What Are the Medical Uses of Nitinol Tubing
Nitinol tubing medical applications are widespread in various medical devices. These include self-expanding stents, guidewires, catheters, heart valves, as well as neurovascular and orthopedic implants. Additionally, nitinol tubing is used in dental and endoscopic devices. The unique properties of nitinol, such as superelasticity, shape memory, flexibility, and strength, make it ideal for these medical applications.
The nitinol market is expanding globally, with stents and catheters being the most commonly used devices in minimally invasive surgeries. The table below highlights common medical devices that utilize nitinol tubing:
Medical Device Type | Usage Insight |
|---|---|
Self-expanding stents | Primarily used for treating peripheral artery disease |
Guidewires | A primary application of nitinol tubing |
Catheters | Increasingly popular in various medical devices |
Heart valves | Employed in advanced heart treatment procedures |
Key Takeaways
Nitinol tubing is used in many medical devices. These include stents, guidewires, catheters, heart valves, and implants. It is strong and flexible. It is also safe for the body.
Nitinol tubing has special features. It can bend and return to its shape. This helps make surgeries less invasive. Patients can heal faster.
Nitinol tubing does not rust. It has a titanium oxide layer that protects it. This layer lowers allergy risks. It is good for long-term implants.
Devices made from nitinol tubing last longer. They work better than devices made from other metals. This helps patients get better results. It also means fewer repeat surgeries.
Nitinol tubing is made with strict controls. Quality checks keep it safe. Doctors trust these devices for important treatments.
Nitinol Tubing Overview
Unique Properties
Nitinol tubing is special in medicine because of its unique features. This nickel-titanium alloy is both strong and flexible. At room temperature, nitinol tubing has a tensile strength of about 500 MPa. It can even reach up to 900 MPa. Nitinol tubing can bend or stretch and then go back to its original shape. This is called superelasticity and shape memory. These features help stents and catheters move through tight spaces in the body.
Nitinol tubing does not break easily, even if it bends many times. This makes it good for implants that stay in the body for a long time. There is a titanium oxide layer on the surface of nitinol tubing. This layer keeps it safe in the body and stops it from rusting. It also helps stop nickel ions from leaking out, which lowers the chance of allergies. Special finishing methods like electropolishing make nitinol tubing even safer and stronger.
Note: Studies and tests show that nitinol’s superelasticity and biocompatibility are very important. These features help surgeries go well and make devices last longer.
Why Nitinol Is Used
Medical device makers pick nitinol for many new devices. Its superelasticity and shape memory are much better than stainless steel or titanium alloys. Nitinol tubing can bend and return to its shape after strains between 5% and 8%. Other metals cannot do this as well. This means nitinol devices can flex more without breaking.
Nitinol tubing is also more flexible than stainless steel. This makes it more comfortable for patients. It can be made with very exact shapes and sizes. This helps make good guidewires, stents, and drug-eluting catheters. Making nitinol tubing uses special steps like laser cutting and heat treatment. These steps help nitinol tubing meet strict medical rules.
Property | Nitinol (Nickel-Titanium Alloy) | Stainless Steel | Titanium Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|
Superelasticity | Excellent | Poor | Poor |
Shape Memory | Excellent | None | None |
Flexibility | High | Moderate | Moderate |
Fatigue Resistance | High | Moderate | Moderate |
Biocompatibility | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
Nitinol tubing is flexible, strong, and safe. This is why it is used in so many medical devices.
Nitinol Tubing Medical Applications

Cardiovascular Devices
Nitinol tubing is important in heart care. Doctors use it to make stents, guidewires, catheters, and heart valve frames. These tools help fix blocked arteries and repair heart valves. They also help blood flow better. Nitinol’s superelasticity and shape memory let these devices fit inside small blood vessels. They expand when they are in place. This makes nitinol tubing great for heart devices that need small cuts.
