How to Choose the Right Niti Tubing OD and ID for Medical Devices
Choosing the right Niti Tubing OD/ID sizes is crucial for medical devices, as it directly impacts both safety and performance. Recent studies highlight that selecting the appropriate nitinol size, wall thickness, and surface finish significantly improves the durability and fracture resistance of nitinol tubing. Minimizing flaws and manufacturing errors in nitinol tubing further reduces the risk of breakage.
Cyclic life testing demonstrates how stress affects the strength of nitinol tubing.
Controlling wall thickness and surface finish enhances tubing strength.
A robust internal structure enables medical devices to function reliably over many cycles.
By focusing on the correct Niti Tubing OD/ID sizes and these factors, you help ensure nitinol tubing remains safe and long-lasting.
Key Takeaways
Pick nitinol tubing sizes that fit your device’s job. Make sure you balance strength and flexibility for safe use.
Think about the body’s environment when choosing tubing. Pick tubing with smooth surfaces and corrosion resistance to keep patients safe.
Follow medical rules and test tubing well to check quality. Make sure it is strong and meets all the needed rules.
Work with experts and trusted suppliers to get the right tubing sizes. Make sure you get certifications that help your device work well.
Test and model your tubing choices to stop failures. This helps your medical device work better and be more successful.
Key Factors
Device Function
When picking nitinol tubing, think about how the device works. Each medical device needs something different. Stents, guidewires, and catheters all need special tubing. You should check if the tubing is strong and flexible enough for your device. Nitinol’s shape memory and superelasticity help it work well under pressure. Wall thickness is the space between OD and ID. This affects how bendy and strong the tubing is. You need the right balance for easy movement and carrying weight. Mechanical properties like tensile strength and fatigue life matter for devices used a long time. Every device has its own needs, so you must think about what your device will face.
Tip: You can change nitinol tubing sizes to fit your device’s needs.
Biological Environment
You also need to think about where the device will be used in the body. Nitinol tubing touches tissues, blood, and fluids. If the surface is rough, it can hurt tissue or cause infection. It can also make blood clots more likely. Smoother tubing is safer for patients. The tubing’s size and finish change how much of it touches the body. Bigger or rougher tubing can cause more problems. Things like pH and reactive oxygen species at the implant site are important too. These can make more nickel ions come out of the nitinol. This can be toxic or cause swelling. The surface finish and oxide layer thickness help stop corrosion and nickel release. Devices that move a lot, like heart devices, can make nickel exposure worse. Pick tubing sizes and finishes that are safe for the body and resist corrosion.
Compliance
You have to make sure your nitinol tubing follows medical rules. ASTM F2063 and other standards check if the tubing is made right. Testing and quality checks, like fatigue tests and surface treatments, show if the tubing will last. Manufacturers use special methods to control tubing size and how it works. Always check that your tubing fits your device’s needs and meets the rules for medical devices.
Niti Tubing OD/ID Sizes

Measurement Basics
It is important to measure niti tubing od/id sizes very carefully. Even a tiny mistake can change how a medical device works. Manufacturers use special tools like laser micrometers and measuring machines. These tools help them check every tubing size closely. This keeps the sizes very close to what is needed. For example, wall thickness can be checked to within ±0.005 mm. You should always look at both the outer diameter (OD) and inner diameter (ID). This makes sure the thin wall nitinol tubing fits your design. Measuring the tubing the same way each time helps stop problems during assembly and use.
Note: Careful batch testing and quality checks make sure every nitinol tubing piece meets strict medical rules.
Wall Thickness
Wall thickness is the space between the OD and ID. You need to find the right mix of flexibility and strength. Thinner walls make the tubing bend more easily. This is good for catheters and guidewires. Thicker walls make the tubing stronger. This is better for devices that need to handle more force. Thin wall nitinol tubing can have a wall as small as 0.0007 inches (0.018 mm). You should pick the wall thickness that fits your device’s needs. Special ways of making tubing, like centerless polishing and bore polishing, help get exact sizes and smooth surfaces.
