Understanding the Superelastic Properties of Niti Tubing

Imagine a doctor guiding a small, bendy tube through twisty blood vessels. Normal metals bend or get stuck, but superelasticity helps Niti tubing snap back to its shape. Nitinol is a special mix of nickel and titanium. It changes how medical devices work. Niti tubing for medical devices bends with ease but stays strong. This is because of its superelastic and shape memory powers. Nitinol’s special features help doctors make better devices. These devices are safer and need smaller cuts. The world market for nitinol in medical devices is growing fast. This is because more people want things like stents, guidewires, and filters. Niti tubing lets medical devices go back to their shape inside the body. It stops kinks and works well in hard medical jobs. Nitinol’s safe use in the body and its bendiness make medical care better.
Key Takeaways
Niti tubing bends easily and goes back to its shape. This makes medical devices safer and better in the body. Its superelastic and shape memory properties help devices move in twisty body parts. The tubing does not kink or break. Niti tubing does not rust and is safe for the body. This lowers the chance of allergies and tissue problems. Doctors use Niti tubing to make smaller surgical tools. These tools hurt less and help patients heal faster. Niti tubing is strong and can be changed to fit needs. It is better than other metals like stainless steel. It lasts longer and bends more in medical devices.
Superelasticity
Niti Tubing for Medical Devices
Niti tubing is used in many medical devices. It has changed how doctors help patients. Nitinol tube bends and goes back to its shape. This is important for many tools. Stents, guidewires, and endoscopic tools use nitinol tubing. These tools must move through twisty parts of the body. Niti tubing does not kink or stay bent. Doctors use nitinol tube in heart, bone, and brain devices. Nitinol tubing can stretch or squeeze and still work. This makes it a good choice for strong and bendy tools. Niti tubing is as flexible as bone. This helps with implants and catheters. Nitinol tube can lower problems like vessel injury and more surgeries. Medical teams trust nitinol tubing because it works well many times.
Nitinol tube bends up to ten times more than normal metals. This helps doctors reach hard places in the body.
How Superelasticity Works
Superelasticity in nitinol tube comes from a special change inside the metal. When doctors bend nitinol tubing, the atoms move to a new crystal form. This is called a reversible martensitic transformation. Nitinol tube can stretch up to 5.2% and snap back. The secret is how nitinol tube switches between two phases. Temperature and stress make this happen. At body temperature, nitinol tubing stays superelastic. The atomic structure lets nitinol tube recover from big stretches. Tiny grains and chemical spots help nitinol tube keep its superelastic powers. Nitinol tube does not kink as much as stainless steel. This makes nitinol tubing great for tools that move with the body. Doctors use nitinol tube because it is strong, bendy, and always returns to shape.
Shape Memory and Flexibility
Shape memory nitinol tubes can go back to their first shape after bending or twisting. This happens because the metal changes between martensite and austenite phases. Medical devices made from niti alloy tubing can bend or squeeze inside the body, then return to their shape. This helps medical tools last longer and work better.
The table below shows the main properties of shape memory nitinol tubes and how they help medical devices:
Property | NiTi Tubing Characteristics | Benefit for Medical Devices |
|---|---|---|
Shape Memory Effect | Can return to original shape after bending because of phase changes | Lets devices bend or squeeze in the body and go back to shape, making them last longer and work better |
Superelasticity | Can stretch up to about 7% and go back without damage | Lets devices bend many times without breaking, which is important for moving through the body |
Tunability | Nickel-titanium mix can be changed to set different temperatures | Makes devices fit special jobs and body temperatures |
Fatigue Resistance | Can last over 48,000 bends at lower stretches | Makes sure devices work well for a long time |
Biocompatibility | Safe with body tissues and does not rust | Keeps patients safe and helps devices last inside the body |
Mechanical Compatibility | Strong and bendy like bone | Helps bone health and comfort, better than other metals |
Niti alloy tubing is very flexible. It bends more easily than stainless steel and beta-titanium. This is because nitinol shape memory alloys have a lower Young’s modulus in the martensite phase. They can bend a lot and still go back to their shape. Doctors use these special features to make devices that move through the body without hurting it.
