How to Compare Surface Treatments for Nitinol Tubing Performance
Selecting nitinol tubing surface treatment can seem hard. Every nitinol tubing use needs special performance, especially in medical devices. You have to think about how the best surface treatment affects corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and the tubing’s strength. Studies show that nitinol tubing surface treatment, like electropolishing or passivation, makes a stable, thin titanium dioxide layer. This layer lowers nickel release and makes medical use safer. You should match nitinol tubing surface treatment to what your tubing needs, like for medical implants or places with lots of stress. Picking the right one helps your nitinol tubing meet strict medical rules and last longer.
Key Takeaways
Pick the best surface treatment for nitinol tubing by thinking about what your project needs. This is very important for medical devices because safety and strength matter most.
Electropolishing gives the tubing the best protection from rust and makes it very smooth. This lowers nickel release, so the tubing is safer and lasts longer.
Biocompatibility is very important for medical uses. A smooth titanium dioxide layer keeps the body safe and follows strict safety rules.
Mechanical strength and fatigue resistance help the tubing bend and move many times without breaking. This is important for things like stents and guidewires.
Work with experts and suppliers, test the tubing after each step, and follow the rules. This helps you get the safest and best nitinol tubing.
Nitinol Tubing Surface Treatment Criteria
When you look at nitinol tubing, focus on four main things. These things help you choose the best tubing for your project. This is important for medical devices, tools, or anything that needs to be strong and safe.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is very important for nitinol tubing. You want tubing that lasts in tough places, like inside the body. Different surface treatments change how well tubing fights corrosion. Electropolished tubing has the best corrosion resistance. It does not break down up to 1000 mV. Chemically treated tubing protects well, but not as much as electropolished. Mechanically polished and heat-treated tubing can get pitting more easily. The table below shows how each treatment works:
Surface Treatment | Corrosion Resistance Indicator | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
Electropolished (EP) | Breakdown potential up to ~1000 mV | Highest corrosion resistance; no breakdown observed up to 1000 mV in some tests. |
Oxidized Finish (AO) | Breakdown potential around -117 mV | Lowest corrosion resistance among tested finishes. |
Mechanically Polished + Heat Treated (MP + HT) | Prone to pitting corrosion | More susceptible to pitting compared to chemically treated or electropolished surfaces. |
Chemically Treated (CE) | Intermediate corrosion resistance | Better resistance than mechanically polished but less than electropolished. |
Always check corrosion resistance if your tubing will touch body fluids or chemicals. This helps stop nickel from getting out, which can be bad for health.
Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility means the tubing is safe with living tissue. Medical devices must follow strict rules like ISO 13485 and ASTM F2063. You need to test for blood safety, gene safety, and tissue reactions. A smooth TiO2 oxide layer helps make tubing safer and lowers nickel exposure. This is very important for implants and other medical uses.
Mechanical and Fatigue Properties
Your nitinol tubing should handle bending and stretching many times. Fatigue resistance and strength are important for stents and guidewires. Surface finish and heat treatment change how long tubing lasts. Good surface treatments make tubing stronger and safer. Nitinol’s superelasticity and biocompatibility help it keep its shape and stay strong.