Size Ranges
Nitinol tubing comes in many sizes for different medical jobs. Some ultra-fine thin wall nitinol tubing has OD as small as 0.003 inches (0.076 mm). Most medical nitinol tubing has OD between 0.2 mm and 5 mm. Some special devices use tubing up to 25 mm OD. The ID changes based on the wall thickness you pick. The table below shows common nitinol tubing size ranges for medical devices:
Parameter | Size Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Outer Diameter (OD) Range | 0.003 inches (0.076 mm) to 25 mm | Ultra-fine tubing starts at 0.003 inches; common medical tubing typically 0.2 mm to 5 mm OD |
Wall Thickness Range | 0.0007 inches (0.018 mm) to 1.00 mm | Ultra-fine tubing with thin walls used for flexible medical tools |
Neurovascular Stents OD | 0.2 mm to 2 mm | Wall thickness 0.05 mm to 0.3 mm; balances flexibility and strength |
Medical Device Grade OD Ranges | Standard: 0.254 – 1.65 mm; Precision: 1.65 – 5 mm; Premium: 1.65 – >5 mm | Different grades for guidewires, stents, and implants |
You need to watch the tolerances for each tubing size. The chart below shows how tolerances change with different nitinol tubing sizes:
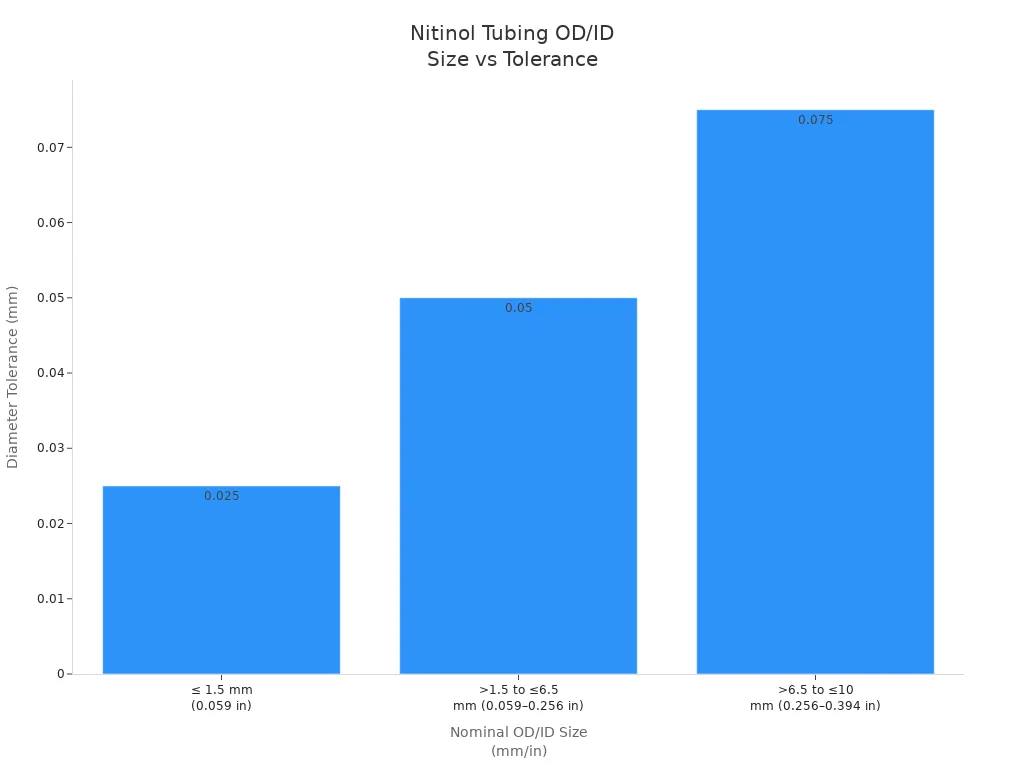
Manufacturers use strict controls and advanced ways to keep nitinol tubing od/id sizes exact. This helps your medical device work safely and well.