The table below shows how nitinol tubing helps different heart implants:
Cardiovascular Device | Nitinol Properties Utilized | Reported Clinical Outcomes and Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Stents | Flexibility, shape memory, durability, biocompatibility | Better blood flow, keeps vessels open, moves with vessels, lasts long, lowers health risks |
Guidewires | Superelasticity, shape memory | Moves easily through tricky blood vessels, gives good control, hurts tissue less, helps doctors be more accurate |
Heart Valve Frames | Strength, shape memory | Easy to squeeze for putting in, expands to fit, handles heart movement and pressure, helps patients heal faster |
Occlusion Devices | Shape memory, superelasticity, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility | Treats aneurysms and vessel problems with small cuts, stays in place, fewer problems, better healing |
Nitinol tubing in stents and guidewires has many benefits over stainless steel or cobalt-chromium:
Nitinol stents bend and go back to their shape. They fit vessel curves and handle lots of stress.
The tubing does not rust and is safe for the body. This lowers swelling and blood clot risks.
Tests show nitinol stents last 8 to 15 years. This means fewer repeat surgeries.
Doctors pick nitinol for heart implants because it moves with blood vessels and helps healing. These features help patients get better faster and have fewer problems. Nitinol tubing also lets devices be smaller and more bendy. This makes heart surgeries safer and easier.
Neurovascular Devices
Nitinol tubing is also used for brain treatments. Surgeons use it to make guidewires and stents for brain blood vessels. These tools must move through tight, twisty spaces without hurting anything. Nitinol’s superelasticity and shape memory help guidewires reach hard spots safely.
Hospitals say nitinol neurovascular devices lower problems by 25%. The Cordis Enterprise stent, made from nitinol, worked perfectly for treating wide-necked brain aneurysms. Patients often leave the hospital with no new brain issues. The tubing’s bendiness and strength help new brain treatments work better.
The chart below compares how well four nitinol brain devices work:
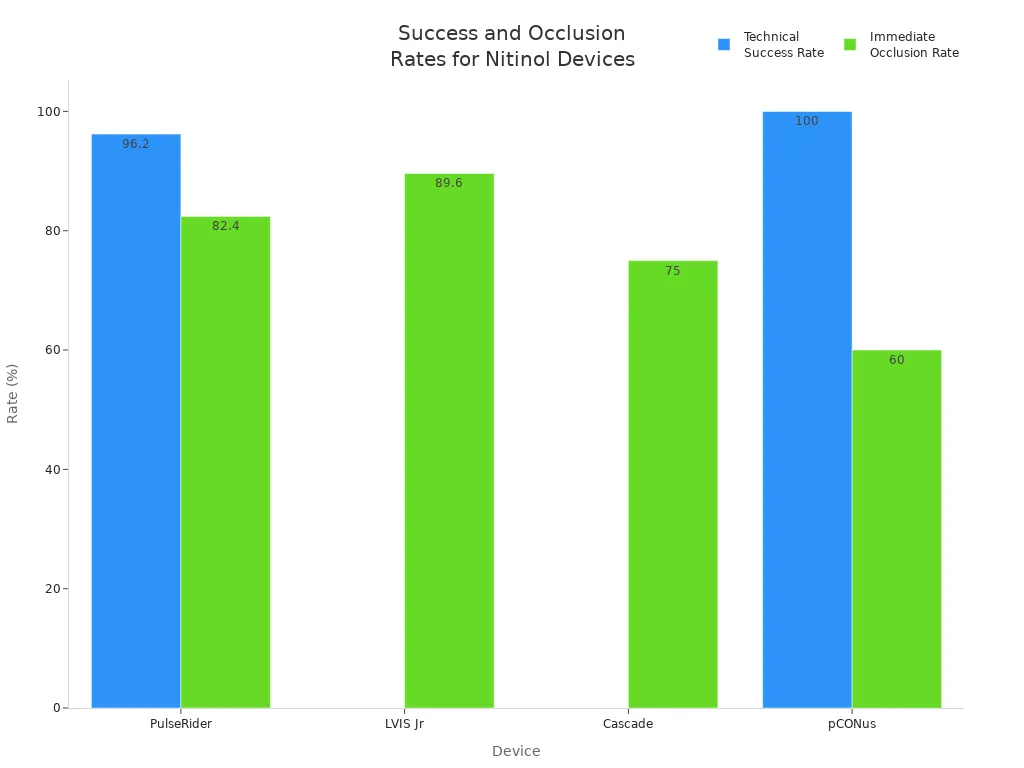
Nitinol tubing lets brain devices be smaller. Smaller devices mean doctors can do less invasive surgeries. This helps patients heal faster and feel less pain. The tubing is safe for the body and does not rust. This helps stop problems during and after surgery.
