What Are the Medical Applications of Nitinol Tubing

Nitinol tubing plays a crucial role in medical applications due to its unique ability to bend and return to its original shape. This special alloy is not only flexible and strong but also biocompatible, making it safe for use inside the body. These qualities make Nitinol tubing ideal for advancing new medical technologies. In healthcare, Nitinol tubing medical applications include:
Cardiovascular treatments with self-expanding stents
Minimally invasive surgeries using guidewires and catheters
Orthopedic implants and surgical instruments
Precision neurosurgery involving microcatheters and stents
Research shows that incorporating Nitinol tubing in medical applications often leads to improved patient outcomes.
Key Takeaways
Nitinol tubing bends without breaking and goes back to its shape. This makes it great for medical devices that need to be strong and flexible. It is safe to use in the body because it does not rust. It also does not cause bad reactions if treated right. Doctors use nitinol tubing in many tools. These include heart stents, brain tools, bone implants, and dental tools. These devices help doctors take better care of patients. Nitinol tubing helps make smaller medical tools. These tools do not need big cuts, so patients heal faster and feel less pain. Its special features like superelasticity and shape memory help devices last longer. They also help devices work better inside the body.
Nitinol Tubing Overview
Nitinol Properties
Nitinol is a special material used in medical devices. It is made from nickel and titanium. This alloy has many helpful features for healthcare.
Shape memory means Nitinol goes back to its shape after bending.
Superelasticity lets it bend and stretch more than most metals. It does not break or stay bent.
Biocompatibility means Nitinol is safe inside the body. It does not cause bad reactions.
Corrosion resistance helps Nitinol avoid rust and damage. This is important for things that stay in the body.
Kink resistance means Nitinol tubes do not bend sharply. They keep their shape during use.
MRI compatibility means Nitinol does not mess up scans. It is good for patients who need imaging.
These features help companies make stents, catheters, and braces. Nitinol wire, coils, and sheets also use these benefits. Superelastic Nitinol lets devices move with the body. This lowers the chance of harm or pain.
Note: Nitinol is safe for the body if the surface is treated right. Good finishing stops nickel from coming out and keeps patients safe.
Manufacturing for Medical Use
Making Nitinol tubes for medicine needs careful steps. First, workers control the nickel and titanium mix. It is usually 55% nickel and 45% titanium. Special tools check the mix to make sure it is right. Vacuum arc melting makes the alloy pure and even.
After melting, the tube is shaped by hot working, extrusion, and cold drawing. These steps make the tube strong and smooth. Heat treatment at set temperatures gives Nitinol its shape memory. Surface treatments like passivation and electropolishing stop rust and make it smoother.
Each tube is tested with ultrasonic and eddy current tools. Workers check wall thickness, surface, and size with exact instruments. Rules like ISO 13485:2016 and ASTM F2063 guide the work. Companies keep records and track each tube from start to finish. These steps make sure Nitinol tubes are safe and work well in medical devices.
Nitinol Tubing Medical Applications
Nitinol tubing is used in many areas of healthcare. Doctors and engineers put nitinol tube in devices for the heart, brain, and blood vessels. Nitinol has special features like shape memory and superelasticity. These make it great for small heart devices and new brain treatments. Here are the main ways nitinol tube helps patients.
Cardiovascular Devices
Nitinol tubing is very important in heart devices. It is used in stents, guidewires, and catheters. Doctors use nitinol stents to open blocked arteries. The stent can squeeze small to go in and then gets bigger inside the vessel. This lets blood flow again and keeps the artery open.
