What makes heat shrink tubing MRI compatible

You need heat shrink tubing for MRI compatible cables that follows tough MRI rules. Non-magnetic and non-metallic materials stop problems. Biocompatible choices keep patients safe. Medical rules help make things safe. When you pick heat shrink tubing for MRI compatible cables, you make them work better and last longer. Heat shrink tubing also provides important insulation and protection.
Key Takeaways
Pick heat shrink tubing that is not magnetic or metal. This helps keep MRI scans safe and clear. - Check that the tubing follows medical rules like USP Class VI and ISO 10993. This keeps patients safe and stops germs from spreading. - Use a simple checklist when you pick heat shrink tubing. Make sure it fits right, can be cleaned with heat, and has safety labels.
Key Materials and Properties of Heat Shrink Tubing
Non-Magnetic and Non-Metallic Materials
When picking heat shrink tubing for MRI compatible cables, you need to use non-magnetic and non-metallic materials. These materials help keep MRI scans clear and safe. Magnetic metals can mess up images or cause safety problems. You should not use anything that could cause trouble in the MRI room.
Some common non-magnetic and non-metallic materials for heat shrink tubing are:
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride)
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
These materials give great insulation and stop contamination. They also protect medical devices well. PVDF and FEP are picked a lot because they are safe for the body and stay strong. The chart below shows how PVDF and FEP are different:
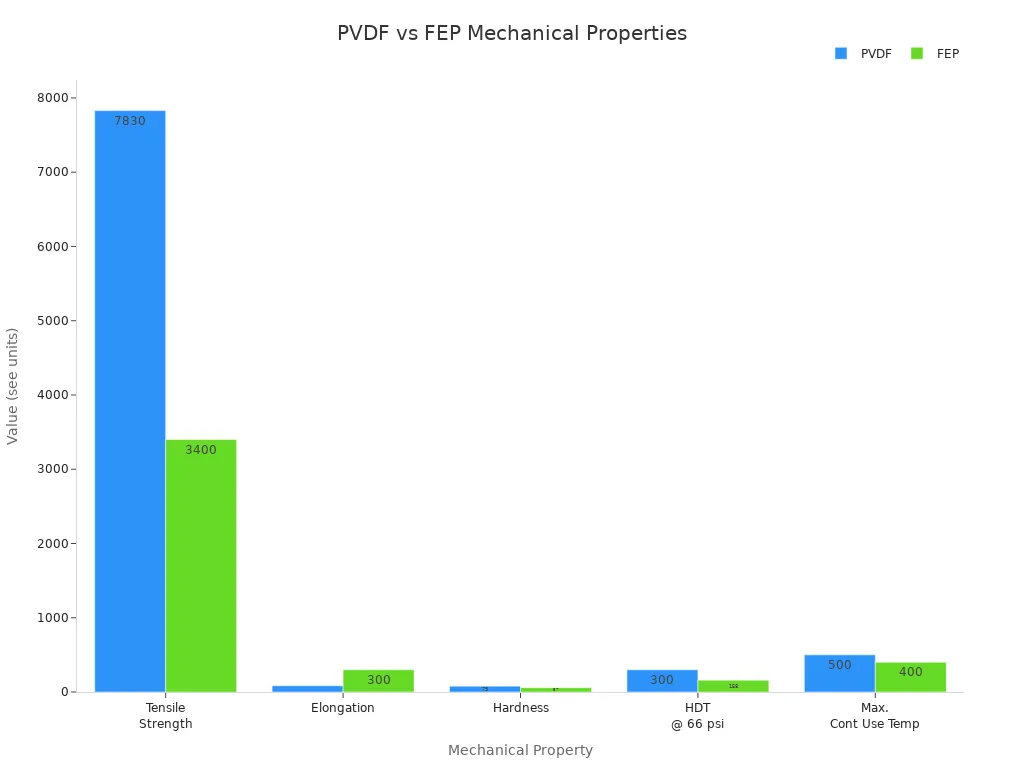
The chart shows PVDF is stronger and harder. FEP can stretch more. Both are good for heat shrink tubing in MRI rooms.
Biocompatibility and Medical Grade Standards
You have to make sure heat shrink tubing follows strict medical rules. Medical grade heat shrink tubing keeps patients safe and stops contamination. It must be safe to use with medical devices and not cause bad reactions.
Look for tubing that meets these rules:
Medical-grade FEP heat shrink tubing meets USP Class VI biocompatibility.
It also follows ISO 10993 standards.
These rules show the tubing is safe for medical use and will not hurt patients. Following health rules is very important. Always check for these labels before using tubing in medical devices. This helps stop contamination and makes sure the tubing works with other materials.
Durability in MRI Environments
Heat shrink tubing must be tough in MRI rooms. It needs to handle lots of cleaning and sterilization. The tubing should stay strong and keep protecting over time. The table below shows important features:
Evidence Description | Detail |
|---|---|
Non-magnetic properties | Stops mistakes in MRI scans and keeps results clear. |
Strength retention | PET tubing keeps 98% of its strength after 2,000 uses, so it lasts through many procedures. |
FDA compliance | Follows safety rules for medical use, so it is trusted in hospitals. |
Sterilization resistance | Handles 135°C autoclaving, so it works for tools that get cleaned a lot. |
You need heat shrink tubing that can go through many cleaning cycles. PET heat shrink tubing can handle big changes in temperature. This matters because MRI rooms can get very hot or cold. PET tubing also stands up to strong cleaning chemicals. This keeps the insulation from breaking down. It helps your medical cables last longer and makes devices last more years.