Orthopedic Implants
Bone doctors use nitinol tubing to make implants for bones and joints. Compression staples made from nitinol are common in these surgeries. Nitinol’s superelasticity and shape memory let implants bend and return to their shape. This matches how bones and tissues move.
Nitinol tubing in bone implants has many good points:
Implants move with the body, so bones and tissues feel less stress.
The tubing is safe for the body and lowers swelling and rejection.
It is bendy and strong, so doctors can make smaller cuts. This means less damage and faster healing.
Implants hold broken bones and spine parts steady. This helps people get better for a long time.
Feature | Impact on Patient Recovery and Surgical Outcomes |
|---|---|
Superelasticity and Shape Memory | Implants move with the body, lower stress, and help healing go faster. |
Biocompatibility | Lowers swelling and rejection, keeps patients safe and comfortable. |
Flexibility and Durability | Lets doctors make smaller cuts, hurts tissue less, helps patients heal faster and have less scarring. |
Stable Fixation | Holds broken bones and spine implants steady, helps implants work well for a long time. |
Use in Robotic-Assisted Surgery | Makes surgery more exact, lets doctors do smaller cuts, helps patients heal faster and have fewer problems. |
People with nitinol bone implants often hurt less, stay in the hospital for less time, and get back to normal faster. The tubing does not rust or wear out easily. This means implants last longer and need fewer replacements.
Dental and Endoscopic Devices
Dentists and surgeons use nitinol tubing in braces, endoscopic guidewires, and retrieval tools. Dental arch wires made from nitinol gently move teeth and help smiles look better. In endoscopy, nitinol tubing helps make bendy guidewires and stents for the digestive system.
Nitinol tubing in dental and endoscopic devices has many benefits:
Superelasticity and kink resistance let devices move through twisty paths without breaking.
Shape memory helps devices go back to their shape after bending.
Being safe for the body lowers tissue damage and keeps patients safe.
Not rusting and lasting long makes devices stronger.
Nitinol stents like HANAROSTENT® and Mega stents keep the digestive tract open during small surgeries. These stents keep their shape even when bent. They help healing and lower the need for big surgeries. The tubing’s bendiness and strength let doctors make smaller devices. This makes surgeries easier and helps patients heal faster.
Tip: Nitinol tubing’s special features let medical devices be smaller, bendier, and more reliable. This helps doctors do less invasive surgeries, so patients heal faster and have fewer problems.
Nitinol Applications and Benefits
Superelasticity
Superelasticity is one of nitinol’s best features. This means nitinol tubing can stretch and bend a lot without breaking. Other metals cannot do this as well. Medical devices made from nitinol can handle big stretches. They can stretch up to 100% in one direction. In real stent use, they can stretch 300-360%. Stents and guidewires can bend through tight blood vessels. After bending, they go back to their shape. The table below shows how superelasticity helps devices work better:
Measurement Type | Value/Range | Medical Impact |
|---|---|---|
Uniaxial stretching | Up to 100% strain | Stops flexible devices from buckling |
Biaxial stretching | 300-360% strain | Acts like stent expansion in vessels |
Fracture limit strain | 12% | Very strong before breaking |
Fatigue life | Millions of cycles | Implants and tools last a long time |
Studies show nitinol thrombectomy devices work well 97% of the time. Only 4.1% of cases have big problems. This means superelasticity makes treatments safer and more reliable.