Surface Smoothness and Cleanliness
Smooth and clean surfaces help with safety and strength. For medical devices, look for tubing with roughness below 0.2 µm. Clean tubing lowers infection risk and helps tissue grow better. The chart below shows how cleaning changes surface cleanliness:
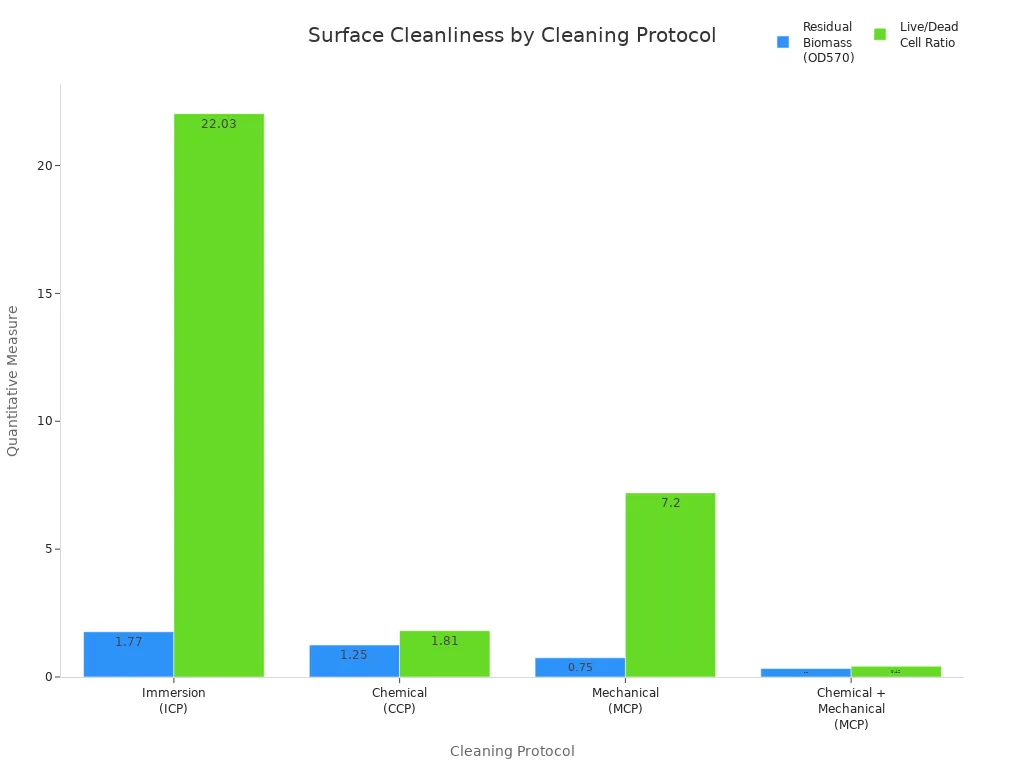
You can use special microscopes to check for dirt and measure roughness. Clean, smooth tubing helps healing and makes devices last longer.
Tip: Always pick the right surface treatment for your use. Medical devices need the best corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and strength. Industrial uses may care more about fatigue resistance and strength.
Application Needs for Nitinol Tubing
Picking nitinol tubing depends on what your project needs. You should think about how you will use the tubing. This is very important for neurovascular stents and medical devices. Each use has its own needs, like flexibility and strength. Biocompatibility is also important for neurovascular uses. Custom tubing is helpful because every patient and surgery is different.
Medical and Implantable Devices
If you use nitinol tubing for neurovascular stents, safety is very important. The tubing must be safe inside the body. It should work well with neurovascular procedures. Here are some things to look for:
The tubing needs a thin, smooth titanium dioxide layer. This helps make it safe for the body and stops nickel from leaking.
Electropolishing and magnetoelectropolishing are common ways to treat the surface. These make the tubing smoother and help it last longer.
The tubing should bend and stretch many times without breaking. This is needed for neurovascular stents and guidewires.
Custom tubing lets you get the right size and shape for each procedure.
The tubing should also be very clean and have no defects. Sterilizing with steam or plasma keeps the tubing safe for medical use.
Industrial and High-Fatigue Uses
Nitinol tubing is also used in machines and tools. These need to last a long time. Durability is very important here. Here is what you should know:
Heat treatment and cold working make the tubing stronger. This helps it last through many cycles.
Electropolishing adds a strong titanium oxide layer. This protects the tubing from rust and damage.
Passivation or special coatings give extra protection in tough places.
Quality checks make sure the tubing has no cracks or dirt.
Custom tubing helps you get what you need for your job. This is true for both neurovascular stents and heavy-duty machines.
