How Nitinol Tubing Improves Precision in Minimally Invasive Surgical Tools

Nitinol tubing for minimally invasive surgical tools is essential for achieving high precision in medical procedures. This material is flexible, superelastic, and has shape memory, making it ideal for delicate and accurate surgeries. Manufacturers produce nitinol tubing for minimally invasive surgical tools with extremely tight tolerances, sometimes as precise as ±0.005mm. This level of control ensures consistent tool performance and reduces risks for patients. The tubing is strong enough to withstand pressures over 400 bar and is biocompatible, minimizing adverse reactions in the body. These qualities make nitinol tubing for minimally invasive surgical tools a critical component in delivering better outcomes for every patient.
Key Takeaways
Nitinol tubing bends without breaking and goes back to its shape. This helps doctors use tools that are both exact and bendy in surgery. Its superelasticity and shape memory make tools tough and long-lasting. These tools still work well after being used many times. Nitinol tubing is safe for the body. It lowers the chance of rejection and tissue harm. This helps patients heal faster and have less pain. Tools with nitinol tubing do not kink and keep their shape. This lets doctors reach hard spots safely and with care. Using nitinol tubing in tools makes surgeries better. It also helps patients get better faster and feel more comfortable.
Nitinol Tubing Properties
Shape Memory
Nitinol tubing is special because it has shape memory and superelasticity. Shape memory means you can bend or twist the tubing, and it goes back to its old shape when heated. This helps doctors use tools that fit in small spaces and then change back inside the body. Shape memory and superelasticity let doctors move tools very carefully during surgery.
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
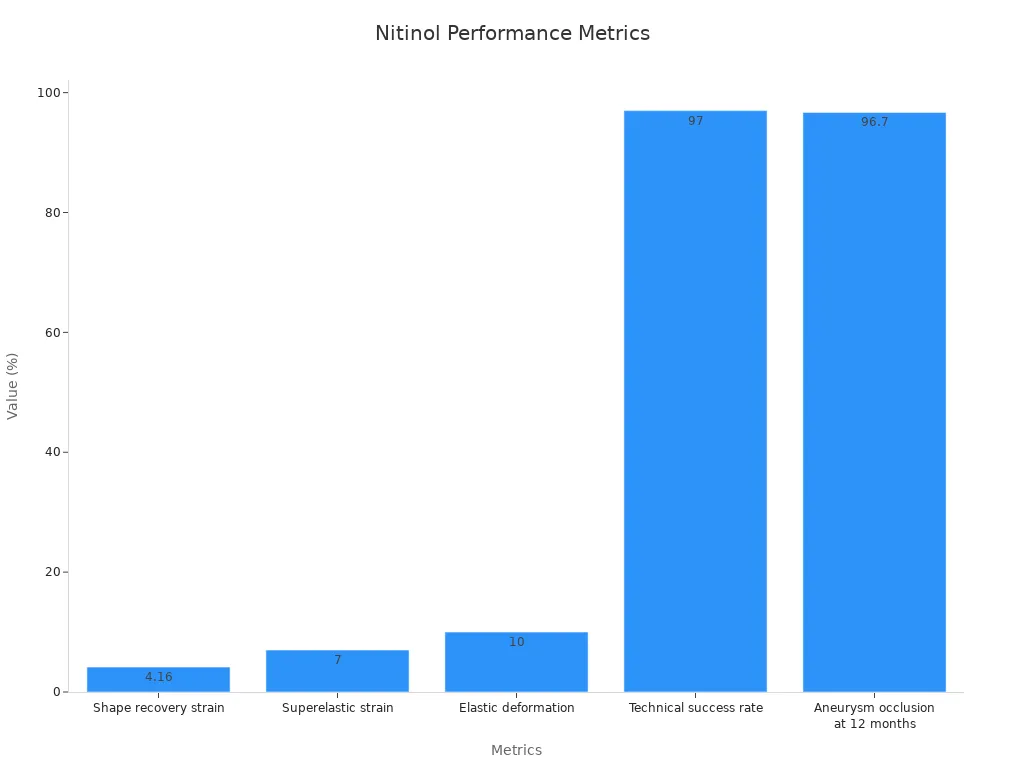
Shape recovery strain | 4.16% |
Superelastic strain | 7% |
Elastic deformation | Up to 10% strain |
Technical success rate | 97% (70 of 72 patients) |
Aneurysm occlusion at 12 mo | 96.7% (29 of 30) |
Shape memory and superelasticity make surgical tools last longer. These tools can bend and twist many times and not break. This makes them good for tough surgeries where tools need to be used again and again.
