How to Select the Best Niti Tubing Size for Your Application
Choosing the right nitinol tubing for your project can be confusing because there are many options available. Understanding how to choose Niti Tubing size is essential since nitinol tubing comes in various sizes, each with its own advantages. Selecting the wrong size could lead to safety issues or poor performance. The nitinol tubing must match your project’s specific requirements, including diameter, wall thickness, and tolerance. Knowing how to choose Niti Tubing size ensures your project functions smoothly and helps avoid costly mistakes. Nitinol tubing also complies with strict industry standards, making the right choice even more important. Its popularity comes from its strength and flexibility, but how you pick the Niti Tubing size depends entirely on your application. With so many options, understanding how to choose Niti Tubing size will help you find the best fit for your needs.
Key Takeaways
Pick the nitinol tubing size that fits your project. Think about the diameter and wall thickness. This helps you get the right strength and flexibility.
Use tight tolerances, like as small as ±0.005 mm. This makes sure the tubing fits well and works safely. This is very important for medical devices, like neurovascular stents.
Choose the tubing type, either superelastic or shape memory. Pick based on how your device moves and the temperatures it will face.
Make sure the tubing meets quality standards and certifications. Look for things like ISO 13485 and ASTM F2063. These help keep the tubing safe and strong.
Think about custom tubing if you have special needs. But remember, it may take longer to get and cost more.
Project Requirements
Application Type
First, you need to know what your project is. Different industries use nitinol tubing for different reasons. In medicine, nitinol tubing is used in neurovascular stents and guidewires. Medical grade tubing must be safe for the body. This helps stop bad reactions inside people. Neurovascular stents need tubing that can stay in body fluids for a long time. Special surface treatments like electropolishing help stop rust. This is very important for medical devices.
Nitinol tubing is also used in aerospace, robotics, and cars. In these fields, you want tubing that is strong and lasts a long time. Superelastic nitinol tubing is good for medical devices that need to bend and go back to shape, like neurovascular stents and guidewires. Shape memory tubing is best for things that change shape with heat, like actuators or surgical tools. You pick between superelastic and shape memory tubing based on how the device moves and the heat it faces.
Tip: Always choose the tubing type that fits your device. Neurovascular stents need to bend and not kink. Implants that hold weight need to be strong and not rust.
Functional Demands
You also need to think about what your project needs to do. The size of nitinol tubing depends on many things, especially in medical and neurovascular uses. Here is a table that shows some important needs:
Functional Demand Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Dimensional Precision | Tight tolerances (±0.005mm to ±0.030mm) help devices fit and work well. |
Biocompatibility | Medical devices must pass ISO 10993 tests to stop bad tissue reactions, which is important for neurovascular stents. |
Fatigue Resistance | Nitinol tubing must last through millions of bends, especially in neurovascular stents that move with blood flow. |
Corrosion Resistance | Surface treatments keep tubing safe from body fluids, so it lasts longer in medical devices. |
Regulatory Compliance | Medical devices must meet ISO and CE rules for safety and tracking. |
Tubing Type | Seamless tubing is best for high-stress neurovascular stents. Welded tubing is okay for less tough devices. |
Wall Thickness | Thin walls make neurovascular stents flexible. Thick walls make implants stronger. |
Customization | You can order tubing with special sizes or features for unique medical devices. |
Medical devices often need very thin nitinol tubing. The outer diameter is usually between 0.2mm and 2mm. The wall is thin, between 0.1mm and 0.3mm. Neurovascular stents need tubing that is both flexible and strong. Thin walls help the stent move through small blood vessels. The tubing still needs to be strong so it does not bend out of shape. You also need to think about where the tubing will be used. For example, neurovascular stents are in body fluids that can cause rust. So, you need tubing that does not rust easily.
Nitinol tubing can bend and handle stress many times. This makes it great for neurovascular stents and other medical devices. You should always check that the tubing meets all quality and safety rules. This keeps people safe and makes sure the tubing works in neurovascular procedures.
How to Choose Niti Tubing Size

Selecting the right nitinol tubing for your project starts with understanding tubing size and diameter. You need to match the size to your application for the best performance and safety. Knowing how to choose niti tubing size helps you avoid mistakes and ensures your device works as planned.
Tubing Size and Diameter
Nitinol tubing comes in many sizes. You can find outer diameters as small as 0.25 mm and as large as 10 mm. Most medical devices, like neurovascular stents, use tubing with diameters between 0.2 mm and 2 mm. For industrial uses, you might need larger sizes. The right tubing size and diameter depend on your project’s needs.