Property/Feature | How It Improves Cardiovascular Devices |
|---|---|
Lets stents and guidewires bend and return to shape, adapting to vessel movement without damage. | |
Shape Memory | Allows devices to compress for insertion and expand to fit vessels, improving placement accuracy. |
Flexibility | Helps guidewires and catheters move through winding blood vessels, giving doctors better control. |
Durability | Keeps stents strong under constant blood flow, supporting long-term use. |
Biocompatibility | Makes nitinol safe for implants, reducing bad reactions in the body. |
Corrosion Resistance | Stops rust and damage, making devices last longer inside the body. |
Nitinol tubing is also used in heart catheters for treatments. These catheters use nitinol tube because it bends but does not kink. This helps doctors reach tricky spots without hurting vessels. Studies show nitinol stents lower the chance of arteries getting blocked again. TASC II guidelines say nitinol stents are good for some artery diseases. Doctors pick nitinol stents when balloon angioplasty does not work well. Even though problems like restenosis and stent breaks can happen, nitinol tubing keeps helping patients get better.
Neurovascular Devices
Neurovascular devices treat problems in the brain and spine. Nitinol tubing is used in microcatheters, stents, and coils for these areas. Nitinol’s superelasticity and shape memory help these tools move through tiny, twisty brain vessels. The nitinol tube bends and stretches but always goes back to its shape. This keeps the device and vessel safe.
Nitinol tubing lets catheters reach deep into the brain.
Electropolishing makes the tube smooth and safe for blood.
High fatigue resistance means the device bends a lot without breaking.
Studies show nitinol neurovascular devices work very well. For example, they have a 98% success rate and a 98.6% patency rate. Problems and deaths are rare, so these devices are safe for patients.
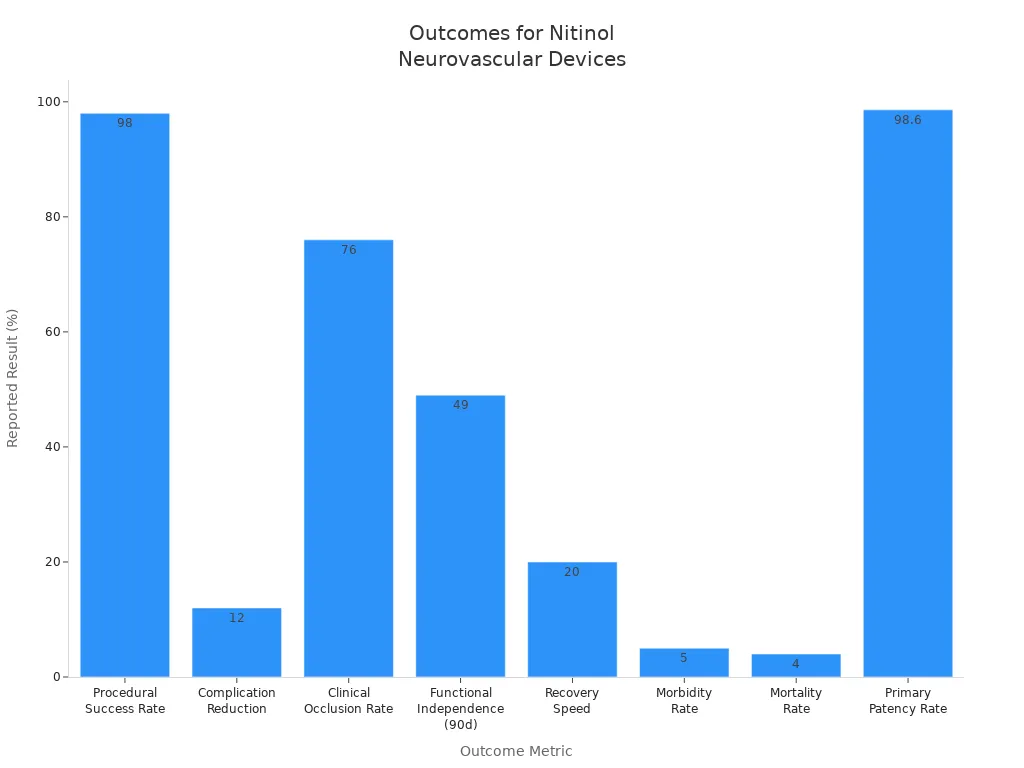
Doctors like nitinol tubing for new brain treatments because it is flexible, safe, and lasts a long time.
