Why FDA Registration Is Essential for Nitinol Tubing Suppliers in the USA

FDA registered nitinol tubing suppliers USA play a critical role in the medical device industry. FDA registration requires suppliers to follow strict scientific and statistical standards, ensuring nitinol tubing meets high safety and quality benchmarks for medical use. Suppliers must provide well-controlled clinical data, showing that nitinol devices deliver consistent safety and effectiveness for patients. Choosing certified manufacturers with ISO 13485 certification supports safety, quality, and regulatory trust. Medical device companies rely on suppliers who meet these standards, knowing that ISO 13485 certification, safety, and quality are non-negotiable. FDA registered nitinol tubing suppliers USA demonstrate a commitment to safety, quality, and the best outcomes for medical applications.
Key Takeaways
FDA registration is a legal must for all nitinol tubing suppliers in the USA to ensure product safety and quality.
Following FDA rules and ISO 13485 certification helps suppliers maintain strong quality systems and meet strict medical standards.
Non-compliance with FDA regulations can cause serious legal trouble, financial penalties, and loss of market access.
Certified suppliers gain trust from medical device companies, improving patient safety and speeding up product approval.
Choosing FDA registered and ISO certified suppliers supports reliable products, protects patients, and boosts business growth.
FDA Registration for Nitinol Tubing Suppliers

What FDA Registration Means
FDA registration serves as a mandatory process for all establishments involved in manufacturing, processing, packing, or holding medical devices like nitinol tubing for sale in the United States. The FDA uses this registration to track the locations and activities of these suppliers, ensuring that every nitinol product meets strict medical safety and quality standards. Registration is not optional; it is a legal requirement for any company producing or distributing nitinol tubing as a medical device. This process helps the FDA respond quickly to public health concerns and maintain oversight of the entire supply chain. Suppliers who complete FDA facility registration show their commitment to regulatory standards and compliance with industry regulations. The FDA’s definition of a medical device includes instruments, implants, or materials like nitinol tubing that diagnose, treat, or prevent disease. By registering, suppliers demonstrate their dedication to safety, efficacy, and compliance.
Note: FDA registration applies to all businesses in the nitinol tubing supply chain, including manufacturers, distributors, and importers. This broad coverage ensures that every step in the process meets regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Oversight and Traceability
Regulatory oversight by the FDA ensures that nitinol tubing suppliers follow strict compliance protocols. The FDA enforces 21 CFR Part 820, which sets out requirements for testing, record-keeping, quality control, and documentation. These rules guarantee that every nitinol product is safe and effective for medical use. Suppliers must maintain a robust Quality Management System (QMS) and provide continual staff training to meet compliance standards. Design Controls require suppliers to validate and verify each nitinol tubing batch, keeping detailed Design History Files for traceability. Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) help identify and fix problems, supporting ongoing regulatory compliance.
The FDA uses advanced tools, such as AI-powered audits and centralized QMS platforms, to monitor compliance with industry regulations. These systems provide real-time traceability, document approvals, and automated CAPA workflows. Internal audits and mock FDA facility inspections prepare suppliers for regulatory reviews. The modular structure of 21 CFR Part 820 covers all stages of the medical device lifecycle, from design to distribution. Subpart F requires proper identification and traceability of nitinol tubing, while Subpart M mandates the creation of Device Master Records and Device History Records. These records ensure that every nitinol product can be traced back to its source, supporting accountability and compliance.
Case Example | Consequence | Reason for Legal Action |
|---|---|---|
United States ex rel. Crocano v. Trividia | FCA liability (amount N/A) | Non-compliance with FDA regulations |
United States ex rel. Wu v. Alere San Diego | $33.2 million settlement | Erroneous rapid testing device results |
AmerisourceBergen Corp Settlement | $625 million settlement | Sterility violations in injectable drugs |
United States ex rel. Wall v. Baxter Int'l | $18 million settlement | Manufacturing violations causing adulteration |
These cases show that non-compliance with FDA regulations can lead to severe legal and financial consequences. Suppliers who follow FDA registration, maintain ISO 13485 certification, and meet regulatory standards protect their reputation and ensure patient safety. Compliance with FDA regulations, ISO 13485 certification, and robust traceability systems are essential for nitinol tubing suppliers in the medical industry.