Here is a table showing standard nitinol tubing dimensions:
Specification | Range |
|---|---|
Outer Diameter | 0.25 mm to 7.0 mm |
Inner Diameter | 0.3 mm to 8 mm |
Wall Thickness | 0.05 mm to 0.5 mm |
You can also find nitinol tubing with diameters from 0.5 mm up to 10 mm. Some suppliers offer even smaller sizes for special uses. When you choose a size, think about how the tubing will fit in your device. Smaller diameters and thinner walls make the tubing more flexible. This is important for devices that need to move or bend, like neurovascular stents. Larger diameters and thicker walls make the tubing stronger but less flexible.
Tip: For dimensional considerations for neurovascular stents, use tubing with an outer diameter between 0.2 mm and 2 mm and wall thickness between 0.05 mm and 0.3 mm. This balance gives you both flexibility and strength.
The size you pick affects how well the tubing works. If you choose a size that is too big, it may not fit your device. If you choose a size that is too small, it may not be strong enough. Always check the dimensions before you order.
Wall Thickness and Tolerances
Wall thickness is another key part of how to choose niti tubing size. Thin walls make the tubing easy to bend. Thick walls give the tubing more strength. You need to match the wall thickness to your project’s needs.
Precision is very important when you pick nitinol tubing. Manufacturers control wall thickness and diameter with tight tolerances. Tolerances show how much the actual size can differ from the target size. For example, a tolerance of ±0.01 mm means the size can be a little bigger or smaller, but not by much.
Here is a table showing industry-accepted tolerances for nitinol tubing:
OD Range (mm) | OD Tolerance (mm) | ID Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|---|
≤ 0.3 | ±0.005 | ±0.010 |
0.3 to 0.5 | ±0.007 | ±0.015 |
0.5 to 1.5 | ±0.015 | ±0.020 |
1.5 to 2.5 | ±0.020 | ±0.030 |
2.5 to 3.5 | ±0.020 | ±0.040 |
Wall thickness tolerances are usually within ±0.01 mm. This level of precision and tolerances is needed for medical devices. It helps the tubing fit perfectly and work safely.
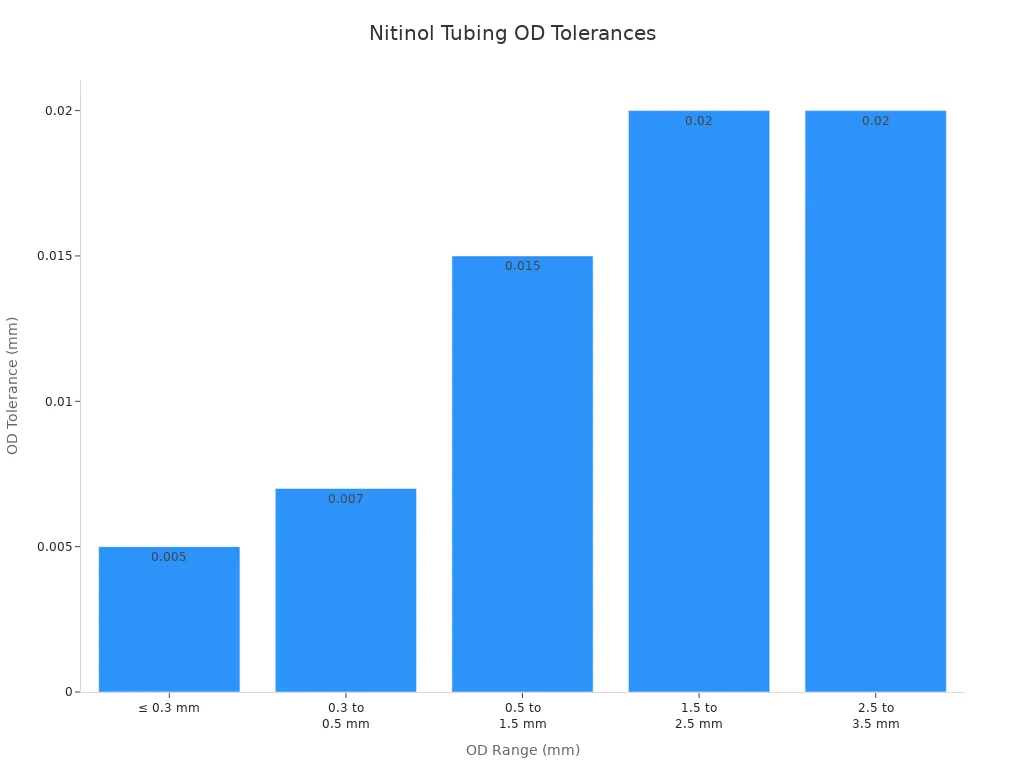
Tight tolerances in nitinol tubing help you get a precise fit. This is very important for devices that go inside the body. If the tubing is not the right size, it may not work or could even be unsafe. High precision also keeps the tubing strong and durable. For example, a heart stent needs an outer diameter tolerance as tight as ±0.005 mm and wall thickness within 0.01 mm. This ensures the stent fits well and lasts a long time.
