Why Nitinol Tubing Is the Top Choice for Drug-Eluting Stents
Nitinol tubing for drug-eluting stents is the best material choice because it offers unique features like shape memory, superelasticity, and excellent biocompatibility. These qualities make nitinol tubing for drug-eluting stents ideal for heart stents and other medical devices. Nitinol tubing for drug-eluting stents allows the stents to expand at body temperature, ensuring a perfect fit against blood vessel walls. It also prevents stents from wearing out after repeated heartbeats. Recent studies show that nitinol tubing for drug-eluting stents can hold more medication and release it more effectively than other materials. These advantages improve the performance of medical devices and lead to better patient outcomes in heart care. The special properties of nitinol tubing for drug-eluting stents help stents last longer, reduce complications, and support patients who need heart stents.
Key Takeaways
Nitinol tubing can remember its shape and is very stretchy. This helps stents open up and fit blood vessels well. The stents stay bendy and strong at the same time.
Nitinol stents do not wear out or rust easily. They can last for many years inside the body. This means fewer surgeries and less chance of harm.
Nitinol is very safe for the body and works well with tissue. It does not bother tissue much and lets out very little nickel. This helps people heal faster.
Nitinol bends better and lasts longer than stainless steel or cobalt-chromium. It also fits blood vessels better. This makes it the best choice for drug-eluting stents.
Nitinol helps make new medical tools like self-expanding stents. It also helps doctors do less invasive surgeries. This makes care better for patients and helps future treatments.
Nitinol Tubing for Drug-Eluting Stents
Shape Memory
Nitinol tubing for drug-eluting stents has a special ability called shape memory. This lets the stent get squeezed small so doctors can put it in the body easily. When the stent warms up to body temperature, it goes back to its bigger shape. Scientists found that nitinol changes its phase when heated, which helps the stent open up and fit tightly in blood vessels. Because of this, doctors can use smaller cuts and less invasive ways to place the stent. The shape memory also helps the stent stay where it should and support the vessel after many heartbeats. Studies show nitinol tubing for medical stents keeps its shape and strength, even after being squeezed and let go many times. This is why nitinol is a top pick for cardiovascular stents, especially when doctors need more flexibility for tricky blood vessels.
Superelasticity
Nitinol is special because it has superelasticity, which means it is very flexible. This lets nitinol tubing for medical stents bend and stretch without breaking. When the stent feels pressure from blood or vessel walls, it can bend and then go back to its normal shape. Tests show nitinol can stretch up to 6% without getting damaged forever. Fatigue tests prove nitinol tubing for drug-eluting stents keeps its superelasticity after millions of bends. Computer models show nitinol stents fit well in many vessel shapes, so they work in different parts of the body. Superelasticity helps the stent stay open and support the vessel, even if the vessel moves or changes shape. This is important for stents in places that move a lot, like the heart or legs.
Fatigue Resistance
Fatigue resistance is another important thing about nitinol tubing for medical stents. Nitinol can bend and stretch millions of times without cracking or breaking. Industry tests show nitinol stents last more than 10 million bends, which is more than the number of heartbeats in a year. Clinical studies say nitinol stents can last 8 to 15 years, depending on where doctors put them. This long-lasting nitinol tubing means fewer repeat surgeries. Superelasticity and shape memory together help nitinol resist damage from constant movement. Making nitinol with heat treatment and surface polishing makes it even stronger and more reliable. These things make nitinol tubing for drug-eluting stents a safe and tough choice for long-term use.