Key FDA and Quality Requirements
21 CFR Part 820 Compliance
Nitinol tubing suppliers must follow 21 CFR Part 820, which sets the foundation for quality in medical device manufacturing. This regulation, known as the Quality System Regulation (QSR), outlines the steps for achieving compliance. Suppliers develop and maintain a quality management system that defines clear quality policies and objectives. Management takes responsibility for quality goals and provides resources, including trained staff and proper infrastructure. Employees receive ongoing training to understand their roles in compliance and quality.
Suppliers use secure systems for document control, ensuring all records are accessible and up to date. Facility and equipment controls prevent contamination and maintain product safety. Regular internal audits help identify gaps and improve processes. The Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) process addresses nonconformities and prevents them from recurring. Suppliers keep comprehensive records using advanced software, which supports regulatory requirements and real-time monitoring. They review and update procedures regularly to keep up with changing regulations.
Tip: A strong quality management system helps nitinol tubing suppliers avoid costly delays and ensures compliance with FDA regulations.
Key steps for 21 CFR Part 820 compliance include:
Develop and maintain a comprehensive quality management system.
Ensure management accountability and resource management.
Implement thorough employee training.
Establish and maintain document controls.
Maintain facility and equipment controls.
Conduct regular internal audits.
Implement CAPA processes.
Maintain comprehensive records.
Leverage advanced tools and automation.
Continuously review and update procedures.
ISO 13485 and Certified Manufacturers
Certified manufacturers of nitinol tubing must achieve ISO 13485 certification to meet global regulatory requirements. This standard adds specific requirements for medical devices, such as risk management, documentation, and supply chain auditing. Certified manufacturers follow current good manufacturing practices and demonstrate their commitment to safety and quality. They keep detailed device history records and undergo annual audits to ensure compliance.
ISO 13485 certification provides objective third-party evaluation, proving product safety and quality. Certified manufacturers gain global recognition and easier market access. Many medical device companies prefer working with certified manufacturers because certification reduces costs, avoids recalls, and supports regulatory compliance. Certification also helps automate tasks, manage risks, and centralize documentation for quality assurance agreements.
Key requirements for ISO 13485-certified manufacturers include:
Device master records that define quality management systems.
Feedback and review systems for non-conformance detection.
Monitoring and measuring product quality throughout production.
Documentation of advisory notices, rework, and release of non-conforming products.
Access to procedures and reference materials at the point of work.
Unique records for every approved device batch.
Documented installation, verification, and servicing activities.
Regular management review of quality management system goals and compliance.
Procedures for shelf life, data analysis, risk management, adverse event flagging, product conformity, and labeling.
Note: ISO 13485 certification supports compliance with FDA regulations and strengthens the safety and quality assurance chain in medical nitinol tubing production.
Cleanroom Standards and Biocompatibility
Cleanroom standards play a vital role in the production of medical nitinol tubing. Cleanrooms control contamination by maintaining strict temperature, humidity, pressure, and cleanliness levels. Suppliers design cleanrooms according to ISO 14644 standards, matching the ISO classification with process risk. Integrated monitoring systems, such as particle counters and pressure sensors, help maintain compliance and support regulatory requirements.
Personnel behavior and adherence to standard operating procedures prevent contamination. Regular maintenance and requalification keep cleanrooms compliant over time. Documentation and audit readiness are necessary for inspections. Prefabricated cleanrooms offer precise solutions that simplify compliance and speed up qualification. Real-time environmental monitoring ensures continuous audit readiness and regulatory alignment.