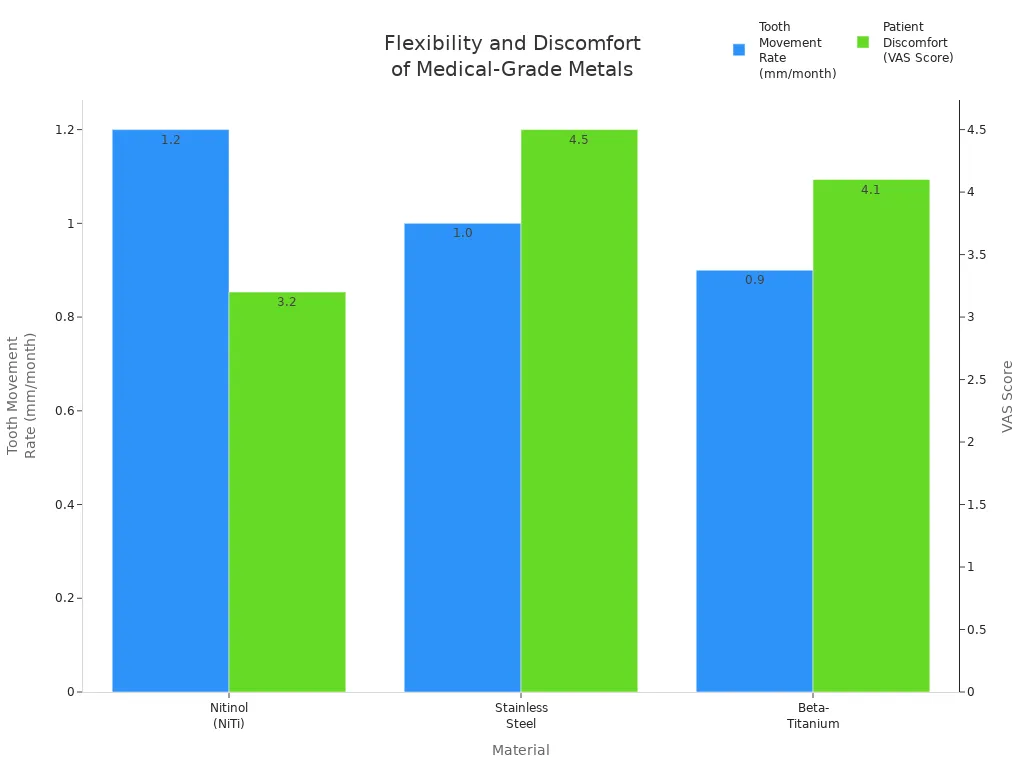
Niti tubing gives gentle, steady pressure. Patients feel less pain and get results faster, like in braces. Nitinol is great for stents, catheters, and guidewires. These tools need to bend and go back to shape many times.
Thermal Conductivity and Corrosion Resistance
Niti alloy tubing has special heat flow values. In the austenite phase, nitinol moves heat at 0.18 W/cm°C. In the martensite phase, it drops to 0.086 W/cm°C. Titanium alloys have heat flow from 6 to 20 W/m·K. These heat features help medical devices keep steady temperatures during use.
Material / Phase | Thermal Conductivity |
|---|---|
Nitinol (Austenite phase) | 0.18 W/cm°C |
Nitinol (Martensite phase) | 0.086 W/cm°C |
Titanium alloys (range) | 6 to 20 W/m·K |
Ti-6Al-4V alloy | 7 to 12 W/m·K |
Pure Titanium (room temp) | ~22 W/m·K |
Niti tubing also resists rust very well. Nitinol makes a thin oxide layer that protects it from body fluids. This strong rust resistance keeps medical devices safe and lasting longer. The TiO2 layer on the surface stops metal from leaking into the body. This layer also stops pitting rust, which can happen with chloride in blood and tissues.