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations
You must follow rules when picking nitinol tubing for neurovascular stents. These rules help keep people safe. The table below shows some important standards:
Regulatory Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|
ASTM F2063 | Sets rules for medical-grade nitinol tubing. |
ISO 13485 | Sets quality rules for making medical devices. |
ISO 10993 | Checks if tubing is safe for long-term use. |
FDA Registration | Makes sure tubing meets safety rules. |
Always check that your tubing meets these standards. This helps make sure it works for neurovascular procedures. It also helps you follow industry rules. Think about the environment too. Pick surface treatments that use safe chemicals and make less waste. Custom tubing can help you choose options that are safer for people and the planet.
Note: Always pick nitinol tubing that fits your use. This helps you get the best safety, strength, and performance for neurovascular stents and other jobs.
Surface Treatment for Corrosion-Resistant Nitinol Tubing

If you want nitinol tubing that fights rust, you need to look at how each surface treatment changes the tubing’s safety and strength. Each way of treating nitinol tubing gives different results for how well it stops rust, how safe it is in the body, and how long it lasts. Let’s look at the main choices and see how they are different.
Electropolishing
Electropolishing is the best way to treat most nitinol tubing. This method takes off a thin layer from the tubing’s surface. It makes the tubing very smooth and shiny. It also removes tiny cracks and flaws that can start rust or make the tubing break.
Electropolishing makes a strong, even titanium dioxide layer. This layer keeps the tubing from rusting and stops nickel from leaking out. Smoother tubing means there are fewer places for rust to start. Electropolishing can make tubing up to 75% better at fighting rust than other ways. It also lowers how much nickel comes out, which makes it safer for people.
Here’s a table that shows how electropolishing compares to other nitinol tubing surface treatments:
Surface Treatment Method | Surface Roughness (Ra) | Corrosion Resistance Indicators | Nickel Ion Release | Fatigue Life & Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Electropolishing | Below 0.5 μm (very smooth) | High breakdown voltage up to 1000 mV; fewer corrosion sites; up to 75% better | Reduced nickel ion release; safer for implants | Removes flaws; improves fatigue life; better biocompatibility |
Chemical Etching (Passivation) | Around 8.75 μm (less smooth) | Moderate corrosion resistance; may leave residues | Not as effective in reducing nickel ion release | Can thin tubing; uneven surface; possible residues |
Mechanical Polishing | Rougher surface | Lower corrosion resistance; more corrosion sites | Higher nickel ion release | Flaws remain; weaker fatigue resistance |
You can see that electropolishing gives the smoothest and safest tubing. It works for many tubing sizes and shapes. You get tubing that meets strict medical rules and lasts longer.
Electropolishing takes off a thin layer and leaves a clean, smooth finish.
It raises the breakdown potential to about 0.99 V/SCE, which is much higher than mechanical polishing.
The process lowers surface nickel, which helps stop allergies.
Electropolishing makes a strong titanium dioxide layer for better rust protection.
It is about thirty times better than passivation at stopping rust.
The process removes tiny cracks, which helps the tubing last longer.
You can use electropolishing for many tubing shapes and sizes.
If you use electropolishing with wall thickness and roughness below 0.1 µm, you get tubing that resists rust and meets ISO 13485 rules. This makes electropolishing the best choice for most corrosion-resistant nitinol tubing.
Passivation
Passivation is another common way to treat nitinol tubing. You use acids like nitric acid or hydrogen peroxide to change the tubing’s surface. Passivation makes a thin oxide layer that helps protect the tubing from rust.
Passivated nitinol tubing is safer for the body than untreated tubing. Studies show that passivation lowers nickel release, which helps stop allergies and makes the tubing safer. Passivation also helps the tubing fight rust, but it does not make the surface as smooth as electropolishing.
Passivation lowers rust and nickel release.
Less nickel release means the tubing is safer for the body.
Passivated tubing works well for many medical uses.
You still need to test and check the tubing for safety.
Passivation is a good choice if you want better rust protection and safety, but it does not make the tubing as smooth or safe as electropolishing.
Mechanical and Magnetoelectropolishing
Mechanical processing, like drawing or polishing, changes the tubing’s surface. You can use hard or soft mandrels and different dies. Hard mandrels and diamond dies make tubing smoother, but mechanical polishing alone leaves grooves and flaws. These flaws can start cracks and make the tubing weaker.