Biocompatibility is essential for medical nitinol tubing. Suppliers use materials that are compatible with medical devices and cleaning agents, such as stainless steel 316L. Surface finishes must allow for easy cleaning and microbial control. Equipment design supports effective cleaning and sterilization, including clean-in-place and sterilize-in-place systems. Control systems ensure data integrity and support FDA compliance. Preventive maintenance, change control, and requalification maintain compliance and biocompatibility throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Callout: Cleanroom standards and biocompatibility protect patient safety and support regulatory approval for medical nitinol tubing.
Quality and Compliance Metrics for Nitinol Tubing
Metric / Aspect | Evidence / Result |
|---|---|
Technical success rate | 97% success in clinical applications (70 of 72 patients) demonstrating high reliability of ASTM F2063 certified nitinol tubing. |
Complete aneurysm exclusion | 79.2% (57 of 72 patients) showing effective medical outcomes linked to certified tubing. |
Aneurysm occlusion at 12 months | 96.7% (29 of 30 patients) indicating sustained performance and safety. |
FDA clearance delays | 75% of medical device companies experience 12–18 month delays due to compliance challenges. |
R&D cost increase | Compliance with FDA and ASTM standards raises R&D costs by 18–25%, impacting time-to-market and ROI. |
Testing protocols | Includes tensile strength, thermal analysis, biocompatibility, mechanical reliability, and fatigue resistance, all essential for safety and performance. |
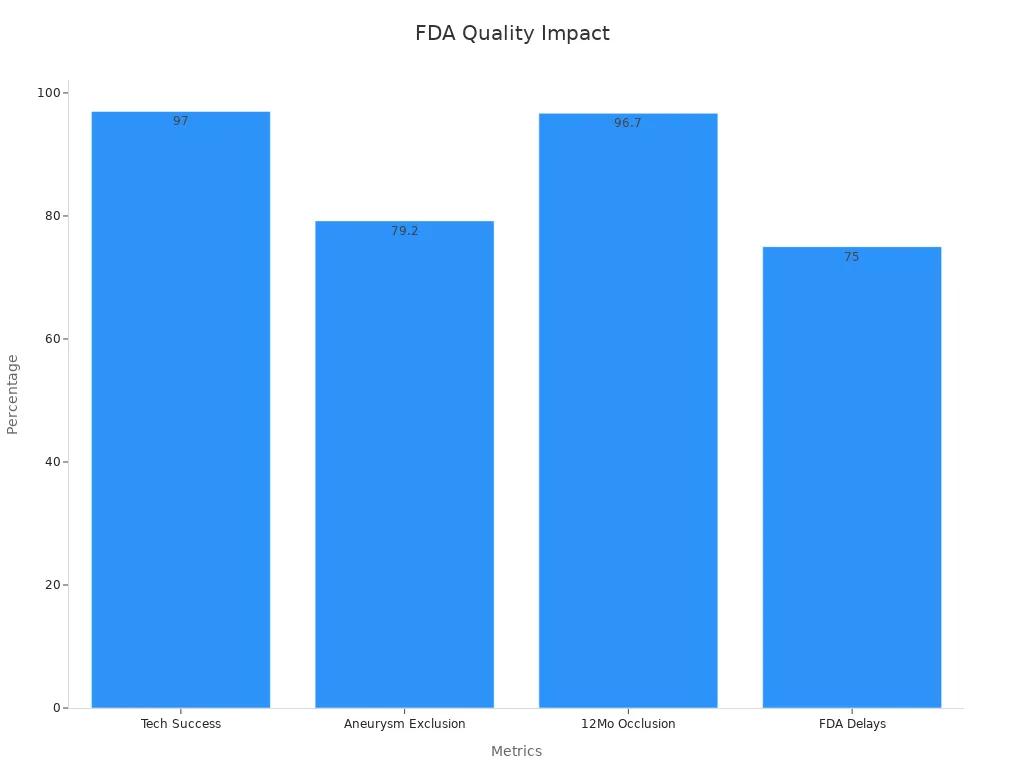
These statistics show that strict adherence to FDA and quality requirements for nitinol tubing suppliers is critical. High technical success rates and sustained safety in clinical outcomes depend on certified manufacturers, robust quality management systems, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Delays and increased costs often result from poor compliance, highlighting the importance of meeting FDA, ISO 13485 certification, and current good manufacturing practices in medical device production.
