Customizable Nitinol Tubing: A Neurovascular Game-Changer

You might ask why nitinol is so important in medicine. Its special traits—bendability, body safety, and shape memory—make it unique. These features help Customizable Nitinol Tubing for Neurovascular Applications fit the tiny paths in the brain's blood vessels. This makes it safer to move through fragile areas, lowering risks during surgeries. Customizable Nitinol Tubing for Neurovascular Applications has changed how medical tools work. By designing nitinol tubing for exact needs, doctors can provide better and more accurate treatments. Using it is a significant improvement for patient care and new ideas in medicine.
Key Takeaways
Nitinol tubing bends easily and is safe for brain surgeries.
Custom designs of nitinol tubing improve surgery accuracy and results.
Nitinol can remember shapes and bend back, fitting blood vessels.
Using nitinol lowers surgery risks, helping patients recover better.
Nitinol does not rust, making it safe and reliable for devices.
Understanding Nitinol and Its Properties

What is Nitinol?
Nitinol is a special material used in medical tools. It is made from nickel and titanium. This mix gives nitinol amazing abilities like shape memory and flexibility. When heated, nitinol goes back to its original shape. This makes it perfect for things like stents that expand on their own. It can bend a lot without breaking, making it strong and useful in tough conditions.
Nitinol changes between two forms based on temperature. At high heat, it becomes austenite, and at low heat, it turns into martensite. These changes give nitinol its shape memory and flexibility. By changing how nitinol is made, its features can be adjusted for specific medical uses.
Property/Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
Composition | Made from nickel and titanium. |
Phase Transformation | Changes from austenite (hot) to martensite (cold) with cooling. |
Shape Memory Effect | Returns to original shape when heated due to phase change. |
Superelasticity | Bends a lot without staying bent, returning to normal shape. |
Tailoring Properties | Features can be changed by heat treatment or mixing metals. |
Key Properties of Nitinol for Medical Devices
Nitinol is very useful for making medical tools, especially for brain surgeries. It is safe for the body, so it doesn’t cause bad reactions. This is important for tools like stents and wires that touch soft tissues.
Nitinol doesn’t rust, even in body fluids for a long time. This makes it reliable and safe to use. Its flexibility helps it move easily through tiny blood vessels without causing harm.
It is also very strong and lasts a long time. Nitinol can handle repeated use without losing its shape. Its ability to transfer heat quickly is helpful for tools that need temperature control.
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Shape Memory Effect | Goes back to its original shape when heated, great for stents. |
Superelasticity | Bends without breaking, making it flexible for medical tools. |
Corrosion Resistance | Doesn’t rust, staying safe and reliable for implants. |
Thermal Conductivity | Transfers heat well, useful for temperature-sensitive tools. |
Fatigue Resistance | Stays strong after repeated use, good for long-term devices. |
These features make nitinol a big deal in medical technology. Its mix of flexibility, strength, and safety helps doctors treat patients better.
Why Neurovascular Applications Rely on Nitinol Tubing
Challenges in Neurovascular Procedures
Neurovascular procedures need tools that are precise and flexible. The brain's blood vessels have tiny, twisty paths. Tools must move through these without harming delicate tissues. Materials like stainless steel are too stiff for such tasks.
Another problem is keeping tools working well during tricky surgeries. Devices must stay strong and keep their shape under pressure. Using new technologies, like robotic tools, raises safety and ethical concerns. These challenges show the need for better materials to improve results and safety.
Challenge Type | Description |
|---|---|
Objective Performance Metrics | Hard to measure and compare how well advanced treatments work. |
Medicolegal Implications | Rules about consent and safety must be followed carefully. |
Ethical Concerns | Questions about whether new tools are better than old ones. |
The Role of Flexibility and Superelasticity
Flexibility and superelasticity are key for neurovascular tools. Nitinol tubing bends easily without breaking or staying bent. This makes it great for stents and wires. Its shape memory helps devices return to their original form, lowering risks.
Studies show nitinol stents work better because of superelasticity. They fit artery shapes, improving blood flow and reducing tissue stress. Unlike steel, nitinol doesn’t kink and stays strong under pressure. This makes it perfect for precise, minimally invasive surgeries.
Property | Nitinol Tubing | Traditional Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility | Excellent | Moderate |
Elasticity | High | Low |
Kink Resistance | Great | Poor |
Shape Memory | Yes | No |
Super Elasticity | Yes | No |
Biocompatibility and Corrosion Resistance
Nitinol is safe for the body and lasts a long time. It forms a layer that stops nickel from leaking into tissues. This makes it safe for long-term use in medical tools. Its resistance to rust adds to its reliability.