Magnetoelectropolishing is a special kind of electropolishing. You use magnets to help remove even more flaws from the tubing’s surface. This process is good for removing heat-affected zones from laser cutting. You get a very smooth surface, which helps the tubing last longer and fight rust.
Mechanical drawing with hard mandrels gives better control and smoother tubing.
Diamond dies make tubing smoother than tungsten carbide dies.
Magnetoelectropolishing removes surface defects and heat-affected zones.
Smoother tubing means it lasts longer and gets fewer cracks.
You should use magnetoelectropolishing if you want the smoothest and longest-lasting tubing.
Chemical Pickling and Etching
Chemical pickling and etching use acids or other chemicals to clean and prepare the tubing’s surface. You can remove rust, scale, and oxides with this method. Pickling and etching also help make a safe oxide layer.
Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Surface Morphology | Makes micro- and nanoscale features for cell growth and attachment. | Deep cracks from some etchants may cause surface irregularities. |
Surface Composition | Forms biocompatible titanium oxide layers that stop nickel from leaking. | Some etchants can cause nickel enrichment, which is toxic. |
Wettability and Biocompatibility | Hydrophilic surfaces help cells attach and grow. | Some etching mixtures may harm the surface chemistry. |
Corrosion Resistance | Improves corrosion resistance with oxide layer. | Nickel-enriched surfaces may lower corrosion resistance. |
Medical Application Potential | Helps bone and cell growth in lab tests. | Not enough long-term studies to confirm safety. |
Pickling and etching are good for cleaning and getting tubing ready. You get a smoother, cleaner surface, but you must control the process to avoid damage. Some chemicals can leave harmful leftovers or make the surface rougher. Always check the tubing after pickling or etching.
Heat Treatment Methods
Heat treatment changes the tubing’s strength and shape. You can use strand annealing, box furnaces, molten salt baths, or joule heating. Each way heats the tubing in a different way.
Strand annealing gives even strength along the tubing.
Box furnaces let you control temperature and time.
Molten salt baths heat tubing quickly and lower oxidation.
Joule heating uses electricity for fast, even heating.
Heat treatment changes the tubing’s final properties. You can make tubing fight rust better by using passivation after heat treatment. Water-boiling passivation makes a nickel-free oxide layer and lowers nickel release. Dry-heating passivation does not protect as well. Polishing, like electropolishing, after heat treatment gives you the best surface for rust protection and strength.
Tip: If you want the best surface treatment for corrosion-resistant nitinol tubing, pick electropolishing. You get the smoothest, safest, and longest-lasting tubing. Always check your tubing after each step to make sure it is right for you.
How to Choose the Best Surface Treatment
Picking the right surface treatment for nitinol tubing can be tough. This is extra true if you need it for neurovascular devices. You want tubing that lasts and stays safe in the body. It also needs to follow all the rules. Use these steps to help you choose the best option for your neurovascular project.
Define Application Priorities
First, think about what is most important for your neurovascular device. Each neurovascular use is different. You need to set your main goals before looking at surface treatments.
Biocompatibility comes first. For neurovascular stents and implants, you must use nitinol tubing that meets ISO 10993-1, ASTM F2063, and FDA rules. This keeps patients safe.
Corrosion resistance is next. Neurovascular devices stay in the body for a long time. You want a surface treatment like electropolishing or magnetoelectropolishing that creates a strong titanium dioxide layer. This layer stops nickel from leaking out.
Mechanical strength matters. Your nitinol tubing must bend and flex without breaking. You should check tensile strength, fatigue life, and flexibility. Neurovascular stents need to survive millions of cycles inside the body.
Surface smoothness helps. A smooth surface (Ra <0.1 μm) lowers the risk of tissue irritation and infection. It also makes sterilization easier.
Keep good records. You must track every cleaning, treatment, and sterilization step. This helps you follow the rules and keeps patients safe.
Use certified tubing. Only use nitinol tubing that meets all the right standards for neurovascular use.
Test everything. Always test for reaction force, bending, and stress. This makes sure your neurovascular device will last.