Sterilization is very important in medical work. You want tubing that stays strong after being cleaned many times. This keeps your devices safe and working well. When you choose medical grade heat shrink tubing, you help stop contamination and make sure your devices last longer.
Tip: Always check if your heat shrink tubing can handle being cleaned many times. This helps you avoid trouble and keeps your medical devices working right.
By choosing non-magnetic, non-metallic, and medical grade materials, you make sure your heat shrink tubing is ready for MRI rooms. You also help follow health rules and make your devices last longer.
Selecting Heat Shrink Tubing for MRI Compatible Cables
Standards and Certifications for Medical Grade Heat Shrink Tubing
You need to look for important standards when picking heat shrink tubing. These standards show the tubing is safe for medical devices. They also show it works well in MRI rooms. Certifications prove the tubing follows strict rules for safety and quality.
Here is a table that explains some main compliance standards:
Compliance Standard | Description |
|---|---|
ISO 10993 | Biocompatibility standard for medical devices |
UL | Safety certification for materials |
Sterilization Compatibility | Works with autoclaving, gamma irradiation, or ethylene oxide |
You should check for these features in medical grade heat shrink tubing:
ISO 9001 certification means high quality.
Traceability helps meet FDA rules.
USP Class VI materials are safe for medical devices.
PVC and phthalate-free options meet RoHS2, WEEE, and REACH rules.
UL certification is very important in the United States. It checks for electrical insulation and flame resistance. It also checks temperature strength. In Europe, you may see other marks. The main idea is the tubing must keep devices safe and reliable.
Tip: Always ask your supplier for certificates and test reports. This helps you make sure the tubing meets all medical rules.
Testing for MRI Compatibility
You want to make sure heat shrink tubing does not cause problems during MRI scans. Testing helps you know the tubing is safe. It should not heat up or move in the MRI field.
Manufacturers use many tests to check MRI compatibility:
RF-induced heating tests check if tubing gets too hot.
Temperature is measured before and after MRI starts.
Polyimide tubes and polyester heat shrink tubing are tested on guidewires.
In vitro tests use acrylic phantoms to copy real MRI conditions.
ASTM 2182 is a common standard for these tests.
Fiber optic temperature probes track heat during special MRI sequences.
Tubing is placed at the center of the scanner to see how it reacts.
These tests help you know the tubing will not hurt patients or mess up images. You should always ask for test results when you buy heat shrink tubing for MRI compatible cables.
Practical Selection Checklist
You need a simple checklist to help pick the right heat shrink tubing. This list helps you check all important points before you buy.
Step-by-step checklist:
Measure the diameter of the thinnest part of your cable.
Pick tubing with a diameter 20-30% bigger than your cable.
Check the shrink ratio to make sure the tubing fits tight after heating.
Make sure the tubing material is biocompatible and can handle sterilization.
Confirm the tubing can take the heat and chemicals used in cleaning.
Look for ISO, UL, or ASTM certifications.
Check if the tubing is easy to use with your tools.
Make sure the tubing stays strong and flexible after bending.
Ask for datasheets and technical help from your supplier.
Here is a table to help you compare different types of heat shrink tubing:
Material | Operating Temperature | Shrink Ratio |
|---|---|---|
PVC | -20°C to 105°C | 2:1 |
Polyolefin | -55°C to 135°C | 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 |
Adhesive Lined | -45°C to 125°C | 3:1, 4:1 |
Teflon | up to 500°F (260°C) | Specifications |
Specialty | -55°C to 200°C | Specifications |
You should also check these points:
Make sure the tubing fits your cable and protects it well.
Confirm the tubing can handle the temperatures in your MRI room.
Choose a supplier who gives you good support and clear documents.
Note: Suppliers can help you pick the best heat shrink tubing for MRI compatible cables. They offer expert advice, custom sizes, and strong quality control. This makes sure your devices work well and last longer.
When you follow this checklist, you help your medical devices stay safe. You also help them work well in MRI environments. Your devices last longer and meet all safety rules.
You make MRI rooms safer by picking the right heat shrink tubing. The table below lists important things for safety and better protection:
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Material Compatibility | Keeps patients safe during MRI scans |
Thickness Requirement | Helps control heat for safety |
Thermal Impedance | Keeps things safe by managing temperature |
You should always look at the rules and talk to suppliers. This helps you keep devices safe and put safety first.
FAQ
What does MRI compatible mean for heat shrink tubing?
MRI compatible means you can use the tubing near MRI machines. The tubing will not cause image problems or safety risks.
Can you reuse heat shrink tubing after sterilization?
You should not reuse heat shrink tubing. Most tubing is for single use. Reusing can lower safety and performance.
How do you know if tubing is non-magnetic?
You can check the product datasheet. You can also ask your supplier for test results. Non-magnetic tubing will not react to magnets.
See Also
The Importance of Gamma Radiation Resistant Tubing in Healthcare
Comparing Medical and Industrial Grade Heat Shrink Tubing
The Significance of Ultra-Thin PET Tubing in Medicine
Selecting Optimal FEP Biocompatible Tubing for Various Uses
Applications of Heat Shrink Tubing for Electrical Wire Insulation
