What’s Driving the Evolution of Nitinol Tubing in Wearables

The year 2025 marks an important milestone with the introduction of 2025 new type Nitinol tubing for wearable devices. This advanced Nitinol tubing is unique because it can remember its shape, is highly flexible, and is compatible with the human body. These qualities make it ideal for wearable medical devices and innovative medical tools. The 2025 new type Nitinol tubing for wearable devices can bend and return to its original shape, enhancing its medical applications. New developments include alloys that dissolve safely in the body and improved manufacturing techniques for tubing. Nitinol tubing is already widely used in many devices, and as demand for better technology and medical solutions grows, more devices are incorporating it. The 2025 new type Nitinol tubing for wearable devices is set to further advance medical tubing technology.
Key Takeaways
The 2025 new nitinol tubing bends easily and keeps its shape. It is safe to use with the human body. This makes it great for wearable medical devices.
Advanced materials like bioresorbable alloys and smart polymers help safety and comfort. These let the tubing dissolve in the body. They also help the tubing fit natural tissues better.
New ways to make nitinol tubing give us very pure and tiny tubes. These tubes are made very carefully. They last longer and help make smaller, lighter wearable devices.
Strong safety and biocompatibility rules keep nitinol tubing safe for long use. These rules help companies follow world standards. They also help companies sell in more places.
Nitinol tubing helps wearable devices last longer and feel better. It can bend millions of times and still work. It fits well and helps make smart, flexible medical tools.
2025 New Type Nitinol Tubing for Wearable Devices

Material Breakthroughs
The 2025 new type nitinol tubing for wearable devices brings new material ideas. Engineers made advanced niti alloys that are strong, bendy, and safe for the body. These alloys let the tubing bend and twist, then go back to its shape. This is very important for medical devices that move with the body.
Researchers work to make nitinol tubing even safer for people. They use smart materials like shape-memory alloys and special polymers. These materials can change shape or stiffness when needed. Tiny materials now act like real body tissues. This helps the tubing fit in better and lowers the chance of rejection. Materials inspired by nature, like silk fibroin and hydrogels, help the body heal and connect with the tubing.
Note: Hydrogels are special because they are soft and can change. Some hydrogels can fix themselves if they break. They also do not freeze easily. This makes wearable sensors last longer. These hydrogels help medical devices work for more time.
The 2025 new type nitinol tubing for wearable devices uses these new ideas. It gives safer and better options for patients and doctors.
Bioresorbable Alloys
Bioresorbable alloys are a big step for medical tubing. The 2025 new type nitinol tubing for wearable devices uses alloys that can dissolve in the body. This means doctors do not need to remove them with surgery. It makes things safer and helps people heal faster.
New metal materials, like titanium alloys, are stronger and do not rust. These changes help make better niti alloys. Shape memory alloys like nitinol are strong and can be absorbed by the body. Polymer science also helps by making special plastics and hydrogels. These can be used in wearable medical devices.
Hydrogels are soft and safe for sensors on skin or eyes.
Some hydrogels can fix themselves if they get damaged.
Smart materials like shape-memory polymers help devices work better and be safer.
These new bioresorbable niti alloys make the 2025 new type nitinol tubing for wearable devices safer and better for medical and robot uses.
Superelasticity and Shape Memory
Superelasticity and shape memory are important for the 2025 new type nitinol tubing for wearable devices. Niti alloys can stretch and bend, then go back to their shape. This is needed for devices that move a lot.
The table below shows important facts about superelasticity and shape memory in wearables:
Performance Metric | Description and Benefit in Wearables |
|---|---|
Strain Recovery | Niti alloys can stretch up to 8% and return to their shape. |
Young's Modulus Variation | Niti alloys get stiffer with heat, so tubing can be more or less bendy. |
Elastic Deformation Capacity | Tubing can bend a lot without breaking or staying bent. |
Fatigue Life | Niti alloys last longer than other metals, so devices work for a long time. |
Superelasticity | Tubing can handle lots of bending and rough use. |
Shape Memory Effect (SME) | Tubing changes shape with heat, which helps smart wearables sense and move. |
Energy Efficiency | Superelastic tubing works without needing power all the time, saving energy. |
Application Examples | Niti fibers and springs are in smart jackets and shoes. They help sense heat and bending. |
The 2025 new type nitinol tubing for wearable devices uses these features. It helps make medical devices that are strong, comfy, and can change. Niti alloys with better shape memory let tubing react to body heat or the world around it. This makes devices safer and easier to use.