Superelasticity
Superelastic nitinol tubing can stretch or bend a lot and still go back to its shape. This is much more than what stainless steel can do. Shape memory and superelasticity help doctors have better control and flexibility. The tubing stays strong and flexible, even after lots of bending. This means you can trust it to work well every time.
Tip: Superelastic nitinol tubing helps doctors move tools through tricky parts of the body without losing shape or strength.
Scientists tested nitinol tubing in different temperatures and stress. They found it stays superelastic above 7.8 °C. This means it is safe to use in the human body, which is warmer. The tubing is also strong because it can be bent and straightened many times and still work.
Biocompatibility
Doctors want tools that are safe for the body. Nitinol tubing is very safe and does not rust. Studies show that people with nitinol devices have fewer problems and better results. For example, the DAWN trial showed 49% of people with nitinol devices could live on their own, but only 13% could with regular care. The tubing is strong, so there are fewer broken devices and recalls.
Nitinol tubing lowers the chance of implant rejection by 30% compared to other metals.
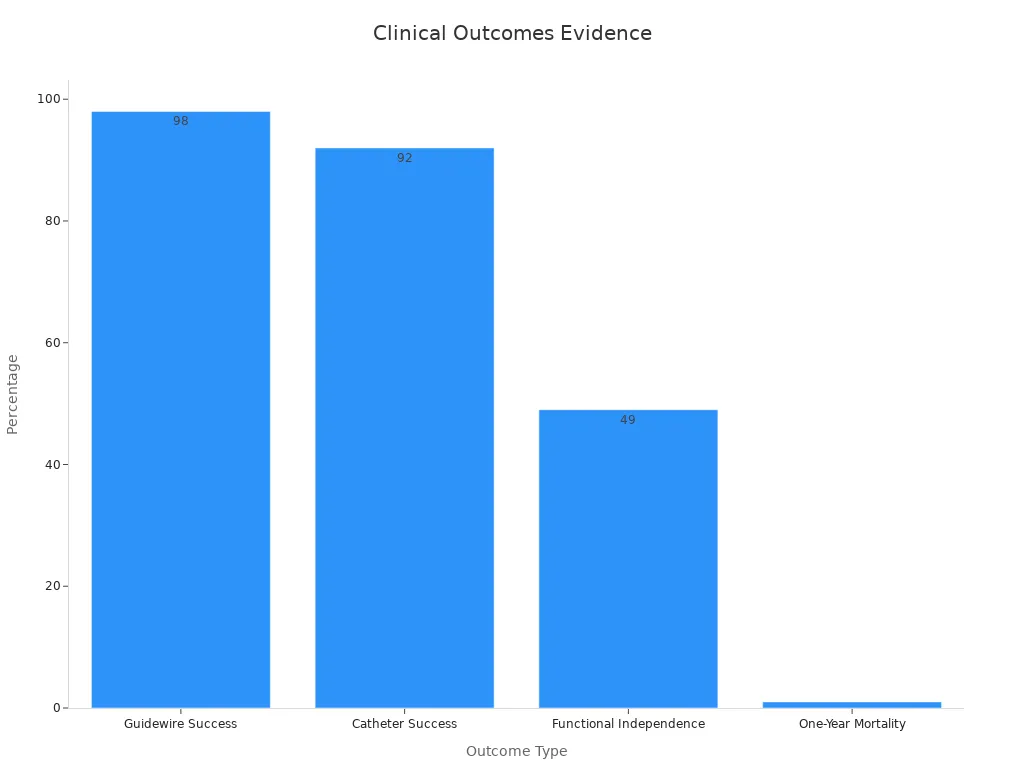
Devices with nitinol tubing work well, with guidewires crossing vessels 98% of the time.