Shape Memory
Shape memory lets nitinol tubing return to its shape after bending or squeezing. This helps doctors put devices in the body in a small shape. Once inside, the device can expand to fit. Some main benefits are:
Stents and guidewires can be squeezed small for easy use. Then they expand to fit blood vessels.
The martensitic phase change in nitinol allows big, fixable bends. Other metals cannot do this.
Shape memory helps make custom devices for each patient.
This feature makes nitinol great for heart and brain devices. It also makes treatments safer for patients.
Flexibility and Strength
Nitinol tubing is both flexible and strong. It is stronger than many other metals used in medicine. Nitinol can handle being bent and still go back to its shape. The chart below compares important features:
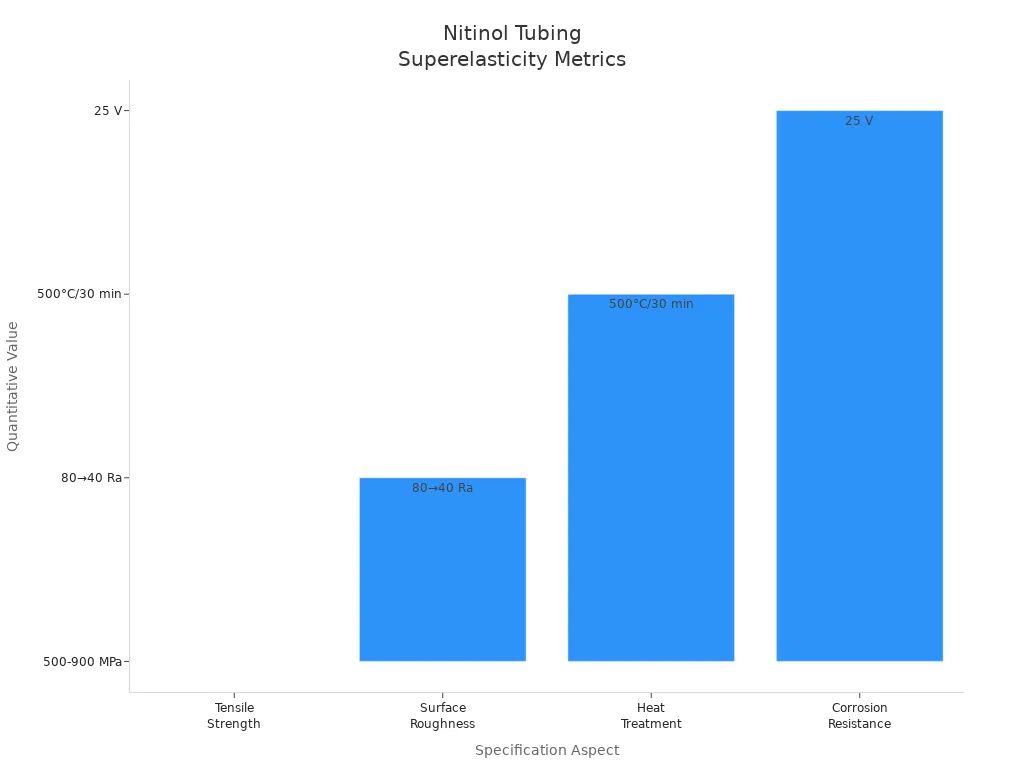
Nitinol’s tensile strength is between 500 and 900 MPa. This makes it strong enough for long use. Its flexibility lets devices move with the body. This lowers the chance of damage or breaking. That is why nitinol is used in stents, catheters, and bone implants.
Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility means nitinol tubing is safe inside the body. Tests show nitinol implants stay safe and work well for over 10 years. The titanium oxide layer on nitinol stops rust and keeps nickel from leaking. This lowers allergy risks. Tests for safety, irritation, and body reactions show nitinol meets tough rules. Doctors trust nitinol for long-term implants. It helps new tissue grow and does not wear out fast.
Considerations in Medical Use
Manufacturing Precision
Making nitinol devices needs very careful work. Medical devices must have the right shape and size to be safe. Companies use special tools to make sure they are exact.
Laser cutting helps shape the tubing with great detail.