Studies show nitinol works well with body tissues and causes few problems. Doctors trust nitinol tools to work safely and consistently. These features make it ideal for stents and other flexible medical devices.
Nitinol’s protective layer blocks harmful nickel from escaping.
It doesn’t rust in body fluids, staying safe and strong.
Nitinol tools fit well with tissues, reducing complications.
Choosing nitinol tubing means using a material that is safe, strong, and flexible. These qualities make it a top choice for safer and better neurovascular treatments.
Customizable Nitinol Tubing for Neurovascular Applications

Tailored Solutions for Neurovascular Procedures
Custom nitinol tubing helps with brain blood vessel challenges. It is made to fit specific needs for safer surgeries. Superelastic tubes bend easily without harming soft tissues. They adjust to the twists in brain vessels, lowering risks.
Studies prove nitinol tubing works well in neurovascular care. Results show better surgery success and improved patient health. For example:
Metric | Result |
|---|---|
Surgery success rate | 97% (70 of 72 patients) |
Full aneurysm removal | 79.2% (57 of 72 patients) |
Aneurysm removal at 3 months | 98.6% (70 of 71 patients) |
Aneurysm removal at 12 months | 96.7% (29 of 30 patients) |
Major surgery problems | 4.1% (3 patients) |
Death after surgery | 1.4% (1 patient) |
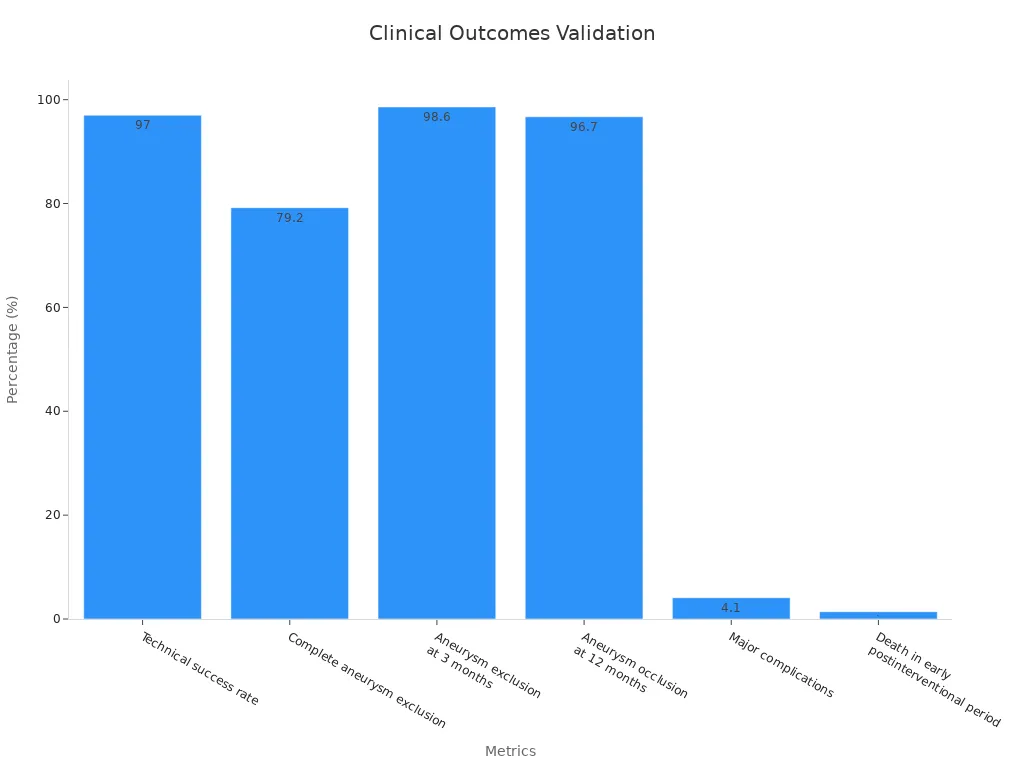
These results show nitinol tubing makes surgeries safer and more successful. Companies like Confluent Medical Technologies create advanced tools using custom nitinol tubing. This shows the growing need for better solutions in brain surgeries.
Enhancing Innovation in Medical Devices
Custom nitinol tubing helps make new medical tools possible. It combines bending ability, shape memory, and body safety for better devices. These tools work well in small surgeries and fit patient needs.
