinol tubing helps medical devices stay safe and work well for years. Its strength means fewer problems, quicker healing, and better results for patients.
Innovations in Nitinol Tubing

Precision Manufacturing
Manufacturers use special steps to make nitinol tubing for medical devices. They melt metals together, shape them, heat them, and finish the surface. These steps help nitinol tubing work well and be safe for the body. They check the size and follow ISO 13485 rules to make sure nitinol tubing is safe for medical use. Surface treatments like electropolishing and plasma coating help stop nickel from coming out. This lowers allergic reactions and helps devices last longer.
AI and data tools help engineers design stents for each patient. These tools also help guess how well devices will work. Using less energy, like induction heating, helps the planet and saves money. Factories reuse extra nitinol tubing so there is less waste. Scientists and engineers work together to make nitinol tubing better and faster.
Advancement Area | Description | Impact on Nitinol Tubing Production |
|---|---|---|
Multi-stage Production Process | Alloying, ingot formation, forming, heat treatment, surface finishing | Optimizes mechanical properties, biocompatibility, corrosion resistance |
Advanced Quality Control | Dimensional accuracy testing, ISO 13485 compliance | Ensures reliability and safety |
Surface Treatments | Electropolishing, plasma coating, advanced coatings | Enhances biocompatibility, reduces allergic reactions, extends product lifespan |
AI-driven Design and Data Methods | AI algorithms for patient-specific stent designs, predictive modeling | Improves customization and precision |
Energy-efficient Production | Induction heating, optimized machinery | Precise temperature control, lower environmental impact |
Closed-loop Recycling Systems | Recovery and reuse of excess materials | Minimizes waste, maintains material integrity |
Collaborative Innovation | Joint product development, knowledge sharing | Improves shape memory and superelasticity |
Miniaturization and Robotics | Ultra-thin, flexible tubing, integration with robotic neurosurgery tools | Enables less invasive procedures, improved accuracy |
Complex Shapes
Nitinol tubing helps make medical devices with tricky shapes. Engineers design guidewires and catheters that bend easily and do not kink. This lets nitinol tubing move through twisty body parts during surgery. Nitinol tubing is safe for the body, so it works well for gentle surgeries. It stays strong even when used in tough spots.
Nitinol tubing bends and goes back to its shape, which helps doctors do careful surgery.
Its flexibility lets one tool do many jobs, so doctors change tools less.
Devices made from nitinol tubing can move in tight spaces, which means less harm to tissue and better results.
Self-expanding stents made from nitinol tubing squeeze down to go in and then open up to fit blood vessels, which helps protect them.
Nitinol tubing does not break easily and stays flexible, so it works well in heart, bone, and brain surgeries.
It can change shape when heated, so smart implants can move when the body gets warm or when doctors use special tools.
Smart Device Integration
New nitinol tubing technology helps make smart medical devices. Some catheters use nitinol tubing in certain spots to bend just right. Robotic surgery tools use nitinol tubing to stay flexible at joints. Orthopedic tools use nitinol tubing to turn around curves in the body.
Medical devices like ablation catheters, stent retrievers, and clips use nitinol tubing for its special bending and shape memory. Some catheters open up inside the heart and work as electrodes. EdgeTech’s puzzle-cut joining helps nitinol tubing fit into devices and makes them stronger. Nitinol tubing is easy to see on scans and does not rust, which helps doctors during surgery.
Tip: Smart medical devices with nitinol tubing can fit the patient’s body and change when needed, which helps patients get better care.
Nitinol Tubing Applications
Cardiovascular Devices
Nitinol tubing is very important in heart and blood vessel devices. Hospitals use nitinol tubing in stents, guidewires, and heart valve frames. Each year, doctors put in over 1.5 million stents made with nitinol tubing around the world. More than 80% of self-expanding stents need nitinol tubing for their special bending and shape memory. Surgeons like nitinol tubing because it lets stents squeeze small to go in and then open up inside blood vessels. Guidewires made from nitinol tubing help doctors do over 1.2 million heart procedures in the U.S. every year. Nitinol tubing gives flexibility, strength, and works well with the body. This helps patients get better and have fewer problems.