Note: Nitinol tubing for medical stents can handle up to 400 million pressure cycles in neurovascular stents, showing its great fatigue resistance and strength over time.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is very important for materials used inside the body. Nitinol has great corrosion resistance, especially after treatments like electropolishing. These treatments smooth the surface and take away harmful particles, which helps stop nickel ions from coming out. This makes nitinol tubing for drug-eluting stents safer for patients and improves both biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Nitinol protects better against harsh body fluids than stainless steel and titanium alloys. The table below shows how nitinol compares to other materials:
Material | Corrosion Resistance Characteristics | Unique Properties Relevant to Stents |
|---|---|---|
Nitinol | Great corrosion resistance in tough body environments; surface treatments like electropolishing and passivation lower nickel ion release and make it last longer | Superelasticity, shape memory effect, biocompatibility |
Stainless Steel | Good corrosion resistance; used a lot but not as good at lowering nickel ion release as treated nitinol | Many types, good corrosion resistance |
Titanium Alloys | Great corrosion resistance; strong and light but does not have superelasticity or shape memory | High strength, lightweight, great corrosion resistance |
Nitinol’s biocompatibility and corrosion resistance help stop problems like swelling or blood clots. This makes nitinol tubing a smart choice for cardiovascular stents and other medical devices that stay in the body for a long time.
Biocompatibility for Safe Medical Use
Nitinol is used in medical devices because it is safe for the body. Doctors and engineers pick nitinol for stents and implants since it works well inside people. It does not cause strong immune reactions or much irritation. This helps patients heal faster and lowers the chance of problems. Special surface treatments, like electropolishing, make nitinol even safer by lowering nickel release over time. These things help stop stent failure and make nitinol a good choice for long-term use.
Reduced Tissue Reaction
Devices made from nitinol are less likely to irritate tissue. When doctors put a nitinol stent in a blood vessel, the body reacts less than with other metals. Tests show nitinol tubing causes little swelling and forms a thin, stable capsule around the implant. This means the body accepts the device better and heals faster.
Plasma-treated nitinol surfaces make the capsule around the stent thinner. This leads to less reaction from the body and better healing.
The table below shows how surface treatments on nitinol tubing help the body accept it and lower tissue reaction:
Biocompatibility Metric | Statistical Evidence / Result |
|---|---|
Peri-hADM Capsule Thickness | Plasma-treated samples had thinner capsules, showing less reaction. |
Fibronectin Adsorption Intensity | Plasma-treated surfaces had less fibronectin, showing less response. |
Cell Penetration Efficiency | Treated samples had more fibroblasts, showing better biointegration. |
Blood Absorption Time | Plasma-treated samples absorbed blood faster, showing better surface. |
BSA Adsorption Intensity | Treated surfaces had less BSA, but not always a big change. |
Doctors also use strict rules for making nitinol medical devices. Certifications like ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 13485:2016 show that companies follow high safety standards. These rules help make sure nitinol stents cause less irritation and work well in the body.