Nitinol tubing has changed how medical tools are made. Flexible stents now fit artery shapes, improving blood flow and lowering risks. Nitinol is also used in robotic tools for precise surgeries.
Research shows high demand for custom nitinol tubing in brain surgery tools. Companies invest in superelastic nitinol tubes for safer surgeries. This trend shows how important nitinol is for better patient care.
Choosing nitinol tubing supports medical progress. These tools improve surgery success and make treatments safer for patients.
Nitinol Tubing and Wire Uses in Brain Blood Vessel Tools
Stents and How They Help Patients
Nitinol stents have changed brain blood vessel surgeries. These stents use nitinol’s bending and shape memory abilities. They fit tightly into blood vessels, improving blood flow and lowering risks. Nitinol stents keep their shape under pressure, unlike older materials. This makes them great for fixing aneurysms and blocked arteries.
Tests show nitinol stents work well. Studies compare nitinol stents to balloon treatments. Both have similar heart attack and death rates. But nitinol stents are safer for blood vessels and last longer.
Clinical Outcome | SENS Group (%) | POBA Group (%) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
Cardiac Death | 6.5 | 5.1 | > 0.999 |
Myocardial Infarction | 1.6 | 0.0 | > 0.999 |
Repeat Revascularization | 19.6 | 18.9 | 0.922 |
Target Lesion Revascularization | 13.1 | 17.2 | 0.530 |
Amputation | 4.9 | 0.0 | 0.244 |
These tests show nitinol stents are safe and work well. They fit blood vessels and stay strong, making them important for brain surgeries.
Catheters and Guidewires for Small Surgeries
Nitinol tubing and wire are also used in catheters and guidewires. Guidewires made from nitinol bend easily and don’t kink. They move through blood vessels without causing harm. This makes them great for removing clots or fixing aneurysms.
Catheters use nitinol’s safety and rust-proof features. These keep the tools safe during long surgeries. Nitinol’s shape memory helps catheters keep their form in tough conditions. This makes surgeries faster and helps patients recover better.
Performance Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Fatigue Resistance | Stays strong after repeated use, making tools reliable. |
Biocompatibility | Works well with body tissues, lowering risks of problems. |
Shape Memory | Returns to original shape, helping tools move through vessels. |
Superelasticity | Bends easily, fitting blood vessels without damage. |
Clinical Success Rates | Studies show nitinol tools improve surgery success rates. |
Nitinol wire has changed how doctors treat brain blood vessel problems. Its special traits make it perfect for stents, guidewires, and other tools. Using nitinol means safer and better care for patients.
Nitinol has changed brain surgery tools in big ways. It bends easily to move through tiny brain paths safely. Superelastic nitinol tubes fit tricky shapes, lowering surgery risks. Its body-safe material makes it good for long-term use. Custom designs help make tools that match exact medical needs. These improvements lead to better results and safer treatments for patients.
Nitinol’s special traits make it key in today’s medical tools. Its mix of strength, bending ability, and safety helps doctors care for patients better.
FAQ
Why is nitinol tubing special for brain surgeries?
Nitinol tubing is flexible and superelastic, making it unique. It can safely move through the brain's tiny blood vessels. Its body-safe material and rust-proof nature make it reliable for medical tools.
Can nitinol tubing be made for specific surgeries?
Yes, nitinol tubing can be designed for exact medical needs. Makers change its flexibility and shape memory using heat and metal mixing. This helps it work better for specific brain surgeries.
How does nitinol make brain surgeries safer?
Nitinol bends without breaking and resists kinking, protecting blood vessels. It is safe for the body and doesn’t cause bad reactions. Its rust-proof feature makes it strong and long-lasting, improving surgery safety.
Are there any problems with using nitinol in tools?
Nitinol is mostly safe because it works well with the body. But if made poorly, it might leak nickel, causing allergies. Trusted makers ensure high-quality nitinol to avoid these issues.
Why is nitinol better than stainless steel for brain tools?
Nitinol bends more and remembers its shape, unlike steel. It moves through tricky paths without breaking or kinking. Steel doesn’t have these features, so it’s less useful for delicate brain surgeries.
Tip: Talk to your doctor to learn how nitinol can help your treatment.
See Also
Nitinol Tubing's Impact on Modern Medical Device Innovation
Nitinol Tubing's Contribution to Progressing Medical Technology
Understanding Nitinol Tubing Uses in Healthcare Innovations