Nitinol Tubing Properties

Superelasticity
Nitinol tubing is special because it can bend a lot. It does not kink or break when you bend it. This makes it good for stents, catheters, and guidewires. These devices need to move through tricky parts of the body. Nitinol tubing helps patients feel more comfortable. It also lowers problems by about 25% compared to stainless steel. The shape memory effect lets the tubing go back to its shape after bending. This is important for surgeries that do not cut much. Nitinol tubing is both flexible and strong. It can bend and stretch many times without breaking. Studies show nitinol stents last longer and break less than old ones. Nitinol tubing does not kink and can move through twisty blood vessels. It is safe for the body and does not rust easily.
Nitinol tubing bends a lot and does not kink.
Devices can move safely in hard-to-reach places.
Shape memory lets tubing go back to its shape.
Flexibility and strength help devices last longer.
Nitinol tubing gives more comfort and fewer problems.
Fatigue Resistance
Fatigue resistance means nitinol tubing can bend many times. It can handle millions of bends and stretches. This is good for devices that stay in the body for a long time. The table below shows how nitinol tubing works when bent over and over:
Tubing Lot | Fatigue Life (Cycles) | Observations |
|---|---|---|
1−1 | 10^7 | Few fractures at high cycle counts |
1−2 | 10^7 | Few fractures at high cycle counts |
2−1 | 10^7 | Few fractures at high cycle counts |
Nitinol tubing can take up to 10 million bends. Some tests show it can last up to 1 billion bends. This means it is strong for a long time. Breaks are rare before 100 million bends but can happen after that. Nitinol tubing can get cracks more easily than some other metals. So, you must design devices to stop cracks from growing. Tests before using in people check nitinol tubing for hundreds of millions of bends to make sure it is safe.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance means nitinol tubing does not rust easily. This is one reason it is good for medical devices. Nitinol tubing lasts longer because it fights rust better than many other metals. A smooth finish, like electropolishing, makes a strong layer on the tubing. This layer keeps out rust. The way the surface is made, like how much nickel and oxygen it has, helps it work better. Different finishes can change how well nitinol tubing stops rust. You need to pick the right finish for your device. Nitinol tubing is safe for the body and does not rust, so it is great for implants that stay in the body. You can trust nitinol tubing to be safe and last a long time in many types of devices.
Tip: Always look at the surface finish when picking nitinol tubing to make sure it is safe and lasts longer.
Selecting Nitinol Tubing
Picking nitinol tubing for medical devices takes careful steps. You need to think about both technical and clinical needs. This helps make sure the tubing works well for your device. Good choices lead to high quality, safety, and strong performance.
Define Requirements
First, figure out what your device needs from the nitinol tubing. You should:
Understand the Application
Think about where and how you will use the tubing. Will it get wet, hot, or move a lot? Stents and catheters must handle body fluids and lots of bending. Thin wall nitinol tubing is good for flexible tools. Thicker tubing is better for strong, heavy-duty jobs.Specify Material Properties
Pick the right nitinol grade for your device. Look at shape memory and superelasticity. Use tests like DSC and bend free recovery to check these. Make sure the tubing meets ASTM F2063 standards.Select Tubing Type and Size
Choose between seamless and welded tubing. Seamless tubing is stronger and more even. This is important for most medical devices. Pick the outer diameter, inner diameter, and wall thickness that fit your design. The ratio between OD and wall thickness helps stop buckling and makes sure the tubing fits.Plan for Early Testing
Plan to test for fatigue and performance early. This helps you see if the tubing will last in real use. You can find problems before making lots of devices.Consider Customization
Custom nitinol tubing lets you pick the size, material, and how it is made. This is important when safety and performance matter most.Check Supplier Certifications
Always check that your supplier gives test results and meets industry rules. Certifications like ISO 13485 and FDA compliance show the tubing is safe and high quality.
Tip: Setting clear needs at the start saves time and money later.