Application Area | Evidence Detail |
|---|---|
Medical Devices Market Share | Nitinol tubing makes up most of the nitinol tubing market, mainly for medical use. |
Cardiovascular Stents | Over 1.5 million stents using nitinol tubing are put in each year worldwide. |
Over 80% of self-expanding stents use nitinol tubing for its special properties. | |
Guidewires | In 2023, the U.S. did over 1.2 million heart procedures using nitinol guidewires. |
Neurovascular & Orthopedic Uses
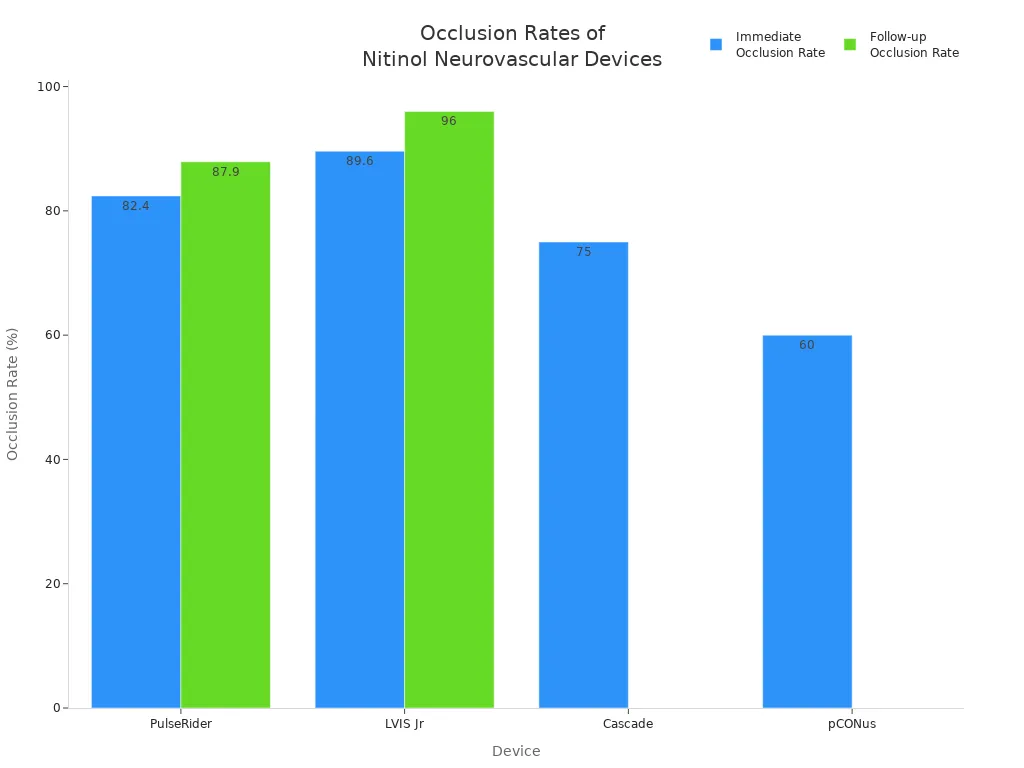
Doctors use nitinol tubing in brain and bone devices because of its special features. Nitinol tubing helps make tools for treating brain blood clots, aneurysms, and spine problems. Studies show nitinol tubing devices work well almost 97% of the time and close off blood flow in over 96% of cases after a year. Nitinol tubing lowers problems and helps people heal faster. In bone surgery, nitinol staples and spine parts fit bones well and help people recover quickly. Special nitinol implants approved by the FDA help bones heal and are less likely to be rejected. Nitinol tubing’s shape memory and toughness make it great for hard surgeries.