Ablation and Denervation Tools
Ablation and denervation tools help with heart rhythm and high blood pressure. Nitinol tubing is used in catheters that send energy to certain tissues. In cardiac ablation, nitinol tube is the main part of catheters that sense force and act as electrodes. Superelasticity and shape memory let the catheter get bigger inside the heart and fit its shape. This makes sure the energy goes to the right spot.
Medtronic’s Symplicity Spyral system uses a nitinol catheter for kidney denervation. The catheter gets bigger in the artery to send radiofrequency energy. This helps lower blood pressure by treating nerves. Doctors say these nitinol catheters are easy to use and safe, with few problems.
Nitinol tubing also helps ablation catheters handle heat well. The tube spreads heat evenly, making the treatment safer. Electropolishing keeps the tube strong and stops breaks. These things make nitinol tubing in ablation and denervation tools both safe and reliable.
Clot Removal Devices
Clot removal devices help by clearing blocked blood vessels. Nitinol tubing is used in catheters and baskets for this job. Nitinol tube bends and remembers its shape, so it can move through twisty vessels to reach clots. When it gets there, the device can open up to grab and remove the clot.
Electropolishing makes nitinol tubing smooth and lowers the risk of new clots. It also keeps nickel from leaking out, so allergic reactions are rare. Nitinol tube is strong and does not rust, so it works well inside the body.
Studies show clot removal devices with nitinol tubing work 97% of the time and remove clots 83% of the time. They are safe for the body and last through many uses. Doctors trust nitinol tubing for clot removal because it is safe, works well, and helps patients heal.
High technical success rates
Low complication and death rates
Strong, flexible, and safe for blood-contacting uses
Nitinol tubing is being used in more ways as doctors and engineers find new uses for this amazing material in medical devices.
Nitinol Tubes for Medical Devices

Orthopedic Implants
Doctors use nitinol tubes in many bone and joint implants. These implants help fix broken bones and joints. Nitinol tube is used in bone staples, fracture fixers, and surgery tools. Superelasticity lets the implant bend and take pressure without breaking. Shape memory helps the implant push on bones as they heal. This makes bones heal faster and stronger.
Nitinol implants give steady pressure while bones heal.
Compression staples made of nitinol are quicker to use than screws.
Nitinol bone plates bend with the body and lower stress.
Spinal implants made with nitinol can squeeze and stretch, which helps during surgery.
Shape memory keeps bones together and helps them heal.
Superelasticity lets implants bend and snap back, good for moving body parts.
Biocompatibility and corrosion resistance keep the implant safe and strong.
Nitinol implants help doctors do surgery with smaller cuts and faster healing.
Studies show nitinol implants lower problems and help bones heal. Surgeons like these implants because they are safe and flexible.
Dental Devices
Dentists use nitinol tube in tools for teeth and gums. Shape memory and superelasticity let dental tools bend and go back to shape. This helps dentists clean curved root canals without breaking tools.
Evidence Aspect | Findings Supporting Nitinol Use in Dental Devices |
|---|---|
Biocompatibility and Safety | Nitinol is safe for people and helps cells grow. |
Mechanical Properties | Nitinol bends more than other metals, so tools break less. |
Heat Treatment Benefits | Heat-treated nitinol files last longer and work better in curves. |
Corrosion Resistance | Nitinol does not rust, so tools stay strong in the mouth. |
Clinical Outcomes | Nitinol tools make treatments faster and help teeth heal. |
Dentist Preference | Dentists pick nitinol for its bendiness and safety. |
Nitinol tubes in dental tools make care safer, quicker, and easier for patients.
Neuromodulation and Endoscopy
Nitinol tube is important in neuromodulation and endoscopy. In neuromodulation, doctors use nitinol implants to help the brain and spine. These implants must bend and last a long time. Nitinol’s flexibility and strength make it perfect for this.
In endoscopy, nitinol tubing helps make tools that can bend inside the body. These tools help doctors see and treat hard-to-reach places. Robotic surgery uses nitinol tubes to move tiny tools. This makes surgery more exact and less painful.