Niti alloy tubing with better structure and surface coatings can slow down damage by up to 74% in tough places. This means medical devices last longer and stay safe for people.
Scientists have made coatings and new mixes to make nitinol even better against rust. These changes lower the chance of nickel getting out, which can cause allergies or problems with implants. Medical devices made from shape memory nitinol tubes are safer and last longer because of these upgrades.
Biocompatibility and Strength
Biocompatibility is very important for materials in medical devices. Niti alloy tubing is very safe for the body, so it is good for implants and surgery tools. Studies show that polishing and chemical treatments make nitinol even safer by making a strong titanium dioxide layer. This layer lowers nickel exposure and the chance of swelling.
Niti tubing passed tests on people and animals.
Scientists look at rust resistance, cell safety, and less nickel release.
Devices like the SIMON NITINOL FILTER™ and Mitek® bone suture anchors have worked well for many patients.
Coatings like TiN lower nickel release, which helps with safety.
These studies show that niti alloy tubing is very safe and resists rust, even for people sensitive to nickel.
Shape memory nitinol tubes are also very strong. Niti alloy tubing can make stress up to 700 MPa when it changes phase. This is much higher than shape memory plastics and even stronger than natural bone. The elastic modulus of nitinol is close to bone, which helps stop bone loss and keeps bones healthy.
Property/Aspect | NiTi Tubing (Additively Manufactured) | Comparison to Other Biomaterials |
|---|---|---|
Tensile Strain | Up to 15.6% (optimized SLM-NiTi, more than twice best reported) | More bendy than many other materials |
Tensile Strength (Stress) | Up to ~700 MPa (from shape change) | Stronger than shape memory plastics; stronger than bone |
Elastic Modulus | Low, close to bone | Better for implants than stiffer materials |
Shape Memory and Superelasticity | Present, allows big shape changes | Only in NiTi, good for medical uses |
Nitinol’s special features, like shape memory, superelasticity, and being safe for the body, make it the best choice for many medical devices. Niti alloy tubing helps bones, lowers pain, and makes devices last longer. The safety and rust resistance of nitinol protect patients and help them heal better.
Benefits in Medical Devices
Minimally Invasive Applications
Niti alloy tubing has changed how doctors do some surgeries. Devices made from nitinol tubing and wire can bend and move easily. They travel through the body’s tricky paths. This lets doctors make smaller cuts. Smaller cuts mean less pain and faster healing for patients. Nitinol’s shape memory helps devices fit just right inside the body. Medical grade nitinol wire keeps its shape and stays strong after many bends. These features help with catheters, endoscopes, and retrieval tools.
Primary Benefit | How It Supports Minimally Invasive Surgery |
|---|---|
Flexibility | Lets tools bend and move through the body with little damage, so doctors make smaller cuts and cause less harm. |
Shape Memory | Makes sure devices fit in place after use, which helps doctors do better work and lowers problems. |
Biocompatibility | Lowers bad reactions in the body, so devices are safe to use for a long time and keep patients safer. |
Durability | Keeps devices working after many uses, which helps patients get better results from surgery. |
Niti alloy tubing helps make very thin and bendy endoscopes and biopsy tools. These devices can reach tough spots in the body. This helps doctors find problems and makes patients more comfortable. Nitinol tubing and wire can be used in many ways. This makes surgeries safer and work better.
Patient Safety and Healing
Doctors pick niti alloy tubing because it is safe for the body. Nitinol tubing does not rust and lets out fewer bad ions. This lowers the chance of tissue problems. Medical grade nitinol wire helps stop the body from rejecting implants by about 30% more than other metals. Superelasticity in niti lets devices move with the body. This stops kinks and damage. It means fewer problems and faster healing for patients.
