Basic Insulation Definition and Its Importance in Today’s Technology

Basic insulation is your first protection from electric shock. This one layer keeps electricity inside wires and devices. In today’s systems, bad insulation causes most generator problems. It also causes over 60% of high voltage equipment damage. You can see that basic insulation is very important for safety and working well.
Basic insulation stops electrical problems and keeps you safe from danger.
It helps find problems early, so there are fewer accidents and less time lost.
New technology checks insulation, so your devices are safer and work better.
Key Takeaways
Basic insulation keeps you safe from electric shock. It stops electricity from leaving wires and devices. Good insulation helps stop accidents and damage to equipment. It also helps avoid costly downtime. There are different types of insulation. Double or reinforced insulation gives extra safety for devices without ground wires. The Basic Insulation Level (BIL) tells how much voltage insulation can take before it fails. This keeps equipment safe from power surges. You should check and take care of insulation often. This helps keep things safe, makes devices last longer, and saves money on repairs.
Basic Insulation Explained

What Is Basic Insulation
Basic insulation is like a shield that keeps you safe. It covers live parts, like wires or metal inside devices. This layer stops electricity from getting out and hurting you. The plastic or rubber on a power cord is basic insulation. That is why you can touch the cord when it is plugged in.
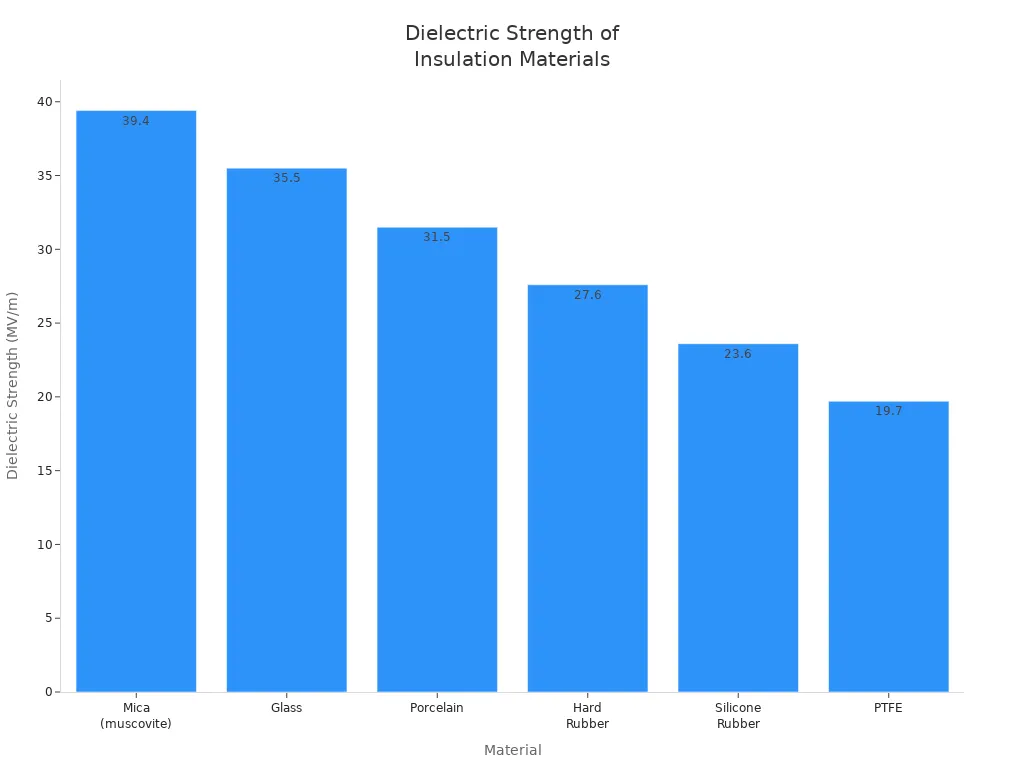
Manufacturers use different materials for basic insulation. Some common ones are plastics like PVC, rubber, and special polymers. These materials have high dielectric strength. That means they are very good at stopping electricity. Here is a table that shows some popular insulation materials and how strong they are:
Material | Dielectric Strength (MV/m) | Dielectric Strength (V/mil) |
|---|---|---|
Mica (muscovite) | 39.4 | 1000 |
Glass | 35.5 | 900 |
Porcelain | 31.5 | 800 |
Hard Rubber | 27.6 | 700 |
Silicone Rubber | 23.6 | 600 |
PTFE | 19.7 | 500 |
These materials give strong protection. The best one depends on where you use it and the voltage it needs to handle.