Consult Experts
Work with nitinol tubing makers and experts. Their knowledge helps you avoid mistakes and pick the best tubing.
Leverage Manufacturer Expertise
Makers know how to control OD, ID, and wall thickness. They use special die designs, hard mandrels, and drawing methods to get the right size. Hard mandrels keep the ID smooth and help control size. Special drawing makes the tubing more even and strong.Access Advanced Capabilities
Makers offer things like electropolishing for better biocompatibility, precision cutting, and design help. These services help you get tubing that fits your device and meets strict quality rules.Ensure Regulatory Compliance
Pick partners with medical-grade certifications. This makes sure your tubing meets all rules and quality needs.
Note: Working with experts helps you pick the right tubing size, makes your device work better, and keeps patients safer.
Validate Choices
After picking nitinol tubing, you must test and check your choices. This step makes sure the tubing works as you want in your device.
Prototype Testing
Build test devices with your chosen tubing size. Do tensile tests to see how the tubing acts under stress. Test both whole devices and multi-wire samples to get steady results.Numerical Modeling
Make computer models and compare them to real test data. This helps you guess how the tubing will act in different situations.Dimensional Accuracy Checks
Measure the tubing after it is made. Look for changes in diameter and shape. Tools can help you predict and control these changes, especially for small or tricky parts.Performance Testing
Test the tubing for fatigue resistance, corrosion, and strength. Make sure it meets all safety and quality rules before making lots of devices.Iterate and Improve
If the tubing does not work as needed, change the design or how it is made. Test again until you get the quality and performance you want.
Validation Step | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Prototype Testing | Check real-world behavior | Makes sure it works well |
Numerical Modeling | Guess performance under stress | Lowers risk of failure |
Dimensional Accuracy | Check tubing matches design | Helps device fit better |
Performance Testing | Test fatigue, corrosion, and strength | Ensures safety and quality |
Iteration | Improve design and process | Gets the best performance |
Remember: Matching tubing size to your device design helps make devices faster and better. Controlling nitinol tubing size well stops tool damage, prevents mistakes, and makes sure your device fits and works right.
Common Mistakes
Overlooking Application Needs
You need to make sure nitinol tubing fits your device’s needs. If you do not think about how your device will work, it might not work well. Sometimes, the device can even stop working. If you forget to set clear goals or ignore where the tubing will be used, you cannot fix problems later. For example, if you do not check how nitinol acts with body fluids or movement, you might see cracks or lose flexibility.
Problems start when you do not design for the right job.
If you let others make tubing without checking quality, it can be weak.
If you do not test tubing in real life, you might miss hidden dangers.
Note: Small mistakes in your process can cause big problems if you do not know how nitinol tubing works with other parts of your device.
Ignoring Tolerances
Tolerances are the limits for nitinol tubing size and shape. If you ignore tolerances, your device might not fit or work right. Bad tolerances can cause leaks, weak spots, or breaks. You need to check tolerances at every step, from design to the last check.
Tight tolerances help keep tubing strong and flexible.
Bad tolerances make nitinol tubing weaker.
Devices with bad tolerances can break during use or tests.
Always ask your supplier for full reports on tolerances. This helps you avoid mistakes and keeps nitinol tubing safe for patients.
Skipping Validation
You must not skip validation if you want good nitinol tubing. Validation means you test and check tubing before using it in devices. If you skip this, you might miss problems with strength, bending, or rust.
Devices that skip validation can break early or not last long.
Without validation, you cannot show your tubing is safe.
Skipping tests can hide problems that show up after many uses.
Tip: Always do real-life tests to check how strong nitinol tubing is. This step keeps your patients safe and protects your good name.