Animal tests show no big problems with tissue, so the tubing is safe for implants.
Shape memory and superelasticity, plus being safe for the body, make nitinol tubing a great choice for minimally invasive surgical tools. You get tools that last longer, work better, and keep patients safer.
Precision in Minimally Invasive Surgery
Flexibility and Control
Doctors need tools that move easily and respond well. Nitinol tubing for minimally invasive surgical tools helps with this. The tubing is flexible and strong. It lets doctors guide tools through small and twisty spaces in the body. When using nitinol guidewire tubing, you can bend and twist the tool. It does not lose its shape or strength. This helps doctors reach hard-to-get places and lowers the chance of hurting tissue.
Evidence Description | Contribution to Surgical Precision |
|---|---|
Exceptional resistance to fatigue | Keeps its shape after many uses, which is important for guidewires and catheters. |
Superelasticity and shape memory properties | Help doctors move through tricky body parts, making mistakes less likely and improving accuracy. |
Exceptional flexibility | Lets tools bend in tight spots but stay steady, which is needed for careful work. |
Doctors see these good things in real surgeries. Nitinol guidewire tubing helps cross blood vessels 98% of the time. Catheters with nitinol tubing reach their target in 92% of cases. These high numbers show that flexibility and control make surgery more exact and dependable.
Measurement Type / Metric | Measured Value | Relevance to Surgical Precision |
|---|---|---|
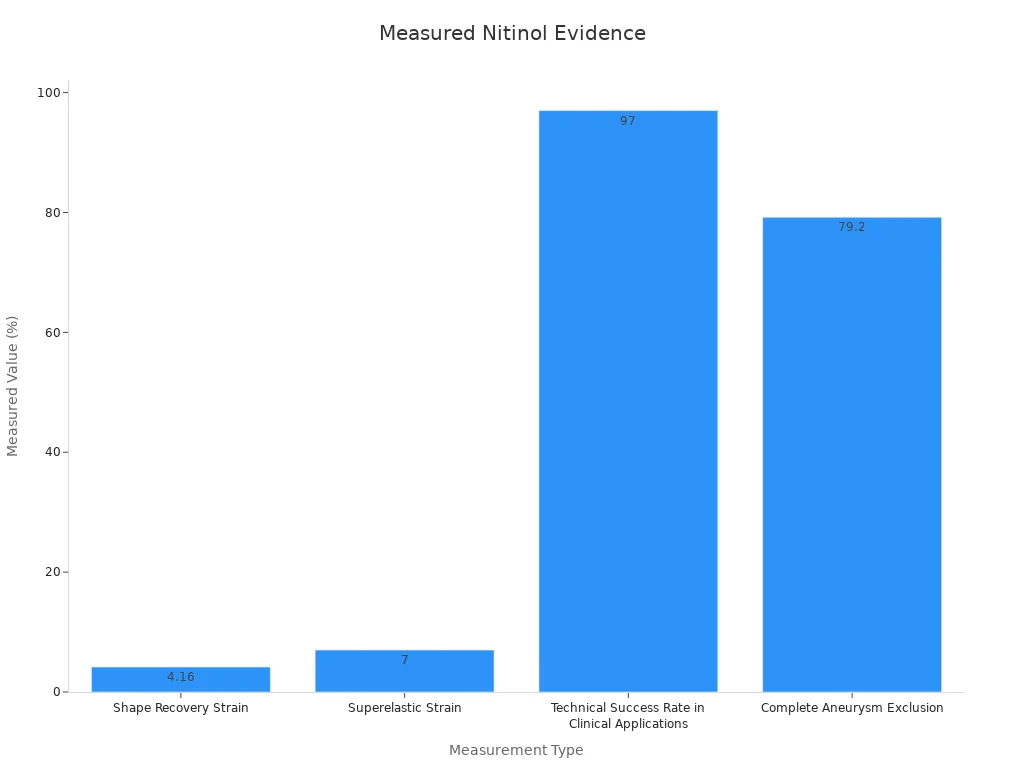
Shape Recovery Strain | 4.16% | Shows the tool can go back to its shape, so it stays accurate. |
Superelastic Strain | 7% | Means the tool can stretch and bend without breaking, which helps in the body. |
Technical Success Rate in Clinical Applications | 97% (70 of 72 patients) | Proves nitinol tools work well and are precise. |
Complete Aneurysm Exclusion | 79.2% (57 of 72 patients) | Shows the tools are reliable and work in tough surgeries. |
Nitinol guidewire tubing lets tools move with your hand. This makes every step of surgery more exact and dependable.