How Basic Insulation Works
Basic insulation blocks electricity from moving to things you touch. Insulators have electrons that do not move easily. This stops electric current from passing through. If you touch a wire with good insulation, the electricity stays inside. The insulation is a barrier that keeps you safe.
Tip: If the insulation has high resistance, less current can get through. This follows Ohm’s Law. When resistance goes up, current goes down.
If insulation breaks, electricity can escape and shock you. Always check for cracks or damage in cords and devices.
Basic vs. Supplementary Insulation
There are other types of insulation, like supplementary, double, or reinforced insulation. Each type gives a different level of safety.
Insulation Type | Description | Protection Level |
|---|---|---|
Basic Insulation | Single layer of insulation applied to live parts to provide basic protection against electric shock. | Provides fundamental protection but no redundancy. |
Supplementary Insulation | Independent additional layer applied on top of basic insulation to protect if basic insulation fails. | Adds a backup layer of protection. |
Double Insulation | Combination of basic and supplementary insulation, providing two layers of protection. | Ensures protection even if one layer fails. |
Reinforced Insulation | Single insulation system equivalent in protection to double insulation. | Provides equivalent safety to double insulation. |
Most power cords use basic insulation, which is one layer of plastic or rubber. Some devices, like phone chargers or hair dryers, use double insulation. This means there are two layers or a thick layer. You stay safe even if one layer breaks.
Note: International safety standards, like IEC 60601 and IEC 60950, need different insulation types for different products. Devices without a ground wire often use double or reinforced insulation.
Always check that the insulation on your devices is not damaged. This helps keep you safe from electric shock.
Role of Insulation in Systems

User Protection
Insulation keeps you safe when you use electrical devices. This layer stops electricity from touching your body. In places with high voltage, insulation covers live parts. It keeps you from getting shocked or hurt. Power leads and cables use insulation to protect you.
Tip: Check cords and plugs for cracks or damage. Broken insulation can be dangerous for you.
People who work with high voltage need extra safety steps. You might wear gloves that do not conduct electricity. You also use grounding to stay safe. Insulation is part of your safety gear. Trained people and regular checks help protect you from electrical dangers.
Insulation stops dangerous currents.
It lowers the chance of accidents.
It helps keep work safe.
Equipment Safety
Insulation does more than protect people. It helps devices work better and last longer. Good insulation stops devices from getting too hot. Materials like mica and silicone help control heat. They keep parts from breaking because of high temperatures. When devices stay cool, they work well for a long time.
Insulation also stops electrical problems. It keeps wires from touching each other or metal. This lowers the risk of short circuits or fires. Good insulation makes equipment safe and reliable. Medical devices use strong insulation to meet safety rules and avoid problems.
Common Applications
You find insulation in many places at home and at work. Power cords, outlets, and appliances use insulation to keep you safe. In factories, insulation connects sensors and controllers. It helps machines work right and stops electrical noise.
Insulated cables connect machine parts.
Robots use flexible insulation for moving parts.
Fire-resistant cables protect important systems.
Insulation keeps control circuits safe from signal issues.
Heat and humidity can change how insulation works. High heat can make materials melt or crack. Humidity can let water get inside insulation. This makes it weaker and can cause leaks. Using the right materials and keeping things dry helps insulation work well and stay safe.
Basic Insulation Level (BIL)
What Is BIL
You need to know how much voltage insulation can take before it fails. The basic insulation level, or BIL, shows the highest surge voltage equipment can handle without breaking. BIL rules help keep things safe. When you see a BIL rating, it means the insulation passed tough tests. These tests use high-voltage bursts to see if insulation can survive things like lightning or switching surges.
BIL is not just a guess. Experts use lots of data and special tests to set BIL rules. Standards like IEC 60076-3 and IEEE C57.12.00-2015 guide these tests. You will see impulse wave shapes like 1.2 microseconds up and 50 microseconds down. These shapes are like what happens during a surge voltage event.
Why BIL Matters
BIL keeps your equipment safe from sudden, dangerous voltages. When a surge happens, surge protection devices act first. They keep the voltage below the basic insulation level. If the surge is too strong, the weakest part of the insulation will break in a safe way. This protects the rest of the system.
Here is how BIL rules keep your system safe:
BIL shows the most surge voltage your insulation can take.
Surge protection devices work below the BIL to stop damage.
Insulation must be stronger than the voltage where protection devices work.
If a surge is too big, the system breaks safely at a planned spot.
This setup keeps your main equipment safe from harm.