Nitinol Tubing Manufacturing Advances
High-Purity Tubing
Manufacturers have made big steps in making high-purity nitinol tubing. They use new ways to control the chemical mix and structure of niti alloys. This helps lower the number of tiny particles that can make tubing weak. Fewer particles mean the tubing lasts longer and works better in medical devices.
Engineers test how long superelastic nitinol tubing can last by using diamond-shaped samples. They follow strict rules like ASTM F2516 and use computers to check how tubing will work. TM-1 tubing lasts two to three times longer than other types. It can go through over 10 million bends without breaking. The process also fixes tiny holes inside, making tubing stronger. High-purity nitinol tubing has better shape memory and superelasticity. These are important for devices that need to bend and return to their shape.
Note: High-purity nitinol tubing uses special tools like polycrystalline diamond dies and hard mandrels. These tools help keep the tubing round and smooth, avoiding defects that could cause cracks.
Quality checks are very important. Manufacturers use tests that do not harm the tubing and watch the process closely. They also stretch the tubing a little to help it last longer. This means the tubing can be used many times without losing its strength or shape. Doctors and patients can trust that high-purity nitinol tubing will work well and last a long time.
Miniaturization
Miniaturization has changed how engineers make nitinol tubing for wearables. Today’s niti alloys can be made into tubes as small as 31 gauge, or 0.010 inches wide. These tiny tubes are smooth and have no sharp edges, which is good for comfort and safety.
Manufacturers use special tools like SYNEO Accu-Cut and Accu-Drill to cut and drill small tubing. Tridex machines help make smooth cuts with tight size limits. New inspection tools measure tubing size very closely, down to tiny units. Tubing sizes are now accurate to within 0.001 inches, and sometimes even 0.0005 inches.
Tubing with thinner walls and smaller diameters is now possible.
Wearable devices can be lighter and less noticeable.
Miniaturized tubing supports minimally invasive procedures.
Nitinol’s super-elasticity makes it great for these small, bendy tubes. Niti alloys let the tubing bend and twist without breaking, even when very small. This helps make new wearable medical devices that are strong and comfortable.
Precision Techniques
Precision techniques are very important for making good nitinol tubing for wearables. Manufacturers use special heat treatments, heating the tubing between 350 and 550°C for different times. This helps the tubing bend better and remember its shape, making it strong and reliable.
Special measuring tools, like laser micrometers and coordinate machines, check the tubing’s size and shape. Drawing the tubing many times and using real-time checks keeps the tubing size and surface smooth. Quality checks like non-destructive testing and watching the process help find problems early. This lowers waste and makes sure every tube meets strict rules.
Tip: Certification to standards like ASTM F2063 and ISO 13485 proves that the tubing is safe and reliable for medical use.
Manufacturers have made their factories bigger and bought new machines and hired more people. This has cut the time to make standard nitinol tubing in half. More material in stock means faster shipping for new designs, helping companies make new products quickly. Premium nitinol tubing now has very tight size limits, better structure, and smooth surfaces. Tests show over 98% roundness and double the strength against bending.
Using high-purity materials, miniaturization, and precision techniques means today’s nitinol tubing is the best for wearable tech. Niti alloys and tubing now help make safer, better, and more comfortable wearable medical devices.
Regulatory and Safety Trends for Wearables
Biocompatibility Standards
Regulatory groups now have strict rules for nitinol tubing in wearables. The ISO 10993 series gives the main rules for testing if materials are safe for people. Both the FDA and TÜV SÜD use these rules to check medical devices. The FDA uses ISO 10993 to sort devices by how they touch the body and for how long. Now, they want more chemical and lab tests instead of animal tests. This helps make sure nitinol tubing is safe and works well in wearables.
The FDA also has special rules just for nitinol. They want proof the tubing will not break, let out too much nickel, or change shape in a way that could hurt people. These rules help keep people safe when they use medical wearables every day. Working with skilled suppliers helps companies keep their nitinol tubing safe and strong.
Compliance in 2025
In 2025, companies must follow new rules to keep nitinol tubing safe in wearables. They need to show their products meet all safety and biocompatibility rules. This means testing for nickel release, checking how long tubing lasts, and making sure it works well in the body. Companies must keep good records and use trusted labs for tests.