Device | Sample Size | Technical Success Rate | Complication Rate | Occlusion Rate (Immediate / Follow-up) | Notes on Catheter Failure or Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PulseRider | 34, 63, 54 aneurysms | ~96% | 3 major problems in 54 cases | 82.4% right away; 87.9% at 6 months | No catheter failure; few problems |
LVIS Jr | 30 patients | N/A | N/A | 89.6% right away; 96% at 5.2 months | Smaller catheter, easier to reach vessels |
Cascade | 12 aneurysms | N/A | None reported | 75% fully closed off | No catheter failure reported |
pCONus | 203 aneurysms | 100% | 7% had problems; 0% died | 60% fully closed; 14% needed more treatment | No catheter failure; no bleeding problems |
Emerging Medical Applications
Scientists keep finding new ways to use nitinol tubing in medicine. Nitinol tubing helps make custom devices for each patient using fast design and special shaping. Doctors use nitinol tubing in stomach stents, robot surgery tools, and smart devices with sensors. These devices can fit tricky body shapes and give doctors live updates during surgery. Nitinol tubing’s shape memory, bending ability, and safety for the body help new surgeries and personal treatments. Bone tools, like Ti-Ni patella concentrators, use nitinol tubing’s strength and special coatings. Nitinol tubing gives doctors more ways to treat patients and helps people heal better.
Emerging Medical Application | Description and Supporting Evidence | Key Properties and Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Cardiovascular Devices | Used in stents and heart valve frames that change shape to fit blood flow; stents squeeze to go in and open up inside; heart valve frames last through many heartbeats. Studies show little tissue reaction and no rust. | Shape memory, superelasticity, biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, strength. Helps patients and lowers surgeries. |
Catheters and Guidewires | Needed for less invasive surgeries; bendy and strong to move through tricky body parts; help doctors work faster and safer. Studies show shorter surgery times. | Flexibility, superelasticity, easy to move. Makes surgeries safer and more successful. |
Orthopedic Solutions | Used to fix broken bones and joints; shape memory helps fit bones; examples are Ti-Ni patella concentrators and wrist bone repairs with faster healing; coatings stop rust and help bone join. | Shape memory, biocompatibility, strength, special coating. Helps bones heal faster and lowers problems. |
Neurovascular and Gastrointestinal Treatments | Self-expanding stents for brain and stomach problems; devices fit tough body shapes; studies show they work well for wide-necked aneurysms; examples include Neuroform™ Microdelivery Stent System. | Shape memory, superelasticity, biocompatibility, corrosion resistance. Gives more ways to treat hard cases. |
Customization for Patient-specific Solutions | Lets doctors make devices that fit each person using fast design and special shaping; fits better, works better, feels better, and lasts longer; used in heart, bone, and brain care; more people want these new devices. | Shape memory, superelasticity, fits different people. Makes medicine more personal and helps patients heal. |
Integration of Smart Technologies | Putting sensors and smart tech in nitinol tubing gives doctors live updates during surgery; examples are force sensors in robot arms and smart tools; helps doctors be more exact and safe. | Live feedback, fits different needs, better control. Makes surgery safer and devices work better. |
Safety & Customization
Long-Term Safety
Nitinol tubing is very safe for medical devices. Studies over ten years show few problems with nitinol tubing implants. ASTM F2063 nitinol tubing works well in the body and lasts long. Medical grade nitinol tubing passes tough safety tests for body reactions. It does not cause cell damage or skin problems. Fatigue tests show nitinol tubing can handle millions of heartbeats without breaking. Special cleaning steps, like boiling in water, lower nickel release to 75 ppb. This makes nitinol tubing resist rust and keeps it safe. ASTM F2063 certification means nitinol tubing meets strict rules for chemicals and strength. In brain surgeries, nitinol tubing works well 97% of the time. It closes off 89% of aneurysms after 18 months. These facts show nitinol tubing is safe and works well for heart and bone implants.
Nitinol tubing does not rust or wear out, so implants stay safe for years.
Outside checks and tracking make sure every batch is safe.
