How to Choose Nitinol Tubing by Af Temperature for Your Project

When you pick nitinol tubing for your project, you must match the af temperature niti tubing to what your project needs. The af temperature niti tubing controls how the shape memory effect and superelasticity work. New studies show that heat-treated nitinol tubing with an af temperature close to 25°C gives steady shape memory and superelasticity. This is very important for medical tubing, where you want it to work the same way every time. The world market for medical nitinol tubing is getting bigger, and medical projects need tubing that meets strict rules. Follow this step-by-step guide to make sure your tubing works well in all uses and projects.
Key Takeaways
Always pick nitinol tubing with an Af temperature that matches where you will use it. This helps the tubing keep its shape memory and superelasticity.
For medical devices, use nitinol tubing with an Af temperature near body temperature, which is about 37°C. This keeps the tubing flexible when you use it and strong inside the body.
Check the tubing’s size, surface finish, and purity very carefully. This helps you avoid problems like corrosion, cracks, or weak spots. These problems can make the tubing unsafe or not work well.
Work with certified suppliers who follow strict quality rules. They should give you test reports to show the tubing is safe and works well.
Do not make common mistakes. Test the Af temperature before you use the tubing. Think about all the things that affect how the tubing works. This helps your nitinol tubing work well in your project.
Af Temperature Niti Tubing Basics
What Is Af Temperature?
It is important to know about Af temperature when using nitinol tubing. Af temperature is the point where nitinol finishes changing from martensite to austenite. This change lets nitinol have its shape memory effect. When nitinol tubing gets hotter than its Af temperature, it goes back to its first shape. This is called setting the memory shape. The Af temperature for nitinol tubing is usually between -20°C and 100°C. You can look at the table below to see the usual range for different nitinol products:
Nitinol Product Form | Typical Af Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|
Wire | -20 to 100 |
Rod/Bar | -20 to 100 |
Sheet/Plate | 20 to 80 |
Tubing (inferred) | -20 to 100 |
You need to pick the right Af temperature niti tubing for your project. This helps the tubing work the way you want.
Why Af Matters for Performance
Af temperature decides how nitinol tubing acts in real life. If you choose the wrong Af temperature, the shape memory effect and superelasticity might not work right. The tubing may not go back to its set shape or could lose its bendiness. Setting the memory shape at the best temperature helps the tubing work well. You want the transition temperature to fit your project’s needs. This is very important for medical tools. Medical tools need to be both bendy and strong. When you set the memory shape at the best temperature, you get good results every time.
Tip: Always check the transition temperature of your nitinol tubing before using it in medical tools.
Af and Medical Applications
Medical tools use nitinol tubing because it has shape memory and superelasticity. You can find nitinol tubing in stents, catheters, guidewires, bone anchors, and spinal implants. These are some common uses for nitinol tubing. For medical tools, the Af temperature niti tubing should match body temperature, which is about 37°C. This makes sure the tubing stays bendy when putting it in and gets strong inside the body. Both heart and bone medical tools use the same Af temperature. Setting the memory shape at this temperature keeps patients safe and helps medical tools work well. You always need to match the Af temperature to the medical setting for the best results.
Selecting Nitinol Tubing by Af Temperature
Define Application Temperature
First, you need to know the temperature where your tubing will work. This is called the application temperature. For medical projects, tubing often works at body temperature, which is about 37°C. In engineering, tubing might face much colder or hotter places. You must check the exact temperature where you want the nitinol tubing to show its shape memory or superelastic effect. This is called the transition temperature. If you pick the wrong temperature, the tubing may not change shape or could lose its strength.