Tip: Picking implant-grade nitinol and working with certified suppliers helps companies pass checks and meet world safety rules.
Regulators now look for materials that do not cause allergies. They want to lower the chance of allergic reactions. Companies use special coatings and pure nitinol to meet these needs. These steps help make sure medical wearables are safe for everyone.
Market Access
Following strict safety rules helps companies sell nitinol tubing for wearables in more places. Regulators in the US, Europe, and Asia now work together more. They share data and accept similar test results. This makes it easier for companies to sell new medical devices around the world.
A table below shows key steps for market access:
Step | Purpose |
|---|---|
Biocompatibility tests | Prove material is safe for the body |
Safety validation | Show tubing will not fail or harm users |
Regulatory approval | Get permission to sell in each country |
Companies that follow the newest safety and biocompatibility rules can reach more markets and help more people. Nitinol tubing that meets these rules helps make wearable medical devices safer and better.
Nitinol Market Growth and Scalability
Cost Reduction
Manufacturers have made nitinol tubing cheaper to make. They use precise machines and new ways to cut waste. These methods save time and lower costs. Eco-friendly steps help use less energy and make less pollution. Companies work together to keep quality high and prices low. Nitinol tubing lasts a long time because it is strong and safe for the body. This means people do not need new tubing often. Fewer replacements and less extra care save money for hospitals. Custom tubing fits better, so doctors do not need to fix or change it much. All these savings make smart devices and medical wearables cost less for everyone.
Precision machining cuts waste and saves time.
Eco-friendly steps use less energy.
Strong niti alloys help lower health costs.
Custom tubing means fewer changes.
Global Expansion
Nitinol tubing is getting more popular all over the world. The market will grow from $500 million in 2024 to $1.2 billion by 2033. More people want it for health care and smart gadgets. Asia-Pacific and North America are the top regions. Asia-Pacific grows fast because of better hospitals and new medical tools. North America stays strong with new devices and many older people. Europe, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa also see steady growth.
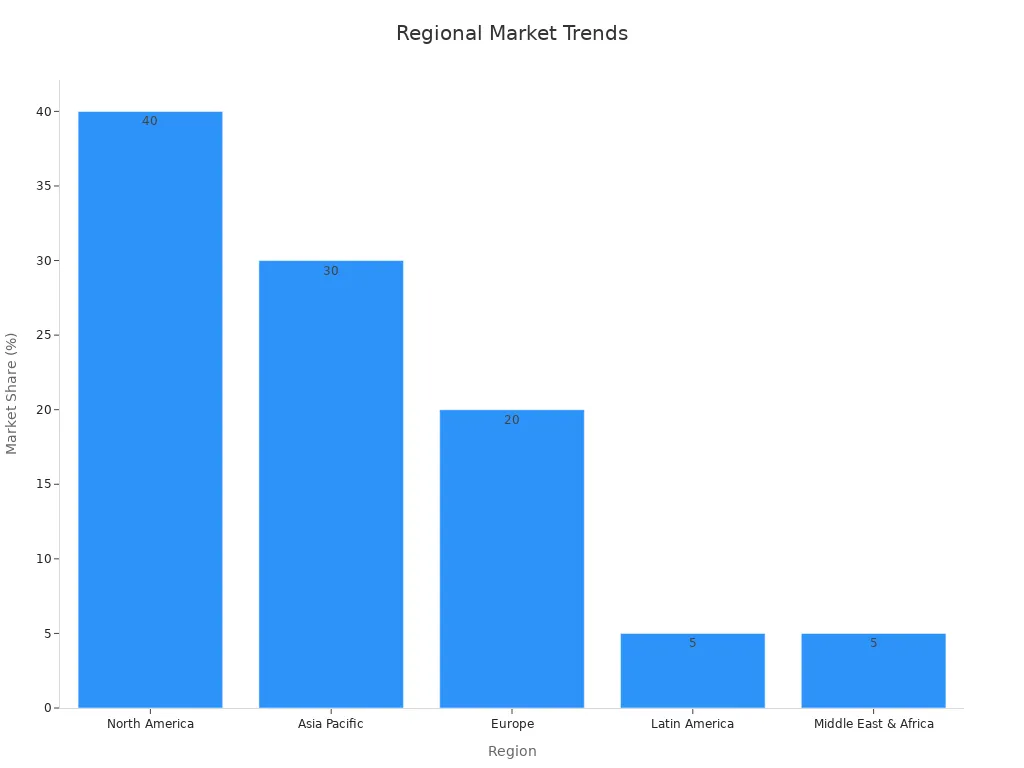
Region | Market Share (2023) | Growth Drivers and Trends |
|---|---|---|
North America | ~40% | More older people, heart disease, small surgeries, brain devices |
Asia Pacific | ~30% | Fastest growth, medical and airplane uses, more elderly, heart disease |
Europe | ~20% | Steady market |
Latin America | ~5% | New market |
Middle East & Africa | ~5% | New market |
Niti alloys and tubing now help make smaller and smarter devices. Special coatings and tiny tubes help patients everywhere feel better.