Best Practices
Summary Steps
Here are some easy steps to help you pick the best nitinol tubing for your medical device. First, choose medical-grade nitinol tubing that follows ISO 13485 and ASTM F2063 rules. This makes sure it is safe for the body and high quality. Next, check if the nitinol tubing is flexible, strong, and can handle lots of bending. Make sure the size, like inner diameter, outer diameter, and wall thickness, fits your device. Getting the right size helps your device work well and saves money. Work with trusted suppliers who give you test reports and certificates. This proves your nitinol tubing is good and you can track where it came from. Watch how the tubing is made. Heat treatment and surface finishing change how well it remembers its shape and fights rust. Look at how long the tubing lasts when bent many times. Pick nitinol tubing made with new methods so it lasts longer. Make sure you can weld or shape the tubing without making it weak. This helps when putting your device together. Always ask for samples and test them before buying a lot. Testing helps you see if the nitinol tubing is right for your device. Think about where your device will be used. Choose nitinol tubing that does not rust and keeps working well over time.
Tip: If you follow these steps, you can avoid mistakes and make sure your device meets tough medical rules.
Quick Checklist
You can use this checklist to help you pick nitinol tubing. It covers things like grade, size, tolerance, and what you will use it for:
Grade | OD Range (inches/mm) | OD/ID Ratio | OD Tolerance (inches/µm) | Concentricity Tolerance | Alloy/Ingot Type | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Standard | 0.010 - 0.065 (0.254 - 1.65) | 1.11 - 2.67 | +0.0003 to +0.001 (10.2 - 25.4) | N/A (Specified OD/ID) | Standard | Grinding parts, guidewires, catheters, needles, dental, disposables, sheaths |
Precision | 0.065 - 0.197 (1.65 - 5) | > 1.08 | ±0.0005 (12.7) for smaller OD | > 90% | Standard | Implants, delivery aides, stents, filters, orthopedic implants |
> 0.198 (>5) | > 1.08 | ±0.0008 to ±0.001 (20.3 - 25.4) | > 90% | Standard | ||
Premium | 0.065 - 0.197 (1.65 - 5) | > 1.08 | ±0.0005 (12.7) | > 95% | Standard & Enduro | Critical implants, heart devices, neurovascular stents, carotid artery devices |
> 0.198 (>5) | > 1.08 | ±0.0008 (20.3) | > 95% | Standard & Enduro | ||
Various (thin wall) | < 1.08 | Dependent on OD & wall | > 95% | Standard & Enduro |
Note: Always pick the right grade and size of nitinol tubing for your device’s job and the quality you need. This checklist helps you remember what is important and makes choosing easier.
When picking Niti tubing for medical devices, use simple steps. First, think about what your device needs. Check the list to look at tubing grade, size, and how close the sizes must be. Talk to experts so you get tubing that fits your device. You need to think about three main things when you choose:
Technical: Pick tubing with the right inside and outside, tight size limits, and good making steps for medical use.
Clinical: Make sure the tubing is safe for the body and stays strong in use.
Regulatory: Follow all the rules to keep medical devices safe and working well.
Look for good sources if you want more help choosing medical tubing.
FAQ
What is the difference between OD and ID in Niti tubing?
OD means outer diameter. ID means inner diameter. You measure OD from the outside edge. You measure ID from the inside edge. Both sizes help you pick tubing that fits your device.
Why does wall thickness matter for medical devices?
Wall thickness controls how strong and flexible the tubing feels. Thicker walls give more strength. Thinner walls bend more easily. You must balance these features to match your device’s needs.
How do you ensure Niti tubing meets medical standards?
You should ask for certifications like ISO 13485 and ASTM F2063. These show the tubing meets strict medical rules. Always request test reports from your supplier.
Can you customize Niti tubing sizes for special devices?
Yes, you can order custom OD, ID, and wall thickness. Many suppliers offer custom sizes for unique medical devices. Custom tubing helps you meet special design needs.
What tests check Niti tubing quality?
You should use tests like tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and corrosion checks. These tests show if the tubing will last and stay safe in the body.
See Also
A Complete Guide To Choosing Proper Nitinol Tubing
Tips For Finding The Ideal Nitinol Tubing Supplier
The Manufacturing Process Of Nitinol Tubing For Medicine
Discovering Nitinol Tubing Uses In Medical Device Technology