Here is a table that shows common temperature ranges for nitinol tubing in different projects:
Alloy Category | Active Austenite Finish Temperature (A(f)) Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
N | 0°C to 20°C | High nickel superelastic nitinol, used for superelastic applications below room temperature |
S | 10°C to 20°C | Superelastic nitinol |
C | 0°C to 10°C | Chromium doped superelastic nitinol |
B | 20°C to 40°C | Body temperature nitinol, suitable for shape memory applications near human body temperature |
M | 45°C to 95°C | Mid temperature range nitinol, for higher temperature shape memory applications |
H | 95°C to 115°C | High temperature range nitinol, for applications requiring shape memory at elevated temperatures |
You can also look at the chart below to see how these temperature ranges compare:
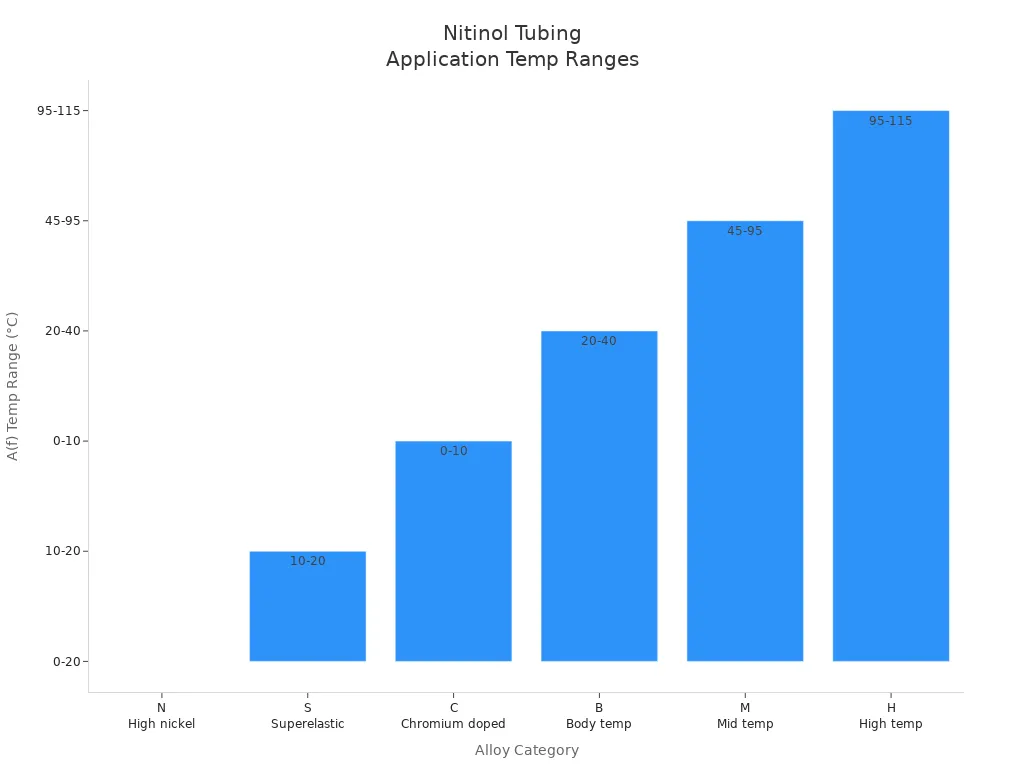
Tip: Always match the application temperature to the right alloy category. This helps your tubing work its best.
Match Af to Environment
You need to match the Af temperature of your tubing to where it will be used. If your tubing goes inside the human body, the Af temperature should be close to 37°C. This keeps the tubing flexible when placing it and strong once inside the body. For engineering, you might need the Af temperature to be lower or higher, depending on the job.
To match the Af temperature to your environment, you can do a few things:
Control the annealing temperature and time during heat treatment.
Use special atmospheres like vacuum or inert gases to keep the tubing clean and stable.
Change the cooling rate after heat treatment. Fast cooling can lower the Af temperature.
Use multi-step heat treatment to fine-tune the transition temperature.
Hold the tubing in a fixture during heat treatment to keep its shape and strength.
Check the Af temperature during processing and adjust as needed.
These steps help make sure your tubing works at the right temperature for your project.
Customizing Af Temperature
You can change the Af temperature of your nitinol tubing to fit your needs. Manufacturers can set the Af temperature anywhere from -20°C to +100°C. You just need to tell them what you want when you order. This way, you get tubing that works perfectly for your medical tools or engineering devices.
Here are some common ways to customize nitinol tubing:
Customization Option | Benefit |
|---|---|
Diameter/Wall Thickness | Matches device specifications |
Transformation Temperature | Optimizes device performance |
Surface Finishing | Enhances biocompatibility |
Enables complex geometries |
Manufacturers use special heat treatment and alloying to set the Af temperature. They can also change the tubing’s size and surface finish to fit your needs. This makes sure your tubing has the right strength, flexibility, and safety for your project.