Kink Resistance
Kink resistance is very important for these tools. When doctors push a guidewire or catheter in a blood vessel, they do not want it to fold or kink. Nitinol guidewire tubing does not kink, even when bent a lot. This keeps tools working safely and smoothly.
Devices made from thin nitinol tubing can open blocked vessels every time and work well in 97% of cases. This shows that kink resistance helps tools work during hard surgeries. Tools that do not kink lower the chance of hurting blood vessels and help avoid problems.
Parameter / Metric | Quantified Data / Description | Relevance to Kink Resistance and Surgical Performance |
|---|---|---|
Fatigue Endurance Limits | TM-1 tubing lasts 2 to 3 times longer at 10^7 cycles than TM-2 | Shows it is tough and does not change shape after many uses |
Wall Thickness | About 0.08 mm is best for both bending and staying strong | Makes tubing bendy but still strong, which helps stop kinks |
Fatigue Life Correlation | Fewer non-metal bits inside make tubing last longer; healing inside the metal helps too | The inside quality makes tubing last and not kink |
Clinical Success Rates | Up to 100% vessel opening and 97% success for nitinol tubing tools | Proves kink resistance helps tools work in surgery |
Mechanical Tests & Simulations | Pulling tests, computer models, and special scans used | These tests show tubing can handle body stress and keep its shape |
Elastic Modulus & Tensile Strength | High enough to stop bending out of shape but still bendy | Helps tubing bend without kinking or breaking |
With nitinol guidewire tubing, doctors know their tools will not fail, even in tough surgeries. This means they can focus on being careful and exact, knowing their tools will work right.
Consistent Performance
Doctors want tools that work the same way every time. Nitinol tubing for minimally invasive surgical tools does this, even under stress. Nitinol guidewire tubing can bend, twist, and squeeze many times. It does not lose its shape or stop working. This is important for safe and steady surgery.
Nitinol tubing is superelastic, so it works where other metals would break.
Tests show nitinol stents and guidewires last longer and break less than other materials.
The Supera™ Stent, made with nitinol tubing, did not break in over 2,000 patients after one year.
Nitinol guidewire tubing can stretch up to 6% and still go back to its shape, so tools stay accurate.
It resists wearing out, so tools work well even after millions of uses.
The surface of nitinol tubing does not rust, which helps it last longer.
Special ways of making the tubing make the surface even better, so tools are more reliable in surgery.
Catheters and guidewires made with nitinol tubing give doctors confidence for careful work. They know their tools will not fail, even in hard cases. This means better results for patients and fewer problems.
Note: Picking nitinol guidewire tubing for catheters and guidewires means you get tools that are very reliable, last long, and are exact for every minimally invasive surgery.
Applications of Nitinol Tubing in Minimally Invasive Procedures
Nitinol tubing for minimally invasive surgical tools has changed surgery. Now, doctors use tools that bend and go back to their shape. This makes surgery safer and more exact. Nitinol tubing is used in many surgical tools. These include guidewires, catheters, compression staples, and new endoscopic and robotic devices. Each tool uses nitinol tubing’s special features to help patients and make work easier.
Guidewires and Catheters
Doctors use guidewires and catheters in many surgeries. Nitinol guidewire tubing gives better control and movement. Superelasticity and shape memory help tools move through tricky blood vessels. The tools bend and return to their shape. This helps doctors reach hard places in the body.