You can check BIL with different tests. The most common ones are:
Testing Method | Purpose and Description | Reference Standards |
|---|---|---|
Lightning Impulse Test | Pretends lightning strikes with high-voltage bursts to check insulation strength and BIL. | IEC 60076-3, IEEE C57.12 |
Power Frequency Withstand Test | Uses high AC voltage to see if insulation holds under normal conditions. | IEC 60076-3 |
Switching Impulse Test | Checks insulation against slow surges from switching, important for very high voltages. | IEC 60076-3 |
Partial Discharge Test | Finds small insulation breaks to make sure the insulation lasts a long time. | IEC 60076-3 |
BIL rules are different for low-voltage and high-voltage systems. High-voltage systems need more insulation and bigger spaces. Low-voltage systems use simpler insulation but still follow strict BIL rules for safety.
Tip: Always check the BIL rating before you use or install electrical equipment. This helps you avoid failures from surprise surge voltage events.
Why Basic Insulation Matters
Safety and Compliance
Insulation keeps you safe when you use electrical equipment. If it fails, you could get shocked or start a fire. Sometimes, explosions can happen too. Many safety rules say you must use the right insulation. These rules protect you and others.
OSHA rules say you need things like insulating mats.
NFPA 70E says insulation helps stop arc flashes and shocks.
IS 15652:2006 (India) has classes for mats by voltage.
IEC 61111:2009 gives global rules for testing mats.
ASTM D178 and BS EN 61111 set rules for risky places.
UL 1446 and IEC rules need basic insulation in many devices.
If you do not follow these rules, you can get in trouble. In the European Union, the Low Voltage Directive says all equipment must be safe. This means you need good insulation and grounding. If you break these rules, you might pay fines or lose your products. You could even be banned from selling them. In the US, you must follow OSHA rules to sell your products. If you do not, you cannot get certified. These laws keep people safe and stop bad products from being sold.
When insulation breaks, real problems happen. In trains, dirt and dust can ruin insulators. This can cause smoke, fires, or explosions. Passengers get stuck, and companies lose money. In factories, bad insulation in breakers can stop work. It can break machines and hurt workers. Cleaning and checking often can stop these dangers.
Note: Most electric motor problems start with insulation damage. Heat, water, and dirt can ruin insulation. This can cause dangerous faults.
Reliability and Longevity
You want your equipment to last a long time. Good insulation helps with this. When you plan insulation, think about heat, electricity, and the environment. If you forget these, insulation gets old faster and can fail.
Good insulation design looks at heat, electricity, and stress.
Too much electricity makes insulation age faster and break down.
Heat makes insulation get old and can cause it to fail.
Water and dirt lower insulation strength and cause more failures.
Checking and testing often helps you find weak spots early.
Insulation failure costs companies a lot of money. Here are some examples:
Cost Component | Details |
|---|---|
Labor Costs | More repairs and work when things break |
Production Losses | Wasted materials, lost products, and restart time |
Financial Impact | Lost money, smaller profits, and higher repair bills |
Safety Risks | Most accidents happen when starting or stopping machines |
If you keep up with checks, you can cut downtime by half. Every dollar spent on checks can save five dollars later. You also keep your good name and make customers happy.
The basic insulation level, or bil, is important for long life. Bil shows the highest voltage your insulation can take. If you meet bil, your equipment is safe from surges and lasts longer. Testing bil often helps you find problems before they get worse. Taking care of insulation and following bil rules makes your equipment safer and better.
Insulation keeps you and your devices safe from electrical dangers. Checking, cleaning, and testing often helps systems stay safe and work well. As smart grids and renewable energy become more common, insulation needs to handle bigger challenges. In the future, there will be greener materials and smart tools to watch insulation. When you focus on insulation safety, you help make technology safer and better for all.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of basic insulation?
You use basic insulation to stop electric shock. This layer covers live wires and parts. It keeps electricity inside the device. You stay safe when you touch cords or equipment.
How do you know if insulation is damaged?
You can look for cracks, cuts, or worn spots on cords and wires. If you see exposed metal or feel heat, the insulation may be bad. Always replace damaged cords right away.
Why do some devices need double insulation?
Some devices do not have a ground wire. You need double insulation for extra safety. This means two layers protect you if one fails. Many small appliances use this design.
What are bil requirements for electrical equipment?
You must check that insulation meets bil requirements. These rules show the highest voltage the insulation can handle. You keep your equipment safe from surges by following these standards.
Can insulation fail over time?
Yes, insulation can wear out. Heat, moisture, and dirt make it weak. You should check and clean your equipment often. This helps prevent problems and keeps you safe.
See Also
Understanding Insulation Barriers To Meet Medical Device Standards
Exploring FEP And Its Importance In Medical Device Insulation
Advantages Of FEP Dielectric Tubing Over Alternative Insulation Options
The Role Of FEP In Enhancing Medical Device Insulation
Essential Information About PET Heat Shrink Tubing For Electronics