Sizing and Surface Considerations
The size and surface finish of your tubing affect how well it works. You need to pick the right diameter and wall thickness for your device. Good size control helps your tubing fit well and keeps its strength. If the tubing is too big or too small, it may not work as planned.
Surface finish is also very important. Smooth surfaces, made by electropolishing or passivation, help the tubing resist corrosion and reduce friction. This is important for medical tools, where you want to avoid tissue damage and infection. Smooth tubing also helps keep bacteria from sticking and makes the tubing safer for patients.
You can add special coatings to the tubing to make it stronger and safer for the body. Quality control checks, like laser micrometry and ultrasonic testing, make sure the tubing meets all requirements. These checks help you avoid problems and keep your tubing strong and reliable under all conditions.
Note: Always check both the size and surface finish of your tubing before using it in medical tools or engineering projects. This helps you meet all safety and performance needs.
Ensuring High-Quality Nitinol Tubing

Supplier Quality and Certifications
You should pick suppliers who follow strict quality rules. Good suppliers use standards like ASTM F2063. This standard checks the tubing’s chemical makeup and Af temperature. It also looks at how strong the tubing is and if the surface is smooth. The standard tells suppliers how to test and measure the tubing. Always ask for proof of certifications before you buy tubing. The most important certifications for nitinol tubing are:
ISO 13485: Shows the supplier uses good rules for medical devices.
FDA 21 CFR Part 820: Sets rules for making medical devices in the U.S.
European Medical Device Regulation (MDR): Proves the tubing is safe in Europe.
TÜV Certification: Confirms the tubing meets tough European rules.
ASTM Standards (like ASTM F2063): Make sure the tubing is tested and safe.
These certifications help you trust the tubing for medical and engineering projects.
Quality Parameter | Description and Relevance |
|---|---|
ASTM F2063 Standard | Checks nitinol tubing quality and Af temperature. |
Af Temperature Consistency | Makes sure the tubing changes shape at the right time. |
Chemical Composition | Keeps nickel and other elements at safe levels. |
Manufacturing Controls | Uses careful steps to keep Af temperature steady. |
Testing and Inspection | Checks strength, corrosion resistance, and Af temperature. |
Certification | Proves the tubing meets all safety rules. |
Seamless vs. Welded Tubing
When you choose nitinol tubing, you pick seamless or welded types. Seamless tubing is stronger because it has no joints. The smooth surface helps during surgery and lowers risk. Seamless tubing is best for stents and catheters. Welded tubing can have weak spots at the seams. These weak spots can make the tubing less strong. For the best safety, use seamless tubing in medical tools.
Seamless tubing has no weak points and is strong.
The smooth surface helps doctors work safely.
Seamless tubing meets strict medical device rules.
Performance and Reliability
Good nitinol tubing must pass many tests to show it works well. Makers use tests like Bend and Free Recovery (BFR) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC). These tests check the Af temperature. They make sure the tubing works as it should every time. Quality teams use rules like ASTM F2063 and ISO 13485. They check the tubing’s strength, surface, and chemical makeup. Good tubing stays strong and keeps its shape under stress. You can trust high-quality nitinol tubing to last long and stay safe in important uses.
Tip: Always ask for test reports and certifications before using tubing in your project.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Wrong Af Selection
You should always check the Af temperature before using nitinol tubing. Picking the wrong Af temperature means the tubing might not work right. The shape memory effect or superelasticity may not happen. This can make medical tools fail when you use them. Some engineers forget that temperature changes how nitinol acts. When the temperature is higher, you need more force for the tubing to work. If you do not match the Af temperature to your project, you could lose safety and performance. Always test the Af temperature with methods like bend and free recovery. This helps make sure your tubing will work as you want.
Tip: Always check the Af temperature before using tubing. This easy step keeps your medical tools safe and high quality.