Aspect | Evidence Summary | Supporting Data / Statistics |
|---|---|---|
Superelasticity and Shape Memory | Lets catheters move through tough heart areas and lowers vessel injury. | Tools bend without pushing too hard on vessel walls. |
Reduced Vessel Trauma | Nitinol guidewires bend and flex, so they hurt vessels less. | Special coatings make tools slide smoothly. |
Procedure Time Reduction | Studies show surgeries are faster with nitinol tubing. | Tests show shorter times with strong proof. |
Clinical Success Rates | Nitinol guidewires work well in heart studies. | In one study, 5 out of 7 patients crossed in one try, 2 in two tries, and no problems happened. |
Durability and Biocompatibility | Nitinol stays strong and safe in the body. | A special layer keeps it from rusting and helps it work well. |
Navigation in Complex Anatomy | Nitinol tubing helps tools move in twisty vessels and hard spots. | Tools keep their shape and slide easily, so doctors can reach the right place. |
Nitinol guidewire tubing helps finish surgeries faster and with fewer problems. These tools last a long time, even after many uses. Their flexibility and strength help doctors feel sure during surgery. Catheters with nitinol tubing also lower the chance of hurting blood vessels. Patients heal better and recover faster.
Tip: Using nitinol guidewire tubing and catheters helps avoid vessel injuries and lets doctors reach the right spot.
Compression Staples
Compression staples made from nitinol tubing close tissue tightly. These staples use shape memory to hold tissue together. There are fewer staple problems and healing is better.
A new study looked at three old ways and two new ways to make nitinol. The new ways made staples last twice as long after many bends. This means staples do not break, even after lots of use. Doctors can trust these staples for hard surgeries.
Nitinol staples move with the body. They keep tissue together without extra harm. This means fewer problems and faster healing for patients.
Endoscopic and Robotic Instruments
Endoscopic and robotic tools use nitinol tubing to reach deep or tight spaces. These tools bend, twist, and go back to their shape. Doctors can do hard tasks with steady hands and careful moves.
Metric/Outcome | Result/Value |
|---|---|
Shape recovery strain | About 4.16% |
Superelastic strain | About 7% |
Technical success rate | 97% (70 out of 72 patients) |
Complete aneurysm exclusion | 79.2% (57 out of 72 patients) |
Aneurysm occlusion at 12 months | 96.7% (29 out of 30 patients) |
Corrosion resistance | Can handle up to 1000 mV |
Fatigue life | Very good, works after many uses |
Biocompatibility | Low chance of rejection, less swelling |
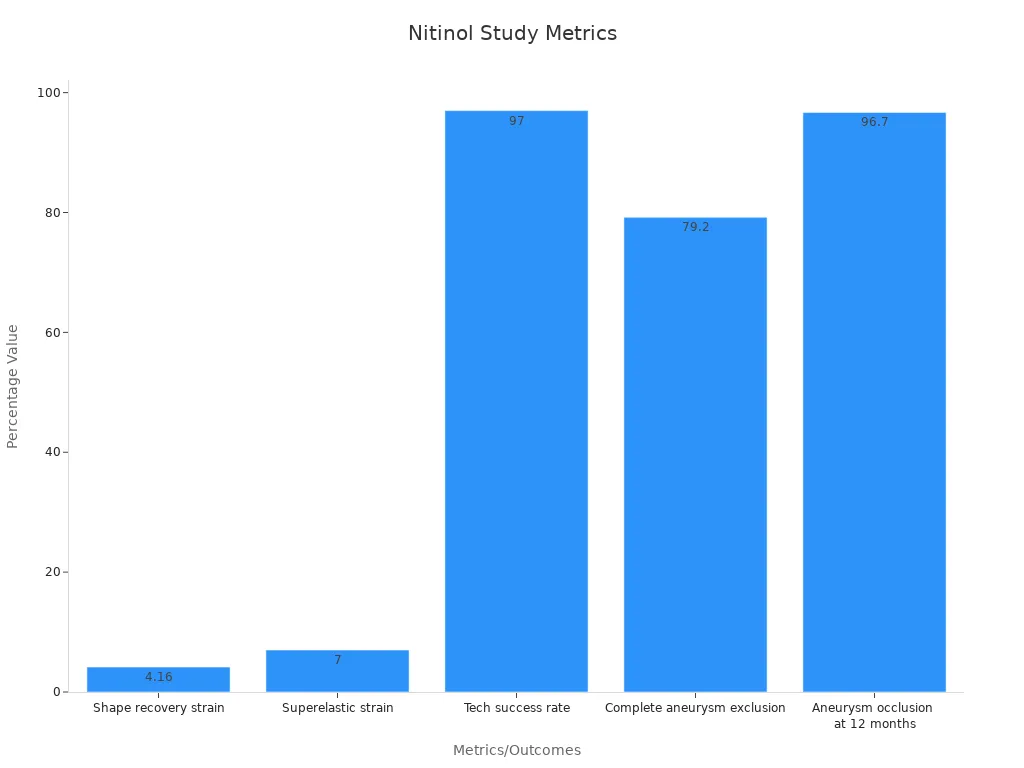
These tools keep working well over time. High success rates and good results show they are helpful. Nitinol tubing does not rust or wear out fast, so doctors can use these tools for long surgeries. There is also less swelling or rejection, so patients get better faster.