Superelasticity, biocompatibility, and MRI compatibility help doctors use these devices safely. New ways to join metals also save money by mixing nitinol with other metals. This keeps devices bendy and not too expensive.
Benefits in Medicine
Flexibility and Kink Resistance
Nitinol tubing is very bendy and does not kink. These features are important for medical tools that move inside the body. Superelasticity and shape memory let nitinol bend a lot without breaking. When it bends, it goes back to its shape. This makes it strong and accurate for doctors.
The nickel-titanium mix and heat make it tough and stop kinks.
Laser cutting, heat, and polishing make the tubing stronger and safer.
Sometimes, steel or nylon is added to make it even tougher.
Kink resistance helps devices last longer and work better for patients.
Flexible tubing lets doctors use new designs for tight or twisty spaces, especially in small surgeries.
When compared to stainless steel tubing, nitinol works better:
Property / Feature | Nitinol Tubing | Stainless Steel Tubing |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility | Very flexible, returns to shape | Not as flexible, stays bent |
Elastic Deformation Capacity | Up to 10% strain | About 1% strain |
Kink Resistance | Much better | Not as good |
Fatigue Resistance | Very high | Medium to low |
Biocompatibility and Safety
Safety is very important for anything used in the body. Nitinol tubing meets strict rules for being safe inside people. It does not hurt tissues or cause bad reactions if treated right. Rules say it must be tested for allergies and rust. Electropolishing and coatings help stop nickel from leaking out, so it is safer for long use.
Studies show nitinol tubing works well in stents and implants. These studies show few allergies or problems. Most people do not have issues, even if they are sensitive to nickel. Careful making and testing keep risks low. Doctors trust nitinol tubing because it is safe and works well.
Note: Regular testing and surface treatments help keep nitinol tubing safe for people.
Device Miniaturization
Nitinol tubing helps make smaller and better medical tools. Its special features allow for thin, bendy tubes that fit in tiny spaces. This helps doctors do less invasive treatments and patients heal faster.
Small stents can reach tiny blood vessels and nerves with less harm.
Smaller tools mean less pain and quicker healing for people.
Bendy, strong tubing helps devices last longer and work better.
Custom shapes and sizes help doctors fix problems more exactly.
New laser micromachining lets makers make nitinol tubing even smaller but still strong. This has led to new tools like robot arms for lung surgery, tiny endoscopes for ear surgery, and MRI-safe catheters. These new tools help doctors do hard jobs with less risk and better results.
Nitinol tubing has changed how doctors use medical devices. They use it in self-expanding stents, flexible guidewires, and tools for fixing bones. New ideas include robot tools and very thin tubing for careful treatments.
Nitinol devices help doctors make smaller cuts. This means people heal faster and have fewer problems.
Experts think nitinol will be used even more. Better surface treatments, custom shapes, and greener ways to make it will help keep patients safe and make devices easier to get.
Scientists are working to make nitinol tubing safer and stronger. This helps doctors treat people with less risk and better results.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing different from other metals in medical devices?
Nitinol tubing can bend and then go back to its shape. Most other metals cannot do this. Doctors like nitinol because it is bendy, strong, and safe for people.
Is nitinol tubing safe for people with nickel allergies?
Most people do not have problems with nitinol. Special coatings and polishing stop nickel from coming out. Doctors check nitinol devices to make sure they are safe for people with allergies.
Can nitinol tubing be used in MRI scans?
Nitinol tubing works well during MRI scans. It does not mess up the pictures. Doctors often pick nitinol for devices that need to be safe in MRI.
How long do nitinol medical devices last inside the body?
Device Type | Typical Lifespan |
|---|---|
Stents | Several years |
Implants | Many years |
Catheters | Single use |
Nitinol devices last a long time because they do not rust or break easily.
See Also
Discovering How Nitinol Tubing Enhances Healthcare Equipment
Understanding Nitinol Tubing's Impact On Medical Innovations
Reasons Nitinol Tubing Is Essential For Modern Medicine
The Process Behind Manufacturing Nitinol Tubing For Medicine
Ways Nitinol Tubing Is Transforming Medical Device Technology