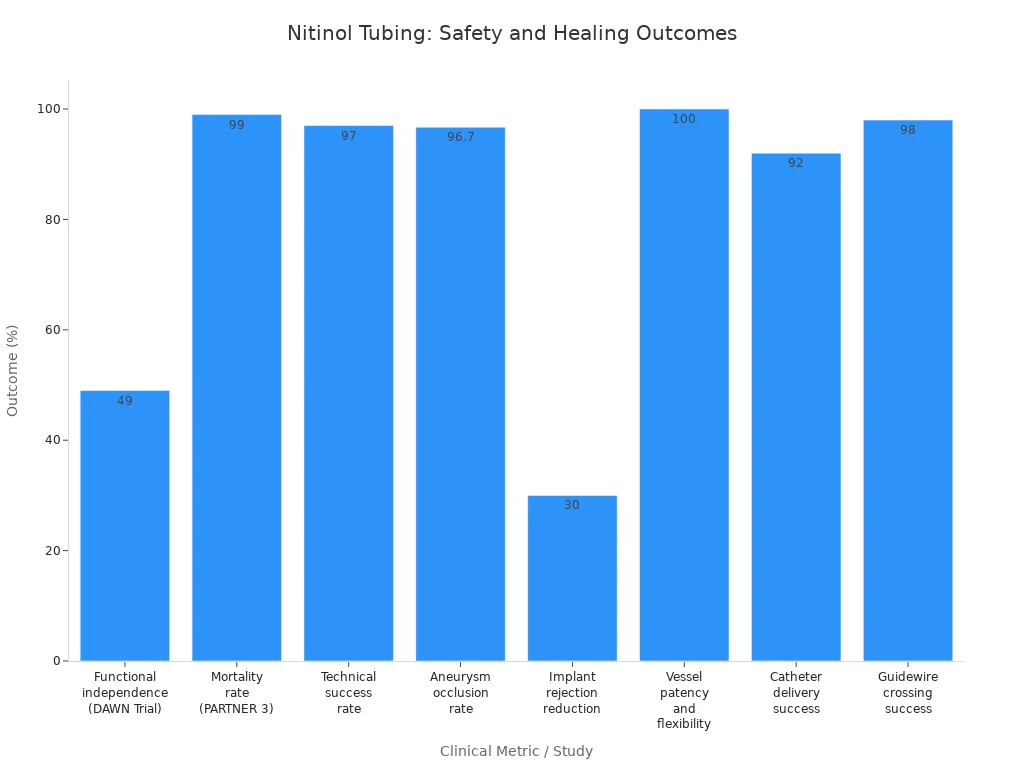
Studies show nitinol tubing and wire help patients get better. For example, the DAWN trial found that 49% of patients with nitinol devices could live on their own after 90 days. Only 13% with normal care did this well. Niti alloy tubing also helps lower death rates and makes surgeries work better. These benefits make niti a top pick for medical devices.
Nitinol Tubing and Wire in Practice
Nitinol tubing and wire are used in many medical tools. Doctors use medical grade nitinol wire in heart valves, stents, and sensors. The Amplatzer self-centering septal occluder uses nitinol wire to close heart holes in kids. Medical nitinol wire and niti alloy tubing are also in stone removers, graft stents, and special heart valves. These devices show how useful niti is in medicine today.
Niti alloy tubing works better than stainless steel and plastics in many ways. Nitinol’s superelasticity and shape memory let devices bend without breaking. Stainless steel cannot bend as much, and plastics may not be strong enough. Nitinol tubing and wire keep their shape and work after millions of uses. This makes them great for tough medical jobs. The safety and body-friendliness of niti alloy tubing help devices last longer and help patients heal.