Note: As technology grows, nitinol tubing is used in more surgical tools. Doctors now have safer and better ways to help patients.
Patient Benefits
Reduced Trauma
You want surgery to hurt less and cause fewer problems. Nitinol tubing helps make tools that move smoothly in your body. These tools fit your body’s shape well. This means doctors do less damage to your tissue. Superelasticity and flexibility let doctors use smaller cuts. You can heal faster because of this. The tools do not push hard on your tissue, so you feel less pain. Studies show patients with nitinol devices stay in the hospital for less time. They also heal with fewer problems. The risk of trauma is lower, and you get better with less pain.
Metric/Device Type | Statistical Evidence | Patient Benefit Description |
|---|---|---|
Silverway guidewire | 98% success rate crossing blood vessels | High reliability and precision in minimally invasive surgery |
Catheters | 92% success rate in surgeries | Effective device delivery with minimal complications |
Nitinol implants | 30% lower rejection rate compared to older materials | Improved biocompatibility and reduced immune response |
Ultra-thin ureteroscopes | Up to 95% stone-free rates | Enhanced stone clearance efficiency and surgical success |
Recovery improvement | 20% faster recovery times | Reduced pain, lower infection risk, and shorter hospital stays |
Nitinol stents | 68% to over 90% vein patency after 1 year | Long-term effectiveness and patient safety |
Complication rates | Lower compared to traditional materials | Reduced tissue trauma and fewer postoperative issues |
Faster Recovery
You want to get back to normal life fast. Nitinol tubing helps make this happen. Shape memory and biocompatibility mean less swelling and irritation. You get smaller cuts, so you have less pain and a lower chance of infection. Studies show people with nitinol implants heal about 20% faster than with old materials. You spend less time in the hospital and feel ready to move sooner. Nitinol is strong, so devices break less often. This means you do not need extra surgeries. You feel better and heal faster, with less pain.
Recovery Metric | Nitinol Implants | Traditional Implants |
|---|---|---|
Mean Skin Incision Length | Smaller (~3.8 cm) | Larger (~8.7 cm) |
Mean Operative Time | Shorter (~19.6 min) | Longer (~48.8 min) |
Bone Union Rate | 100% achieved | 100% achieved |
Implant Discomfort Reported | Lower (~32.3%) | Higher (~71.4%) |
Implant Removal Requested | Lower (~35.5%) | Higher (~75.0%) |
Improved Outcomes
You want the best results from your surgery. Nitinol tubing gives doctors tools that are very precise and strong. These devices help doctors reach the right spot easily. You have fewer problems and a lower chance of your body rejecting the implant. Clinical trials show 49% of people with nitinol devices can live on their own again. Only 13% can do this with regular care. The one-year death rate is just 1.0% with nitinol, but 2.5% with old materials. You feel more comfortable, get fewer infections, and heal safely. Nitinol devices last longer, so you can worry less.