Patient-Specific Solutions
Nitinol tubing can fit each patient’s body. Its superelasticity and shape memory help implants squeeze small and then open up where needed. Doctors use crimping to join nitinol tubing with other parts for flexible tools. Nitinol tubing bends to fit the body and goes back to its shape after cleaning. This means doctors need fewer types of tools. Superelastic nitinol tubing moves through twisty paths and helps soft tools work better. Thin nitinol tubes come in exact sizes to match body parts. Stents made from nitinol tubing squeeze down for delivery and open up inside vessels. Custom nitinol tubing can be up to 6000mm long for many uses. Its bendiness, strength, and toughness let it move with the body and stay safe.
Note: Nitinol tubing helps make custom devices for each patient. This makes people feel better and helps them heal.
Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
Companies now make nitinol tubing in greener ways. They reuse nitinol from old devices to cut waste and save resources. Green methods use less energy and make less trash. New ways like 3D printing and laser cutting help use less material. Robots and smart computers check for mistakes and keep nitinol tubing safe. Top makers use clean energy, lower pollution, and recycle water and materials. They also pick suppliers who follow fair rules. These steps help protect the planet and show care for good nitinol tubing and the environment.
Regulatory Framework | Description |
|---|---|
ISO and ASTM Standards | Set rules for nitinol tubing’s properties and safety. They make sure nitinol tubing is safe for medical use. |
FDA Compliance | Needs hard tests and checks to keep medical devices safe and reliable. |
Supplier Quality Assurance | Tracking systems follow nitinol tubing from start to finish. This helps keep it safe and easy to customize. |
Customization Techniques | Smart ways like laser cutting and shape-setting make nitinol tubing fit special devices and meet safety rules. |
Nitinol tubing helps make new medical devices because it has special features and can be used in many ways. Nitinol tubing has shape memory, superelasticity, and works well with the body. This makes nitinol tubing great for surgeries with small cuts and for implants that stay in the body a long time. Nitinol tubing is good for making advanced tools, custom devices, and smart technology.
The table below shows why nitinol tubing is used so much:
Key Factor | Impact on Medical Devices |
|---|---|
Shape memory | Lets devices change shape as needed |
Superelasticity | Makes devices bend and last longer |
Biocompatibility | Lowers the chance of problems |
Corrosion resistance | Keeps devices safe for many years |
Nitinol tubing is now used in more areas, like smart tools and robots. In the future, companies will make even purer nitinol tubing for better treatments. Doctors and engineers should think about nitinol tubing when making new medical devices. Nitinol tubing will keep helping patients and improve medical care.
Nitinol tubing makes devices work better and helps patients heal.
Nitinol tubing brings new ideas to heart, bone, and brain care.
Nitinol tubing lets doctors do safer and better surgeries everywhere.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing different from other metals in medical devices?
Nitinol tubing can bend a lot and still go back to its shape. These special features help devices move and not break. Doctors like nitinol tubing because it is flexible and strong for hard surgeries.
How does nitinol tubing improve patient safety?
Nitinol tubing does not rust and stays safe in the body. It works well with the body and does not cause many allergies. Hospitals use nitinol tubing for implants that last longer and have fewer problems.
Can nitinol tubing be customized for specific medical applications?
Engineers make nitinol tubing in many shapes and sizes. Custom nitinol tubing fits each patient’s needs. This helps doctors do careful work and get better results.
Tip: Custom nitinol tubing helps make heart and bone devices just for each patient.
Is nitinol tubing safe for long-term implants?
Studies show nitinol tubing stays strong and keeps its shape for years. Nitinol tubing passes hard safety checks. Patients have fewer problems and heal better with nitinol tubing implants.
What are the main uses of nitinol tubing in hospitals?
Doctors use nitinol tubing in stents, guidewires, and catheters. Nitinol tubing is also used in brain and bone devices. Its many uses help doctors do less invasive surgeries and use new medical tools.
Application Area | Example Devices |
|---|---|
Cardiovascular | Stents, guidewires |
Neurovascular | Embolization devices |
Orthopedic | Bone staples, implants |
See Also
Transforming Medical Devices Through Innovative Nitinol Tubing Use
Nitinol Tubing’s Impact On Progress In Medical Technology
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Cutting-Edge Medicine