Risks of Non-Compliance for Certified Suppliers
Legal and Regulatory Consequences
Certified suppliers of nitinol tubing in the medical field face serious risks if they fail to meet FDA requirements. The FDA enforces strict compliance for all medical nitinol products. Suppliers who do not register or maintain certification can face import refusals, product seizures, and even criminal prosecution. The FDA can suspend facility registration, stopping the distribution of nitinol tubing for medical use. Courts may order injunctions, forcing certified manufacturers to halt operations until they resolve compliance issues.
The FDA’s authority comes from the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. This law allows the FDA to take action against suppliers who do not follow regulatory rules. Recent legal cases show that the FDA uses a wide range of evidence to prove violations, including off-label promotion and misbranding. Courts support the FDA’s broad enforcement powers, which increases the risk for certified suppliers who do not comply.
Aspect | Evidence | Implication for Legal Risks and Market Access |
|---|---|---|
High-risk devices (Class III) | Represent about 1% of devices regulated annually but account for ~10% of medical device spending ($13 billion in 2008 on top 6 devices) | High regulatory scrutiny due to safety and effectiveness requirements increases compliance burden; non-compliance risks legal action and market denial |
Regulatory framework evolution | FDA authority over devices solidified post-1976 Medical Device Amendments Act; devices classified by risk (low, moderate, high) | Clear regulatory categories define compliance requirements; failure to meet these can lead to enforcement and market access barriers |
Firm behavior under regulatory uncertainty | Small firms 25-52% less likely to pioneer new device markets due to regulatory costs and uncertainty | Regulatory uncertainty acts as a market entry barrier, especially for smaller firms, increasing risk of delayed or denied market access |
FDA enforcement trends | Increasing scrutiny on off-label promotion, misbranding, adulteration charges; courts affirm FDA’s broad evidentiary standards for intended use | Non-compliance can lead to legal prosecution and reputational damage, restricting market access and increasing legal risks |
Certified manufacturers and suppliers must understand that non-compliance can result in:
Import refusals and product seizures.
Suspension of facility registration.
Debarment and disqualification from medical markets.
Injunctions and forced corrective actions.
Criminal prosecution and financial penalties.
Market Access and Reputation
Certified manufacturers and suppliers of nitinol tubing risk losing access to the medical market if they do not maintain FDA compliance. The FDA can issue warning letters, import alerts, and seize products from non-compliant certified suppliers. Suspension of registration prevents further imports and disrupts business operations. Financial penalties can reach up to $50,000 per violation, with some cases exceeding $1 million for workplace safety issues. The average cost of non-compliance is about $14.82 million, which can cripple certified manufacturers.
Over 570 million global companies are tracked for compliance.
More than 372 million companies have predicted risk scores.
Over 480 million companies have Probability of Default scores.
These numbers highlight the importance of compliance monitoring for certified suppliers in the medical nitinol market. Non-compliance damages reputation, erodes consumer trust, and leads to increased FDA scrutiny. Certified manufacturers who lose their reputation may find it impossible to regain market access, especially in the competitive medical device industry.
Certified suppliers who prioritize compliance protect their business, reputation, and the safety of patients who rely on medical nitinol tubing.
Benefits of FDA Registered Nitinol Tubing Suppliers USA

Ensuring Product Quality and Patient Safety
FDA registered nitinol tubing suppliers USA set the standard for quality and patient safety in the medical field. Certified manufacturers follow strict FDA guidelines and iso 13485 certification requirements. These steps help ensure every piece of medical nitinol tubing meets high safety and quality expectations. The FDA improves product quality and patient safety by:
Publishing clear regulatory pathways and evidence requirements for medical device approvals.
Requiring disclosure of financial interests to reduce conflicts in clinical trials.
Using advanced recall systems and postmarket surveillance to protect public health.