Tip: If you pick tools with nitinol tubing, you get smaller cuts, heal faster, feel less pain, and stay healthier for a long time.
Future of Nitinol Tubing for Minimally Invasive Surgical Instruments
Technological Advances
Many new technologies are changing nitinol tubing in surgery. High-purity nitinol lasts longer and works better because it has fewer bad parts. New ways to make tubing, like 3D printing and laser cutting, help create special shapes and sizes for each patient. These new methods make the tubing’s shape memory and superelasticity even better, so tools are more exact.
Surface treatments, like electropolishing and magnetoelectropolishing, add a nickel-free layer. This layer makes the tubing safer for the body and stops it from rusting. Smart technology is also making a difference. Some nitinol tubing now has sensors inside that give doctors information during surgery. This helps doctors make safer and more careful moves.
Nitinol tubing bends and goes back to its shape, so doctors can reach hard places in the body.
Its biocompatibility and rust resistance mean it is safe to use for a long time.
More people trust nitinol medical devices, and the market is growing quickly.
These new ideas help save money and make tools last longer. You get tools that work better and stay strong in every surgery.
Expanding Applications
Nitinol tubing is now used in more types of surgical tools. Doctors use it in stents, catheters, and guidewires, and new uses come out every year. For example, neurovascular stents made with nitinol tubing help patients heal about 20% faster and lower the chance of problems. These stents fit tricky blood vessels and help people get better.
Device Type | Market Share (%) | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Endurant II/III | 75 | High reliability in aneurysm repair |
Zilver PTX Stent | 22 | Trusted for peripheral use |
You will also see nitinol tubing in bone and heart implants. The market for these devices could reach $31.4 billion by 2028. This is because more people need less invasive surgeries and the population is getting older. Nitinol’s shape memory and superelasticity make it great for these new uses.
Note: When you pick surgical tools, look for ones that save money and last a long time. These tools help you heal faster and lower the chance of needing more surgeries.
Nitinol tubing’s strength and value will keep bringing new ideas to medical tools. You can expect safer, more flexible, and longer-lasting tools in the future.
Nitinol tubing helps doctors be more exact and careful. This makes surgery tools work better and safer. Patients feel more comfortable and heal faster. Nitinol has special features like superelasticity and shape memory. These help doctors move tools gently and place them right. This means less pain and better comfort for patients. The table below shows why nitinol is good for patient care:
Property | Benefit for Patient Comfort and Care |
|---|---|
Superelasticity | Smooth movement, less tissue damage |
Shape Memory | Accurate placement, better comfort |
Biocompatibility | Fewer reactions, safer for every patient |
New ideas in nitinol tubing will make surgery even safer. Science will keep making patient care better in the future.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing better than stainless steel for surgical tools?
Nitinol tubing bends and returns to its shape. Stainless steel can bend but stays bent or breaks. You get more control and safety with nitinol. Doctors trust nitinol for tough surgeries.
Is nitinol tubing safe for your body?
Yes, nitinol tubing is biocompatible. It does not rust or cause bad reactions. You can feel safe with nitinol devices inside your body.
How does nitinol tubing help you heal faster?
Nitinol tubing lets doctors use smaller cuts. You feel less pain and heal quicker. The tubing’s smooth surface lowers swelling and infection risk.
Can nitinol tubing be used in robotic surgery?
Yes! Nitinol tubing works well in robotic tools. It bends and moves with the robot’s arms. You get more precise and gentle surgery.
Will nitinol tubing last a long time inside your body?
Nitinol tubing resists wear and corrosion. It stays strong after many bends. You can expect nitinol devices to last for years.
See Also
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Minimally Invasive Surgery
Ways Nitinol Tubing Is Transforming Modern Medical Equipment
Nitinol Tubing’s Impact On Progress In Medical Technology
The Critical Use Of Nitinol Tubing In Advanced Medicine
The Process Behind Manufacturing Nitinol Tubing For Medicine