Accessibility for Wearables
Lean manufacturing makes nitinol tubing easier for wearable makers to get. Companies buy new machines, like laser cutters and better materials. These steps help make new designs faster and more exact. Quick testing and robots help companies try ideas in days or weeks. This means smart devices can be sold sooner. Lean steps let companies work on new treatments and better results. Now, more people can use advanced niti alloys and tubing every day.
Note: Lean manufacturing and robots help wearable makers sell new products faster and for less money.
The market for nitinol tubing in smart wearables keeps growing. By 2025, people will want $7 billion worth of nitinol and shape memory alloys. Smart glasses and bendy sensors will use 65% more nitinol by 2026. These facts show that niti alloys and tubing will be very important for future wearable tech.
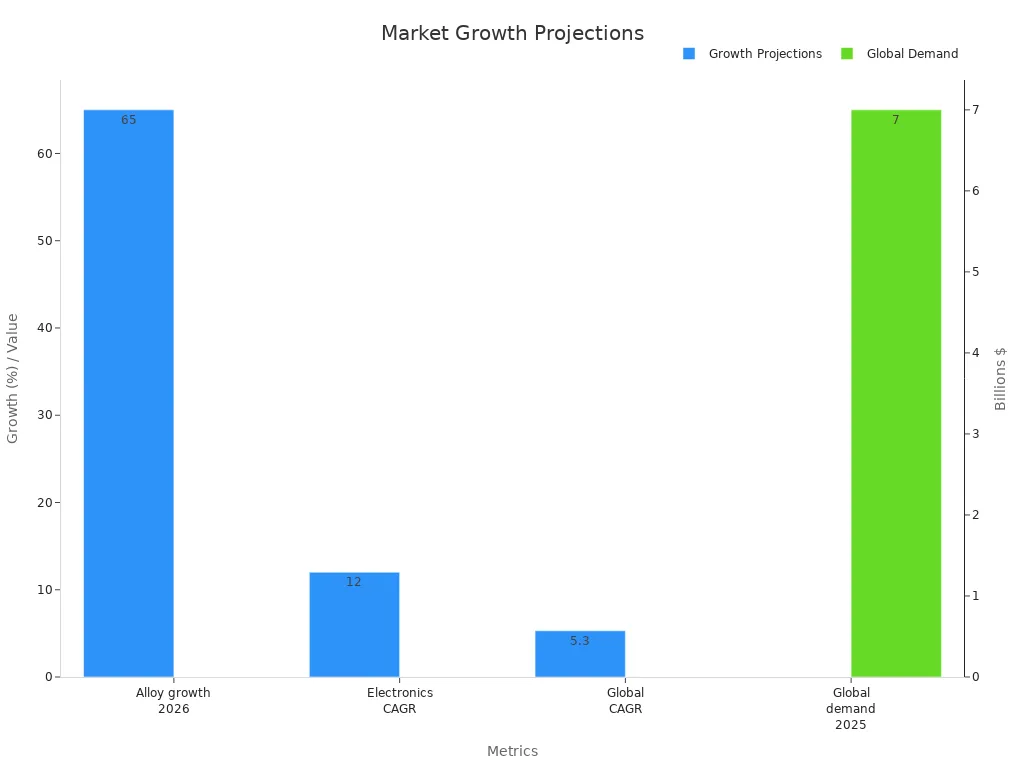
Metric/Projection | Value | Context/Application |
|---|---|---|
Nitinol alloy use in electronics by 2026 | 65% more | Wearable tech, bendy sensors, smart glasses |
Yearly growth in electronics sector | 12% | More use in gadgets and wearables |
Nitinol and shape memory alloys demand by 2025 | $7 billion | Market size for all industries |
Yearly growth for nitinol and shape memory alloys | 5.3% | Steady growth helps more people use it |
Nitinol use in electronics in 2022 | 2,100 metric tons | Starting amount |
Thin-film process | Made for wearables, helps save money and grow market |
Impact on Wearable Device Performance

Durability
Nitinol tubing makes smart devices last much longer. Engineers tested nitinol tubing by bending and stretching it many times. The tests showed niti tubing can bend millions of times without breaking. It keeps its shape even after lots of use. Nitinol tubing can survive up to 10 million bends. This is much better than stainless steel or cobalt-chromium. Special coatings like anodization and chitosan make the tubing even stronger. These coatings help stop wear and damage. Clinical trials show nitinol devices stay safe and work well for a long time. There are no harmful reactions from using them. The table below shows how nitinol tubing improves performance:
Performance Aspect | Improvement with Nitinol Tubing |
|---|---|
Fatigue Life | Up to 3x longer than traditional materials |
Kink Resistance | Maintains shape in complex pathways |
Recovery Improvement | 20% faster patient recovery times |
Complication Risk | Lower due to high biocompatibility |
These new features help patients get better results. Smart wearables last longer and work better with niti tubing.
Comfort
Smart devices with nitinol tubing are very comfortable to wear. Niti tubing is light and bends easily, so wearables are not bulky. People find smart watches, fitness trackers, and earbuds with nitinol parts fit better. They also feel lighter on the body. The tubing remembers its shape and goes back after being bent. This lets smart devices move with you and not press too hard. It helps stop sore spots and makes wearing them nicer. Headphones and other wearables can be adjusted for a perfect fit. This makes users happier and gives better results. Flexibility, light weight, and strength make smart wearables both comfy and high-performing.