Comparison and Considerations
Niti vs. Other Materials
Niti and nitinol are special in medical devices. They have shape memory and superelasticity. Other metals do not have these features. Niti tubing bends and goes back to its shape many times. Stainless steel and polymers cannot do this. Nitinol is strong and stays stable under stress. This makes it tough and bendy for doctors to use. Heat treatment helps niti tubing keep its shape and hold heavy things. Surface finishing, like electropolishing, helps stop rust and lowers nickel release. These steps make nitinol safer for people. Stainless steel and polymers do not have these special powers. They cannot remember their shape or be superelastic. Niti alloy tubing gives doctors more choices for hard jobs in the body.
Nitinol is flexible, strong, and safe for the body. That is why doctors use it in many medical tools.
Customization and Performance
Doctors and engineers can change niti and nitinol for different needs. They can pick the alloy, size, shape, and finish. This helps them make devices that fit each person or job. The table below shows ways to change niti alloy tubing:
Customization Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Alloy Compositions | NiTi, NiTiFe, NiTiCu, NiTiCo, NiTiCuCr, NiTiNb, etc. |
Diameter | Starting from 0.25 mm, customizable sizes available |
Shapes | Rod, Bar, Rectangular Bar, Threaded Rod, or customized shapes |
Surface Finishes | Black, Pickled, Polished |
Niti and nitinol work well for a long time in the body. Studies look at how much bending they can take before breaking. Fatigue strain limits for nitinol tubing are about 0.4–0.8%. This matters for heart valves and stents. How the tubing is made and how pure it is changes how long it lasts. A smooth surface and oxide layer help stop rust and nickel from coming out. Doctors must follow rules and test each device to keep people safe.
A rough surface can hurt tissue or cause infection.
Nickel release can make swelling or sickness.
Rust and cracks can happen if the tubing is not made well.
Testing and checking are needed for safe tools.
Niti and nitinol will be used more in the future. New ideas include 3D printing for custom parts and better bending strength. Scientists want to make shape memory and superelasticity even better. Smart materials and IoT may work with niti alloy tubing soon. These materials will help doctors care for patients in new ways.
Nitinol tubing has changed medical devices by making them stronger and safer. It is also very bendy. In the last ten years, nitinol went from simple parts to smart devices. These new devices move like real body parts and help people feel better. Studies show nitinol stents last longer and help people heal quicker.
Nitinol’s superelasticity and shape memory let devices bend and go back to shape. This helps lower pain and risk for patients.
Nitinol’s rust resistance and body safety keep patients safe when used for a long time.
Future Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
Advanced Implants and Tissue Regeneration | Nitinol implants help the body heal and grow new tissue. |
Integration with Smart Technologies | Nitinol lets smart sensors and IoT devices work better for care. |
Innovations in Manufacturing Techniques | 3D and 4D printing make custom nitinol parts that can change shape. |
Surface Modifications and Coatings | New coatings make nitinol even safer and help it last longer. |
Experts say to pick medical-grade niti tubing from good suppliers and test it for each tool. Nitinol will keep leading new ideas in medical technology.
FAQ
What makes Niti tubing different from regular metal tubes?
Niti tubing can bend a lot more than other metals. It goes back to its shape after bending. Doctors like it because it does not kink or break fast. This helps medical tools work better inside the body.
Is Niti tubing safe for people with metal allergies?
Niti tubing has a special layer that keeps nickel away from tissues. Most people do not have a reaction to it. Doctors use Niti for patients who need safe and lasting implants.
How long do medical devices made with Niti tubing last?
Niti tubing does not rust or get damaged easily. Devices made with it can last many years in the body. Tests and special layers help them stay safe and strong.
Can Niti tubing be used in children’s medical devices?
Yes, doctors use Niti tubing in tools for kids. Its bendiness and safety make it good for growing bodies. Devices can be made in many sizes for young patients.
Why do doctors prefer Niti tubing over stainless steel?
Doctors choose Niti tubing because it bends more and goes back to shape. Stainless steel can break or stay bent. Niti tubing helps tools move with the body and lowers injury risk.