Precision also affects the surface finish. A smooth surface reduces the risk of corrosion and helps the tubing last longer. Manufacturers use special tools and machines to keep the diameter and tolerance exact. Even small changes in size can cause problems, so you must always check the tubing size and tolerances before using it.
Note: Always ask your supplier for the exact dimensions and tolerances. This helps you avoid problems and makes sure your device meets all safety rules.
When you learn how to choose niti tubing size, you see that size, dimensions, and precision matter at every step. The right tubing size and tolerances help your device fit, stay strong, and last longer. This is why you must pay close attention to diameter and tolerance when you select nitinol tubing.
Nitinol Tubing Performance

Flexibility and Strength
You want nitinol tubing that bends but does not break. The tubing size affects how much it can bend. Small-diameter nitinol tubing is very flexible and superelastic. This is needed for neurovascular stents and guidewires. These devices must move through tiny, twisty blood vessels. Thin walls and small sizes help the tubing bend without breaking or kinking. This makes neurovascular procedures safer and helps the stent fit well.
Bigger nitinol tubing sizes are stronger. These are used more in cars or factories. In medical work, you need tubing that bends and goes back to shape. Both diameter and wall thickness change how the tubing works. You must find the right mix of flexibility and strength for each device. Neurovascular stents need tubing that bends but also keeps its shape under pressure.
Here is a table that shows how tubing size and wall thickness change flexibility and strength in different uses:
Tubing Size Range | Wall Thickness | Flexibility Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
0.2 mm to 2 mm OD | As thin as 0.05 mm | High flexibility, kink resistance, superelasticity | Neurovascular stents, guidewires, catheters |
2 mm to 15 mm OD | Moderate thickness | Moderate flexibility, more strength | Automotive sensors, actuators |
5 mm to 25+ mm OD | Thick walls | Low flexibility, high strength | Aerospace, structural parts |
Tip: For neurovascular stents, pick nitinol tubing with a small size and thin walls. This gives you the best flexibility and accuracy.
Fatigue Resistance
You want your neurovascular stents to last a long time in the body. Nitinol tubing is special because it can bend many times and not break. This is called fatigue resistance. In medical uses, the tubing moves a lot from blood flow and body movement. High fatigue resistance means the tubing keeps working for years.
Smaller nitinol tubing sizes last longer when bent many times. Thin walls and even thickness help the tubing survive longer. If the wall thickness is not even, the tubing can break sooner. Making the tubing with care is very important. For neurovascular stents, nitinol tubing can last up to 400 million bends in body-like conditions without breaking. This makes it great for long-term medical implants.
Manufacturers use special steps like electropolishing to make the tubing smooth. This helps lower stress and makes the tubing last longer. You should always check that your nitinol tubing meets the right rules for fatigue resistance, especially for neurovascular stents and other important medical devices.
Note: Always ask for test results on fatigue resistance when you buy nitinol tubing for neurovascular stents or other medical devices. This helps make sure your device will last and work safely.
Shape Memory Alloy Tubing Factors
Environmental Conditions
When you pick shape memory alloy tubing, think about where it will be used. Nitinol tubing can change when the temperature, humidity, or chemicals around it change. In medical devices, the tubing touches body fluids and must stay safe for a long time. If you use nitinol tubing in wet places or near strong chemicals, check if it can resist rust. Surface treatments like electropolishing help stop rust and make the tubing last longer.
Tiny non-metallic spots inside nitinol tubing can make it weaker. These small spots are weak points and can cause the tubing to break sooner. Manufacturers work carefully to lower these spots and make the tubing stronger. In medical devices, you want shape memory alloy tubing to last through many bends. Tests at body temperature show how nitinol tubing handles stress. These tests help you know how long the tubing will last in real life.
Temperature changes also affect shape memory alloy tubing. The tubing changes from martensite to austenite when it gets warmer. This change gives nitinol tubing its special shape memory effect. If the tubing gets too hot for too long, it can lose its superelastic abilities. You must keep the tubing in the right temperature range for your device.
Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
Martensite start temperature | 43 °C | Tubing starts to change phase |
Martensite finish temperature | 32 °C | Tubing finishes phase change |
Young's modulus (Austenite) | 69 ± 1 GPa | Stiffness at high temperature |
Young's modulus (Martensite) | 26 ± 1 GPa | Stiffness at low temperature |
Logistic function midpoint (Tm) | 38.3 °C | Middle of phase change |
Logistic function slope (k) | -1.4 (°C)^-1 | Rate of change with temperature |
If you raise the programming temperature, the tubing may not return to its old shape as well. This means the recovery ratio drops. The nickel-titanium mix in nitinol tubing can also change the temperature when the tubing changes phase. You can adjust this mix to make the tubing work better for your needs.
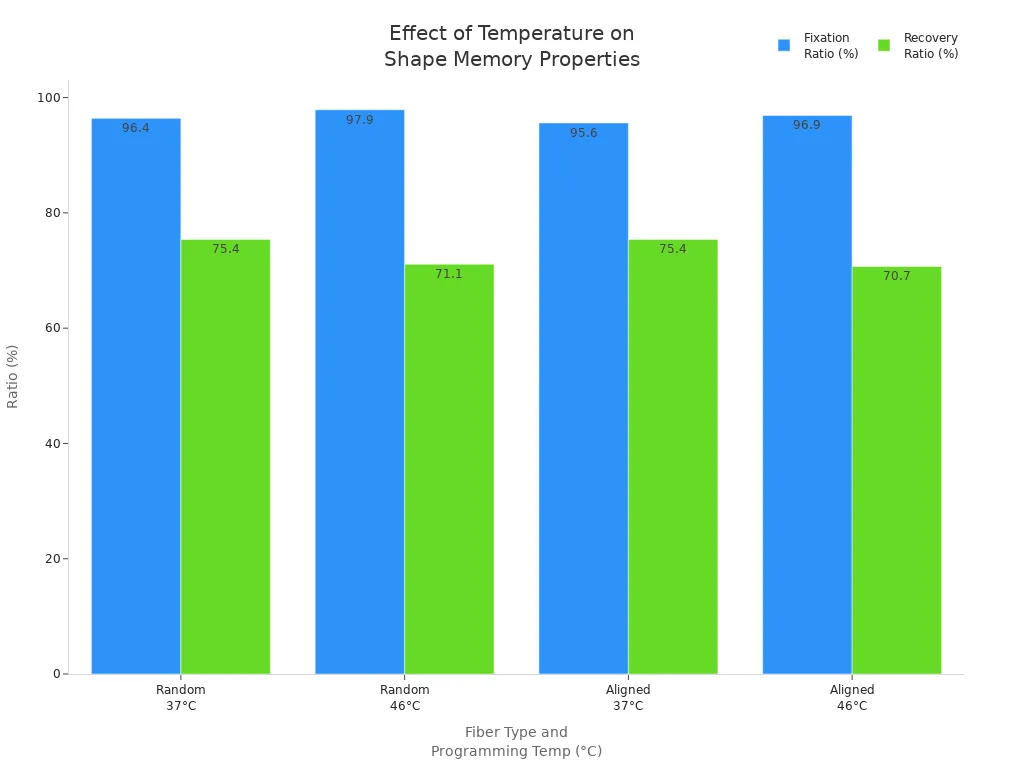
Tip: Always match the tubing’s phase change temperature to your device’s working temperature. This helps your device work well and fit neurovascular procedures.
Regulatory Standards
You have to follow strict rules when using shape memory alloy tubing in medical devices. Standards like ASTM F2063 and ASTM F2082 tell you what nitinol tubing must be like. These rules cover what is in the tubing, how strong it is, and how smooth the surface is. For example, ASTM F2063 says the nickel content must be between 54.5% and 57%. This keeps the tubing’s shape memory and superelastic abilities steady.
Regulatory Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Chemical Composition | Nickel-titanium mix must be controlled for stable properties and safety in neurovascular uses |
Mechanical Properties | Shape memory effect, superelasticity, strength, and fatigue resistance are needed |
Performance Requirements | Fatigue life, rust resistance, and tight size limits must be tested |
Biocompatibility | Passivation lowers nickel ion release for patient safety |
Manufacturing Controls | Careful processing and surface finishing are needed |
Certification | ASTM F2063 certification is needed before medical use |
Quality Assurance | Tests for strength, stretch, and density make sure each batch is the same |
You must make sure your shape memory alloy tubing passes all these tests. The tubing should have high fatigue resistance, strong rust resistance, and be safe for the body in neurovascular uses. Surface treatments like electropolishing and passivation help meet these rules. Certification shows your nitinol tubing is safe and works well for medical use.