New Applications
Nitinol tubing helps make new kinds of smart devices. Its superelasticity and shape memory are great for medical and rehab tools. Smart exoskeletons, bendy sensors, and braces now use niti tubing to help people heal. These devices can sense movement and change support as needed. They help people recover faster. Smart glasses and drug delivery wearables also use this tubing for strength and flexibility. As engineers make better niti alloys, more smart devices will be made for health, sports, and daily life. Nitinol tubing helps doctors care for patients, makes devices work better, and gives users better results everywhere.
Nitinol tubing changes how wearable devices are made in 2025. Experts say there are a few main reasons for this:
New ways to make TM-1 tubing make it last longer. It can handle three times more bending than old tubing.
Careful size checks and following ISO and EU rules keep tubing safe and high quality.
Rules like the EU MDR want tubing to be easy to track and better for the planet.
The market is growing fast, and nitinol sales may reach $14.7 billion by 2032.
These changes will help device makers and users find new options. Learning about nitinol tubing trends helps everyone use the newest technology.
FAQ
What makes nitinol tubing ideal for wearable medical devices?
Nitinol tubing can bend and return to its shape. It is very flexible and safe for the body. These features help make devices comfy and safe to wear every day.
How do bioresorbable nitinol alloys benefit patients?
Bioresorbable nitinol alloys can dissolve inside the body. Doctors do not need to take them out with surgery. This helps patients heal faster and lowers the chance of problems.
Are there any safety concerns with nitinol tubing in wearables?
Regulators check nitinol tubing for safety and nickel release. Certified suppliers follow ISO and FDA rules. This keeps nitinol tubing safe for long use on the body.
Can nitinol tubing be used in non-medical wearables?
Yes. Engineers use nitinol tubing in smart glasses and fitness trackers. It is also in flexible sensors and sports gadgets. Its strength and bendiness help many devices work better.
How does miniaturization impact wearable device design?
Miniaturization lets makers build thinner and lighter tubing. Devices feel smaller and are easier to wear. Tiny tubing also helps make new tools for small surgeries and compact gadgets.
See Also
Transforming Medical Devices With Innovative Nitinol Tubing Technology
Discovering Diverse Uses Of Nitinol Tubing In Healthcare
Nitinol Tubing’s Impact On Progressing Medical Technology Today
Nitinol Tubes Leading The Future Of Medical Devices By 2025
The Importance Of Nitinol Tubing In Cutting-Edge Medical Uses