Ignoring Performance Factors
You need to think about more than just the Af temperature when picking nitinol tubing. Things like material purity, inclusions, and surface finish matter too. If you ignore these, your tubing can break or rust early. Non-metallic inclusions and empty spots can start cracks. These cracks can cause the tubing to break after many uses. For medical tools, this can make them unsafe for patients. Surface treatments like electropolishing help stop rust and make tubing better. High-purity nitinol helps tubing last longer, even after millions of uses.
Performance Factor | Impact on Tubing Quality and Safety |
|---|---|
Material Purity | Higher purity means better fatigue life |
Surface Finish | Smooth finish lowers risk of corrosion |
Inclusions/Voids | Fewer defects mean safer tubing |
Manufacturing Process | Good process keeps tubing strong |
Overlooking Medical Requirements
You must always follow strict medical rules when choosing nitinol tubing. Medical tools need tubing that is very safe and high quality. If you skip these rules, you could put patients at risk. Always check that your tubing has the right certifications and passes all tests. For medical tools, you need the right Af temperature, a smooth surface, and high purity. Testing and paperwork help prove your tubing is safe for the body.
Note: Patient safety depends on checking every part of tubing quality, from temperature to surface finish.
Summary and Key Steps
Picking the right nitinol tubing by Af temperature helps your project succeed. If you follow a simple plan, your tubing will be safe and work well. Here are the main steps experts say to use for good tubing:
Step/Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Heat Treatment (Shape Setting and Annealing) | Heat the tubing to 400°C-500°C to set its shape and lower stress. This step controls the Af temperature, which is important for shape memory and superelasticity. |
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) | Use this test to measure the Af temperature and check if the tubing matches your needs. |
Tensile Testing | Test the tubing’s strength and stretch to make sure it can handle real-world use. |
Bend Free Recovery (BFR) Testing | Check if the tubing returns to its original shape after bending. This shows its superelastic properties. |
Non-destructive Testing (X-ray, Ultrasound) | Look inside the tubing for hidden problems without damaging it. This supports overall quality. |
Tip: Always ask your supplier for test reports and certifications to confirm the tubing’s quality.
Doing these steps helps your tubing work in medical and engineering jobs. Nitinol tubing bends, remembers shapes, and is superelastic. These things help make devices safer and more comfortable for people. The tubing also works well in hard jobs, like in planes or robots.
You should check for quality at every step. Good tubing means fewer problems, better safety, and longer device life. Working with good suppliers and using the right tests helps you avoid mistakes and get the best tubing for your project.
Remember: Picking good tubing gives you better results, helps patients feel better, and makes devices work well.
Making sure the Af temperature matches your project keeps medical tubing safe and reliable. You need to follow every step, like picking the right temperature and checking certifications. This helps keep patients safe and makes devices work well. When you talk to certified suppliers, you get steady materials, help with questions, and fast shipping. For hard medical projects, look at trusted guides:
Reference | Focus Area | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
ASTM F2063-12 | Standard specification | Explains nickel-titanium alloys for medical devices |
Pelton AR et al. (2000) | Processing optimization | Made medical nitinol tubing work better |
Always test nitinol tubing at body temperature to make sure it is safe and works right.
FAQ
What does Af temperature mean for nitinol tubing?
Af temperature is when nitinol goes back to its strong shape. You need to know this so your tubing works right in your project.
How do you test the Af temperature of nitinol tubing?
You can use a test called Differential Scanning Calorimetry, or DSC. This test shows how the tubing changes when it gets hot. Ask your supplier for DSC results before you use the tubing.
Can you change the Af temperature after you buy nitinol tubing?
No, you cannot change the Af temperature after you get the tubing. The manufacturer sets it during heat treatment. Always order tubing with the Af temperature you need.
Why is surface finish important for medical nitinol tubing?
A smooth surface helps stop rust and keeps germs away. It also makes the tubing safer for the body. You should always check the surface finish before using tubing in medical devices.
What certifications should you look for when buying nitinol tubing?
Look for certifications like ASTM F2063, ISO 13485, and FDA approval. These show the tubing meets safety and quality rules for medical and engineering uses.
See Also
Choosing The Ideal Nitinol Tubing Supplier For You
A Detailed Process For Selecting Proper Nitinol Tubing
The Manufacturing Process Of Nitinol Tubing For Medicine