Tip: Write down your top three goals before you look at surface treatments for your neurovascular device.
Match Treatment to Performance Needs
Now that you know your goals, match them to the right surface treatment. Every neurovascular device needs its own mix of features. Use this table to see which treatment fits your needs:
Performance Metric | Surface Treatment or Tubing Feature | Impact on Neurovascular Performance |
|---|---|---|
Fatigue Life | Advanced manufacturing (e.g., TM-1 process) | 2-3x longer life at 10^7 cycles for neurovascular stents |
Dimensional Tolerances | Precise OD and wall thickness (±0.005mm) | Better fit and less risk of failure in neurovascular use |
Biocompatibility | Magnetoelectropolishing | Less nickel release, safer for neurovascular implants |
Corrosion Resistance | Magnetoelectropolishing, thin oxide film | Stops tubing from breaking down in neurovascular sites |
Tubing Type | Seamless tubing | Stronger and safer for neurovascular procedures |
Wall Thickness | Thin-walled for flexibility, thick-walled for strength | Pick based on neurovascular device needs |
Nitinol Grade | High purity, process-optimized | Fewer defects, better for neurovascular fatigue life |
Talk to nitinol and neurovascular experts. They can help you pick the right grade, wall thickness, and surface treatment. Custom tubing lets you get the exact tubing you need for your neurovascular project.
Evaluate Trade-Offs and Limitations
Every choice has good and bad sides. When you pick a surface treatment for neurovascular tubing, you must balance different features. Look at this table to see common trade-offs:
Trade-off / Limitation | Explanation |
|---|---|
Stiffness vs Flexibility | More stiffness helps structure but lowers flexibility. Neurovascular stents need the right balance. |
Surface Roughness and Stress | Rough surfaces can cause cracks. Smooth neurovascular tubing lasts longer. |
Corrosion Resistance vs Treatment | Electropolishing gives great corrosion resistance but needs careful control. |
Wall Thickness and Diameter | Thick walls add strength but lower flexibility. Neurovascular devices often need thin walls. |
Thermal and Plasma Treatments | These need careful control to avoid bad surface changes. |
Chemical Treatments | You must control chemicals to keep neurovascular tubing safe. |
Thermal and plasma treatments need the right heat and gases. Chemical treatments must use the right mix to avoid damage. Always test your neurovascular tubing after each step.
Note: Custom tubing helps you balance these trade-offs. You can change wall thickness, surface finish, and treatment to fit your neurovascular device.
Use a Decision Matrix
A decision matrix helps you compare your choices for neurovascular tubing. List your top needs, then score each surface treatment. Here is a simple example for neurovascular stents:
Criteria / Feature | Electropolishing | Magnetoelectropolishing | Chemical Etching | Mechanical Polishing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Biocompatibility | High | Very High | Moderate | Low |
Nickel Ion Release | Very Low | Lowest | Moderate | High |
Fatigue Resistance | High | Very High | Moderate | Low |
Surface Smoothness | Very High | Highest | Moderate | Low |
Corrosion Resistance | High | Highest | Moderate | Low |
Customization Options | Good | Excellent | Limited | Limited |
Cost | Moderate | Higher | Lower | Lowest |
Score each treatment for your neurovascular device. Pick the one that matches your top needs. For most neurovascular stents, magnetoelectropolishing or electropolishing gives the best mix of safety, strength, and smoothness.
✅ Checklist for Selecting Nitinol Tubing for Neurovascular Devices:
Define your neurovascular application and main goals.
Match surface treatment to performance needs.
Check trade-offs and limits.
Use a decision matrix to compare options.
Test and check after each step.
Work with experts for custom tubing.
Make sure your nitinol tubing meets all neurovascular standards.
By following these steps, you can make smart choices for your neurovascular device. Custom nitinol tubing lets you get the perfect fit for your project. Always test and check your tubing to keep patients safe and follow all neurovascular rules.