Long-Term Implantation
Nitinol is safe for long-term use in medical devices. Studies show nitinol tubing lets out very little nickel, much less than FDA safety limits. The table below shows how much nickel comes out of nitinol stents over time:
Parameter | Measurement / Limit |
|---|---|
Nickel Ion Release (Day 1) | About 6.0 µg/day (max 7.6) |
Nickel Ion Release (Day 6) | About 1 µg/day |
Nickel Ion Release (Day 35) | About 0.2 µg/day |
FDA Acute Nickel Limit | 70 µg/day |
FDA Chronic Nickel Limit | 35 µg/day |
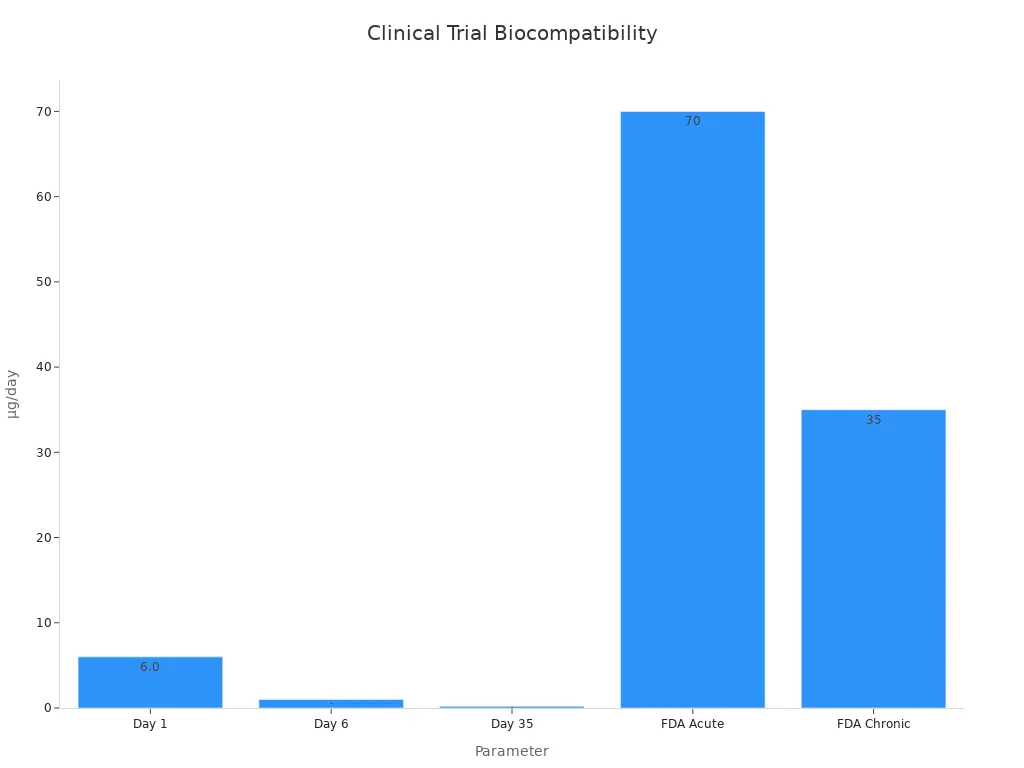
A 24-week study tested nitinol strands in different fluids to see how they last. The results showed only mild corrosion and very low nickel release, even after months. Nitinol stayed strong and flexible, so the stent can last for years in the body. Tests show nitinol is safe and does not hurt cells or blood. Electropolishing nitinol tubing lowers nickel release even more and helps stop tissue reactions.
Nitinol medical devices can handle up to 600 million bends and stretches, which matches what the body needs. This strength, along with being safe for the body, means nitinol stents can stay in place for many years without causing harm. Patients need fewer repeat surgeries and have better long-term health.
Nitinol Tubing for Medical Stents vs. Other Materials

Stainless Steel
Stainless steel has been used for stents for a long time. It is strong and easy to shape. But it is not as flexible as nitinol. When doctors put stainless steel stents in curved or moving vessels, the stents can lose shape or break after stress. Stainless steel does not have great fatigue resistance, so it may not last as long as nitinol tubing for medical stents. Stainless steel stents work well in straight vessels, but they do not bend as easily to fit the body’s curves.
Cobalt-Chromium
Cobalt-chromium alloys are stronger than stainless steel. They let doctors use thinner stent struts. This helps with smaller devices for some procedures. But cobalt-chromium stents do not have superelasticity or shape memory like nitinol. These stents are not very flexible and have only moderate fatigue resistance. Over time, cobalt-chromium stents may not handle lots of stress as well as nitinol tubing for medical stents. They also do not fit vessel walls as closely, which can affect blood flow support.
Material Comparison Table
Nitinol tubing for medical stents is special because it has superelasticity, shape memory, and high fatigue resistance. These features help nitinol stents fit better, last longer, and lower the risk of problems.
Property | Nitinol | Stainless Steel | Cobalt-Chromium |
|---|---|---|---|
Flexibility | Excellent | Low | Low |
Fatigue Resistance | Outstanding | Moderate | Moderate |
Vessel Conformity | High (adapts to curves) | Moderate | Moderate |
Deployment Efficiency | Precise, self-expanding | Manual expansion | Manual expansion |
Durability | Very high (millions of cycles) | Moderate | Moderate |
Biocompatibility | Excellent | Good | Good |
Nitinol tubing for medical stents uses superelasticity and shape memory to bend with vessel curves and bounce back after stress. Tests show nitinol can handle millions of cycles without losing its shape. Studies also show nitinol stents, like those in the heart, need fewer repeat procedures. Nitinol can expand on its own and fit tricky vessel shapes, making it the best choice for today’s stents.