ASTM F2082 checks for superelasticity and shape memory effect.
The standard says you must test for fatigue resistance and rust resistance.
Following these rules helps doctors and patients trust your device.
Note: Always ask your supplier for proof of certification and test results. This helps you follow safety rules and get the best results for your device.
Supplier and Custom Options
Quality Assurance
When you pick nitinol tubing for medical or neurovascular stents, you need to trust your supplier’s quality checks. Good suppliers use ISO 13485:2016 to guide their quality system. This system covers every step, from raw materials to finished tubing. They keep careful records and track each batch and inspection. Suppliers use special tools to check size, smoothness, and material quality. They use machines to measure every piece, so it fits your neurovascular device.
Suppliers also test their process and use data to keep things the same. Cleanrooms stop dirt from getting on medical tubing. Audits happen often to make sure rules are followed. Digital systems track every step, including device history. Risk checks help find and fix problems early. Workers get training so they know how to follow the rules for medical and neurovascular work.
Tip: Always look for certifications like ISO 13485 and ASTM F2063. These show the supplier meets tough rules for medical and neurovascular stents.
Custom Sizing
Sometimes you need nitinol tubing with special sizes or features for neurovascular stents or other medical devices. Top companies let you pick wall thickness, diameter, and shape memory features for neurovascular uses. The table below shows what some top suppliers offer:
Manufacturer | Customization Options | Certifications & Quality Standards |
|---|---|---|
Euroflex GmbH | Custom wall thickness, diameter, shape memory | ISO 13485, ASTM F2063 |
Metalwerks, Inc. | Custom dimensions, tolerances, performance | ISO 9001, AS9100 |
Fort Wayne Metals | Tailored solutions for medical-grade tubing | - |
Memry Corporation | Precise dimensions, surface finishes | - |
AccuPath | Adjust tubing dimensions, surface finishes | - |
Custom nitinol tubing for neurovascular stents takes longer and costs more than regular sizes. Standard tubing ships in about 30 to 45 days, but custom orders can take 90 to 120 days. The price per kilogram is much higher for custom tubing. You also get fewer good pieces and pay more for extra steps. Custom tubing for neurovascular uses needs special making and strict checks.
Note: Always ask about wait times, order size, and costs before you buy custom nitinol tubing for medical or neurovascular devices.
To pick the right nitinol tubing for your neurovascular project, use these steps: First, decide if your device will stay still or move in the body. Next, pick superelastic or shape memory nitinol tubing for your needs. Then, make sure you ask for the exact diameter and tight tolerance for your device. After that, check that the transformation temperature fits your neurovascular use. If your project is tricky, talk to experts for help.
For advanced neurovascular devices, companies like Seisa Medical and TE Connectivity give expert help, technical tools, and advice. They help you follow strict neurovascular and medical rules.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing ideal for neurovascular stents?
Nitinol tubing is great for neurovascular stents because it bends easily. It goes back to its original shape after bending. This helps the stent move through tiny neurovascular vessels. The tubing does not get tired or break quickly. This means your neurovascular device can last a long time in the body.
How do you select the right nitinol tubing size for neurovascular applications?
First, measure the size of the neurovascular vessel. Pick tubing with the right diameter and wall thickness for your device. Always make sure the tubing meets neurovascular safety rules. Ask your supplier for test results before you buy.
Why is wall thickness important in neurovascular nitinol tubing?
Wall thickness changes how flexible the tubing is. Thin walls let your neurovascular stent bend and move in small spaces. Thick walls make your device stronger. You need to find a good balance between flexibility and strength for safety.
What tolerances should you look for in neurovascular nitinol tubing?
You need very tight tolerances for neurovascular tubing. Look for outer diameter tolerances as small as ±0.005 mm. This helps your device fit just right. Tight tolerances also help your stent work well and last longer.
Can you customize nitinol tubing for neurovascular devices?
Yes, you can get custom nitinol tubing for neurovascular devices. You can choose the diameter, wall thickness, and shape memory features. Custom tubing takes more time to make. Always ask about how long it will take and how much it will cost.
See Also
Choosing The Ideal Nitinol Tubing Supplier For You
A Detailed Guide To Selecting Proper Nitinol Tubing
Finding The Most Cost-Effective 2mm Nitinol Tubing Supplier