Expert Tips and Common Pitfalls in Nitinol Surface Treatment
Avoiding Surface Defects
You want your nitinol tubing to work well and last long. Surface defects can make tubing weak and cause it to break early. Experts say you should do these things to stop problems:
Set the right cutting speed, feed rate, and depth. This keeps heat and stress low. Less heat means less chance for hard spots or surface flaws.
Use sharp, good tools. Sharp tools make less friction and heat when cutting.
Control how much you bend and stretch the tubing. Too much bending can make nitinol brittle.
Use the right heat treatment. Heat the tubing to about 470°C for 30–60 minutes. Cool it down fast. This brings back superelasticity and lowers hard spots.
Watch the process with sensors and quality checks. Follow rules like ASTM F2063 and ISO 13485.
Pick tool steels that are tough and have special coatings. This helps tools last longer and stops damage.
You can also use electropolishing or chemical etching. These remove tiny cracks and smooth the tubing. Smoother tubing lasts longer and bends better. If you use lasers to cut or weld, try femtosecond lasers or pulse-shaping. These help avoid hot spots and tiny cracks.
Interpreting Test Data Correctly
You need to read test results the right way. This helps you know if your nitinol tubing is good enough. How you finish the surface changes how strong, safe, and smooth the tubing is.
Electropolishing makes the tubing smoother and helps stop rust.
Passivation adds a thin layer that protects and makes tubing last longer.
Tests should check size, inside flaws, strength, and safety with living tissue.
Make sure your tubing follows ASTM F2063 and FDA rules.
Heating and shaping steps also change how the surface looks and works.
Test and check the tubing often to keep it safe for medical use.
Consulting with Suppliers and Experts
When picking a nitinol tubing supplier, follow these tips:
Choose suppliers who can make samples fast. This helps you test ideas and lowers risk.
Check if they have certifications like ISO 13485, ASTM F2063, and FDA approval.
Work with suppliers who answer questions quickly and clearly.
Ask for samples and look at all test results and papers.
Talk about custom sizes, finishes, and treatments to make tubing safer and stronger.
Keep talking with experts and suppliers to get tubing that fits your project.
Plan for wait times, price changes, and supply problems.
Make sure suppliers test for strength, bending, and safety with living tissue.
Check that surface treatments lower nickel release and make tubing safer.
Use supplier support teams to fix problems and keep your project moving.
Tip: Working closely with your supplier helps you get the best nitinol tubing for your needs.
When you look at nitinol tubing surface treatments, use these steps:
Decide what you need your tubing to do.
Think about where the tubing will be used and check the rules.
Choose the best surface treatment, like electropolishing, for your tubing.
Test and look at the tubing after every step.
Make sure each step is done the same way for good quality.
You can make nitinol tubing work better by picking the right surface treatment for your job. New research finds better ways to make tubing safer and last longer. For hard tubing projects, ask experts for help and learn about new nitinol ideas.
FAQ
What is the best surface treatment for medical nitinol tubing?
Electropolishing is the best choice for most medical tubing. This method makes the surface very smooth and shiny. It also gives the tubing the highest protection from rust. Electropolishing helps keep nickel from coming out. This makes the tubing safer for use in the body.
How do I know if my nitinol tubing is biocompatible?
Check if your tubing follows rules like ISO 10993 and ASTM F2063. You can ask your supplier to show you test results. Look for a smooth titanium dioxide layer on the tubing. This layer helps keep the tubing safe inside the body.
Can I use the same surface treatment for all applications?
No, you need to pick the right treatment for your job. Medical devices need tubing that does not rust and is very smooth. Industrial jobs may need tubing that is stronger or lasts longer. Always check what your project needs before you choose.
How do I test the quality of nitinol tubing after treatment?
You can do these things:
Look at the surface to see if it is smooth and clean.
Test if the tubing resists rust.
Check if nickel comes out of the tubing.
Make sure the tubing is strong and can bend many times.
Tip: Always get test results from your supplier.
See Also
Analyzing Tensile Strength Differences Between Nitinol And Stainless Steel
The Manufacturing Process Of Nitinol Tubing For Medical Use
Discovering Various Uses Of Nitinol Tubing In Medical Devices