Precision drawing makes the tube the right thickness and width.
Surface finishing, like electropolishing and passivation, makes the surface smooth and stops rust.
A nitinol supplier checks the tubing’s size with laser micrometry and ultrasonic testing. They use non-destructive tests, like eddy current testing, to find hidden problems. These steps keep the size very close to perfect, within ±0.0005 inches, and keep the tube round over 95% of the time. Surface finishing also makes the tubing slippery and less likely to hurt tissue, so it is safer for patients.
Most nitinol supplier companies watch every step of making the tubing. This way, every tube meets tough rules. They follow standards like ASTM F2063 and ISO 13485. These rules mean they check and write down everything often. The table below shows some important certification details:
Certification Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Chemical Composition | Nickel-titanium ratio with strict impurity limits for stability and safety |
Mechanical Properties | Defined strength, flexibility, and shape recovery for medical use |
Biocompatibility Testing | ISO 10993 tests for safety in the body |
Dimensional Tolerances | Tight control for reliable device performance |
Surface Treatment | Passivation to reduce nickel ion release |
Quality and Safety
Quality and safety are very important for every nitinol supplier. If the tubing gets dirty during making, it can cause problems. So, companies use cleanrooms and strong cleaning rules. Surface treatments like electropolishing and chemical etching help stop nickel ions from coming out and make the tubing safer for the body.
Manufacturers use special tests, like Digital Image Correlation and ASTM F2129 corrosion testing, to look for tiny cracks and make sure the tubing is strong. Special laser cutting and welding, like femtosecond lasers, keep the tubing from getting too hot and weak. Non-destructive tests, like ultrasonic and visual checks, help find problems early.
Rules say nitinol supplier companies must follow FDA Quality System Regulations and ISO 13485. They have to keep good records, check their work often, and track every batch. These steps help keep patients safe and help get approval from health agencies.
Picking the right nitinol alloy is important for superelasticity and fatigue resistance. The tube’s size and wall thickness must fit what the device needs. Taking out impurities and testing for biocompatibility are needed to keep people safe. Stopping rust is also very important, especially for devices that touch body fluids.
Nitinol wire and coils get the same careful checks. These steps make sure all nitinol products, like tubing or wire, are safe and work well for medical use.
Tip: Choosing a trusted nitinol supplier helps device makers avoid problems and keeps patients safe.
Nitinol tubing is very important in medicine today. Doctors use it in stents, guidewires, catheters, and implants. These tools help make treatments safer and need smaller cuts. Nitinol’s shape memory and superelasticity help devices last longer. Biocompatibility means the devices fit the body well.
Surface treatments help stop rust and lower problems for patients.
Custom designs and smart tech let doctors make devices for each person. They also give real-time updates during treatment.
New research and better ways to make nitinol keep growing its uses. This makes nitinol a key part of new medical ideas.
FAQ
What is nitinol tubing made of?
Nitinol tubing has nickel and titanium. These two metals are mixed together. This makes a strong and bendy alloy. The mix gives nitinol its special features. It can stretch and go back to its shape.
How does nitinol tubing help in minimally invasive surgery?
Doctors like nitinol tubing because it bends and returns to shape. Devices made from nitinol fit through tiny spaces. This lets surgeons do surgery with smaller cuts. Patients heal faster and feel less pain.
Tip: Nitinol tubing lets doctors use smaller tools. This means patients hurt less after surgery.
Is nitinol tubing safe for long-term implants?
Nitinol tubing does not rust or break down in the body. The titanium oxide layer keeps nickel away from patients. Studies show nitinol implants last many years. They do not cause harm inside the body.
Which medical devices use nitinol tubing?
Device Type | Common Use |
|---|---|
Stents | Keeps blood vessels open |
Guidewires | Moves through vessels |
Catheters | Delivers treatments |
Orthopedic Implants | Fixes bones and joints |
Dental Devices | Straightens teeth |
See Also
How Nitinol Tubing Drives Progress In Medical Technology
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Medical Innovations
The Process Behind Manufacturing Nitinol Tubing For Medicine