Nitinol in Advanced Medical Devices
Self-Expanding Stents
Nitinol is important for self-expanding stents. These stents use shape memory and superelasticity to open inside blood vessels. Doctors can squeeze the stent small to put it in the body. When inside, the stent grows to fit the vessel just right. A study tested nitinol self-expanding stents made from SE508 nitinol tubing. The stents were cut with lasers and polished to be smooth. Scientists put them in rabbits with bad artery disease. After 28 days, the stents healed well and caused less harm to the vessel. They also controlled new tissue growth better than balloon-expandable stents. This means nitinol self-expanding stents help treat tough artery problems and help patients get better.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Nitinol has changed how doctors do less invasive surgeries. Its special features let devices bend and move in tight body spaces. Devices made from nitinol tubing can reach hard spots with less harm. Studies show many good things:
Nitinol tubing lowers the chance of vessels getting narrow again.
Shape memory and superelasticity help devices fit each person.
Custom nitinol devices make patients feel better and heal longer.
Nitinol tubing is used for stents, guidewires, and tools for heart, brain, and bone care.
Nitinol helps new ways like robot surgery and implants that dissolve.
Doctors use nitinol in many new medical devices because it makes surgery safer and helps people heal faster.
Future Innovations
Nitinol keeps helping new medical devices get better. New ways to make it, like laser cutting and 3D printing, let doctors design special devices. These new ways help make stents and other tools just for each patient. Nitinol tubing is now used for drug delivery and robot surgery parts. Scientists think nitinol will be very important for future medical devices. Its strength, flexibility, and safety help make treatments better and safer. As technology gets better, nitinol will help doctors treat more problems with less danger and better results.
Nitinol tubing is special in medical devices because it has shape memory, superelasticity, and strong fatigue resistance. Clinical studies prove nitinol stents work well and keep vessels open, as shown in the table below. These features help medical devices lower problems and keep patients safer for a long time. Nitinol’s strength and flexibility let devices move with blood vessels, which makes them work better and last longer. As new technology grows, nitinol will keep helping medical devices and patient care improve.
Study / Stent Type | Patients / Cases | Key Outcomes / Metrics |
|---|---|---|
Mewissen (2004) | 137 legs | 98% success; 92% patency at 6 months |
Zeller et al (2008) | 110 patients | 96% success; 23.3% restenosis at 1 year |
Kickuth et al (2007) | 35 patients | 82% patency at 6 months; 100% limb salvage |
Supera™ Stent | >2,000 patients | Zero fractures; 4x compression resistance |
Solitaire FR Stent | N/A | Flexibility at 0.38 ± 0.11 N |
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing special for drug-eluting stents?
Nitinol tubing can remember its shape and is very bendy. These features help stents fit blood vessels better. Nitinol stents stay strong and do not break easily. Doctors like nitinol because it lasts a long time.
Is nitinol safe for long-term use in the body?
Yes, nitinol is safe for people. It works well with the body and does not cause harm. Studies show nitinol lets out very little nickel, much less than what is allowed. Special treatments make nitinol even safer for patients.
How does nitinol compare to stainless steel in stents?
Feature | Nitinol | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility | Excellent | Moderate |
Fatigue Life | Very High | Lower |
Vessel Fit | Adapts Well | Less Adaptive |
Nitinol is more flexible and lasts longer than stainless steel.
Can nitinol stents be used in children or young adults?
Doctors use nitinol stents for kids and adults. Nitinol is strong and bends easily, so it works in growing bodies. Doctors pick the right size stent for each person.
Why do doctors prefer self-expanding nitinol stents?
Self-expanding nitinol stents open up by themselves inside the vessel. This makes it easier for doctors to put them in. The stent fits tightly and helps patients heal faster.
See Also
The Impact Of Nitinol Tubing On Medical Device Innovation
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Cutting-Edge Medical Uses
Nitinol Tubing’s Critical Role In Minimally Invasive Surgeries
How Nitinol Tubing Drives Progress In Medical Technology Today
The Manufacturing Process Behind Nitinol Tubing For Medical Use