Monitoring device safety through mandatory adverse event reporting and voluntary programs like MedSun.
Leveraging real-world data to identify safety signals and improve effectiveness.
Certified suppliers use these systems to enhance patient safety and maintain quality at every stage of production. Medical nitinol tubing from FDA registered nitinol tubing suppliers USA supports better outcomes for patients and healthcare providers.
Competitive Advantage for Certified Manufacturers
Certified manufacturers gain a strong competitive edge by maintaining FDA registration and iso 13485 certification. These certifications show a commitment to quality, safety, and regulatory compliance. In a crowded market, certified manufacturers stand out because:
FDA registration signals compliance and protects brands from legal risks.
Certifications build consumer confidence in product safety and quality.
Partnering with FDA registered nitinol tubing suppliers USA ensures reliability and transparency.
Certified manufacturers receive expert support for navigating regulations and maintaining continuous training.
FDA approval opens new markets, increases revenue, and encourages innovation.
Medical device manufacturers prefer certified suppliers because they reduce regulatory risks and speed up time to market. Ongoing FDA monitoring and iso 13485 certification reinforce public trust in medical nitinol tubing.
Confidence for Medical Device Companies
Medical device companies show greater confidence in certified suppliers after FDA registration reforms. The following table highlights this trend:
Metric | Pre-FDAAA (n=48) | Post-FDAAA (n=117) | Change Indicating Increased Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Trial Registration | 50% (24 of 48) | 98% (115 of 117) | +48% increase in registration |
Result Reporting | 15% (7 of 48) | 87% (98 of 117) | +72% increase in result reporting |
Publication in Literature | 58% (28 of 48) | 85% (100 of 117) | +27% increase in publication |
These numbers show that medical device manufacturers trust FDA registered nitinol tubing suppliers USA and certified manufacturers. High rates of trial registration and result reporting reflect the reliability and transparency of certified suppliers. This trust leads to better patient safety, improved quality, and stronger partnerships in the medical nitinol tubing industry.
FDA registration remains essential for nitinol tubing suppliers in the USA. This process ensures medical nitinol products meet strict safety and quality standards. Comprehensive documentation, robust quality management, and regular FDA inspections support patient safety and product reliability. Medical manufacturers benefit from transparent traceability and proven safety throughout the supply chain. Choosing FDA-registered nitinol suppliers strengthens business growth, market access, and patient safety. To select the best supplier, companies should review regulatory expertise, quality management systems, and detailed documentation practices.
FAQ
What is FDA registration for nitinol tubing suppliers?
FDA registration means a supplier has listed its facility and products with the FDA. This process allows the FDA to monitor safety and quality. It also helps ensure that nitinol tubing meets strict medical standards.
Why should medical device companies work with FDA registered suppliers?
Medical device companies gain confidence in product safety and quality when they select FDA registered suppliers. These suppliers follow strict regulations and maintain high standards. Choosing certified manufacturers helps reduce risks and supports regulatory compliance.
How does ISO 13485 certification benefit nitinol tubing suppliers?
ISO 13485 certification shows that a supplier follows international quality standards for medical devices. This certification helps suppliers improve their processes, reduce errors, and meet customer needs. It also supports easier market access.
What happens if a supplier does not comply with FDA regulations?
Non-compliance can lead to legal actions, product recalls, and loss of market access. The FDA may issue warning letters or suspend facility registration. Suppliers risk damaging their reputation and losing business opportunities.
What should companies consider when choosing certified manufacturers for nitinol tubing?
Companies should check for FDA registration, ISO 13485 certification, and a strong quality management system. They should also review the supplier’s track record for safety and compliance. Choosing certified manufacturers helps ensure reliable and safe products.
See Also
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Medical Innovations
The Process Behind Manufacturing Nitinol Tubing For Medicine
Choosing The Right Nitinol Tubing Supplier For Your Needs
Nitinol Tubing Transforming The Future Of Medical Devices
Nitinol Tubing’s Contribution To Medical Technology Progress

